Amrit Bharat Station Scheme - Redevelopment of Railway Stations across India
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Prime Minister laid the foundation stone for the redevelopment of 508 railway stations at a cost of over 24 thousand 470 crore rupees under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme across the country through video conferencing.
Key Details:
- The Amrit Station is set to represent the city's blend of modern aspirations and ancient heritage.
- Reports state that approximately 1300 major railway stations across India will be transformed into Amrit Bharat Railway Stations, with redevelopment work already underway on 508 of them.
- According to Mr. Modi, the redevelopment of these stations will receive a significant investment of around 25,000 crores rupees, which will greatly improve the Railway infrastructure.
- He also mentioned that the budgetary support for the Railways has increased fivefold compared to 2014, now at 2.40 lakh crore rupees.
- Modi expressed that this marks the beginning of a new era for the development of Indian Railways, which will benefit all citizens.
- Additionally, he noted that India's global credibility has increased, leading to a shift in the world's attitude towards the country.
- The railway minister said the unprecedented development that has taken place in the last nine years is a testimony to the Prime Minister's vision of developing India.
- These 508 stations are spread across 27 States and union territories. This includes 55 stations each in Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan, 49 in Bihar, 44 in Maharashtra, 37 in West Bengal, 34 in Madhya Pradesh, 32 in Assam, and 25 in Odisha among others.
About Amrit Bharat Station Scheme:
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme was launched in December 2022 by the Ministry of Railways in collaboration with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The scheme is based on the principle of 'City Centres', which means that the railway stations will be developed as hubs of urban activity and connectivity, with proper integration of both sides of the city.
- The scheme also envisages the participation of the private sector, state governments and local bodies in the redevelopment process.
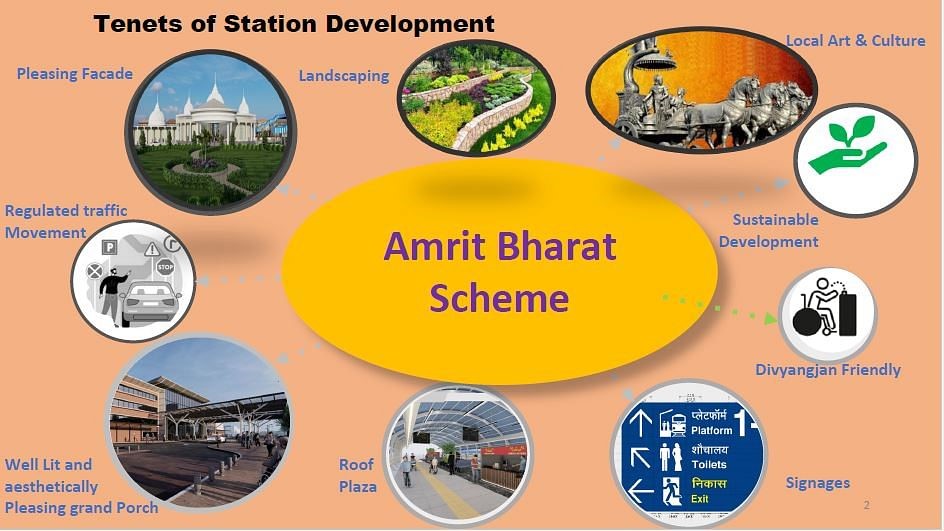
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme aims to transform the station in a way that harmoniously blends infrastructure and connectivity with the aspirations of Mumbai. As the scheme unfolds, the station will reflect this vision and contribute to the thriving city.
- This will improve the travel experience by:
- Elegant Station Building: A new station building will redefine Station's architectural landscape, reflecting a modern and inviting design.
- Focus on Swachh Bharat: Keeping in step with the Swachh Bharat mission, the station will introduce a modular Sewage Treatment Plant, ensuring efficient sewage treatment and a cleaner environment.
- Aesthetic Platforms: Platforms will undergo a resurfacing and aesthetic uplift, with the introduction of captivating landscaping on platform walls.
- Passenger Amenities: Travelers will enjoy improved amenities, including better seating, drinking water facilities, and enhanced lighting and ventilation on platforms and within the station building.
- Enhanced Connectivity: A revamped foot-over bridge, supplemented by additional lift and escalator facilities, will ease passenger movement and accessibility.
- Guidance and Information: Modernized train indication boards and passenger-friendly signages will facilitate seamless navigation within the station premises.
- Functional Upgrades: The existing booking office and other administrative buildings will undergo a thorough renovation, aligning them with the scheme's overarching vision.
- Inclusivity: All improvements will be designed to be divyangjan (specially-abled) friendly, ensuring equal access and convenience for all.
Features of the scheme:
- The redevelopment project will involve the installation of modern passenger amenities such as escalators, lifts, digital signage, CCTV cameras, Wi-Fi, waiting lounges, food courts and shopping areas.
- The project will also ensure a well-designed traffic circulation, seamless inter-modal integration with metro, bus, taxi, and other modes of transportation, and well-designed signage for the guidance of passengers.
- The design of station buildings will be inspired by local culture, heritage, and architecture. For example, Bihar's Muzaffarpur station will reflect the Mithila art form, while Kerala's Shornur and Kasargod stations will showcase the traditional architecture of the state.
The Indian Railways is the largest and busiest railway network in the world. It connects numerous towns and cities, making it a crucial mode of travel for millions of people across the country. As a result, it is an essential component of the nation's transportation infrastructure
Scope of work under Amrit Bharat Station Scheme(ABSS):
The ABSS involves improvement of amenities at the stations like entry and exit, circulating areas, waiting halls, toilets, lift/escalators, cleanliness, free Wi-Fi, kiosks for local products through schemes like ‘One Station One Product’, better passenger information systems, Executive Lounges, nominated spaces for business meetings, landscaping, etc.

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Redevelopment of Railway Stations across India:
Challenges:
Land acquisition:
- Acquiring land for railway projects is a complex and time-consuming process involving multiple stakeholders and legal issues.
Lack of Modern Management:
- There is a lack of modern management as the railway failed to attract adequate incentives and suitable talent. In addition to it, it could not make economic analysis for perspective planning tariff.
Environmental clearance:
- Obtaining environmental clearance for railway projects is also a lengthy and cumbersome process involving various agencies and regulations.
Inadequate Investment:
- Railway transport has lagged behind the requirement due to inadequate investment. The shortcoming has been highlighted by different committees, The National Transport Policy Committee, The Rail Tariff Enquiry Committee and The Railway Reforms Committee.
Financial constraints:
- Funding railway projects is a major challenge as the railways have a huge backlog of pending projects and a low operating ratio (ratio of working expenses to revenue).
Coordination issues:
- Coordinating with various ministries, state governments, local bodies and private partners is also a challenge as they have different priorities, interests and expectations.
Outmoded Technology:
- Adopting new technologies such as high-speed rail, bullet train and train 18 is also a challenge as they require skilled manpower, advanced equipment and quality standards.
Competition with Road Transport:
- The competition with road transport is growing in intensity, both in passenger and goods transport. The lack of coordination between railways and road transport has lowered the earning capacity of the railways. This has further caused delays in traffic movement and inconvenience to passengers.
Important initiatives are undertaken by the government to improve railway infrastructure:
Vision 2024 document
- The Indian Railways has planned to improve its freight transportation model by 2024 through infrastructure development. Priority has been given to capacity enhancement projects like doubling and multitracking, which have been classified as critical and supercritical for timely completion.
The National Rail Plan (NRP)
- The National Rail Plan (NRP) 2030 aims to upgrade infrastructure by 2030 to meet the traffic needs up to 2050 and raise the percentage of rail transportation in freight to 45%.
Semi-High-Speed Rail:
- India has launched semi-high-speed trains such as Vande Bharat Express and Tejas Express with a maximum speed of 160 kmph on select routes.
Dedicated Freight Corridor:
- India is building two dedicated freight corridors - Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC) and Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC) - to increase the speed and capacity of freight movement.
High-Speed Rail:
- India is developing its first high-speed rail corridor between Mumbai and Ahmedabad with technical assistance from Japan.
Bullet Train:
- India is also planning to introduce bullet trains on six routes - Delhi-Mumbai, Delhi-Kolkata, Mumbai-Chennai, Delhi-Chandigarh, Mumbai-Nagpur and Delhi-Varanasi - with an average speed of 250 kmph.
Metro Rail:
- India has expanded its metro rail network to cover 18 cities with a total operational length of over 760 km. More metro projects are under construction or planning stage in various cities.
Way forward:
- Process, structural and cultural reforms are the key elements of transformational changes in any organization. Indian Railways has also embarked upon this journey by bringing in such changes.
- Culture of Innovation is one such aspect that is needed to do such transformation and bring improvements in the organisation.
- The vision of Indian Railways is to be a Global Leader in Railways by leaping as a creator and innovator of technologies and systems.
- Through a new way of thinking and a creative culture ingrained through policies and system enablement, IR in due course will take its place globally, standing true to its reputation as an innovator in rail technology creation and dissemination.
Closing thoughts:
- Indian Railways is surely an organisation where the motivated manpower, industry, research community, academia and leadership come together to create new opportunities, and where an innovative mindset and functionally enabling ecosystem will drive it further to fulfill the aspirations of present and future India.
https://newsonair.gov.in/Main-News-Details.aspx?id=465627
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=PM-Modi-lays-foundation-stone-for-redevelopment-of-508-railway-stations-under-Amrit-Bharat-Station-Scheme-across-India&id=465627
.jpg)
Meri Mati Mera Desh Campaign
Context:
- The nationwide Meri Mati Mera Desh Campaign will be launched today to pay tribute to the Bravehearts who laid down their lives for the country.
Details:
- The campaign will continue till the 30th of this month. It will include programs at national, state, village and block levels as well as local urban bodies.
- The campaign will feature programs like the establishment of memorial plaques or Shilaphalakams dedicated to freedom fighters and security forces, as well as initiatives like the Panch Pran Pledge, Vasudha Vandan, Veeron ka Vandan which venerates the gallant sacrifices of Bravehearts.

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
About No Confidence Motion:
- The ‘Meri Mati Mera Desh' campaign is an idea to celebrate India's soil and valor. And the different events or activities to enhance interaction & promote mutual understanding between people of different states/UTs are
- Dedication of Shilaphalakam-installation of the nameplate of Veers
- Taking the Panch Pran Pledge;
- Vasudha Vandan creation of Amrit Vatika with 75 saplings of indigenous trees;
- Veeron Ka Vandan honouring freedom fighters/braves who protect the nation and families of braves;
- Hoisting of the National Flag and singing of National Anthem.
- Under the campaign an 'Amrit Kalash Yatra' will also be conducted, carrying soil from all corners of the country in 7,500 Kalash to create an 'Amrit Vatika' in Delhi.
- This 'Amrit Vatika' will symbolize the commitment to 'Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat. The campaign is the concluding event of the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav which began on 12th March 2021 and has witnessed widespread public participation, with over two lakh programs organized across India.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Nationwide-Meri-Mati-Mera-Desh-Campaign-to-be-launched-today&id=465781

Parliamentary Standing Committee
Context:
- A Parliamentary Committee has recommended bringing legislation to make it mandatory for Supreme Court and High Court judges to declare their property returns on an annual basis.
Details:
- The Standing Committee, chaired by BJP Rajya Sabha MP Sushil Kumar Modi said the Supreme Court has gone to the extent of holding that the public has a right to know the assets of those standing for elections as MPs or MLAs.
- He added that in that case if anybody holding public office and drawing a salary from the exchequer should mandatorily furnish annual returns of their property.
- The government told the parliamentary panel that there is a need to institutionalise the mechanism for regular filing of assets and uploading them in the public domain.
- The Committee recommended that the Union government bring about appropriate legislation to make it mandatory for judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts to furnish their property returns on an annual basis to the appropriate authority.
- It said that the declaration of assets by the judges of the higher judiciary will only bring more trust and credibility into the system.
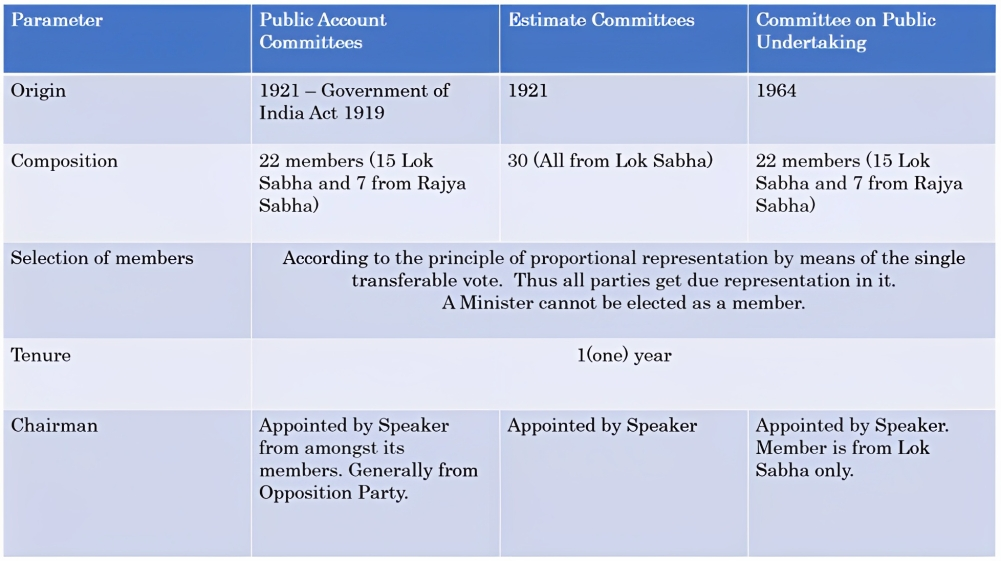
About the Parliamentary Standing Committee:
- There are two types of parliamentary committees:
- Standing or permanent committees and ad hoc committees.
- Standing committees are constituted for a fixed term and work continuously. Ad hoc committees are created for a specific purpose and are dissolved after they complete their task.
- There are 6 categories of standing committees: financial committees, departmental standing committees, committees to inquire, committees to scrutinize and control, committees relating to the day-to-day business of the House, and house-keeping or service committees.
- There are 2 categories of ad hoc committees: inquiry committees and advisory committees.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Parliamentary-Standing-Committee-recommends-mandatory-declaration-of-assets-by-Supreme-Court-and-High-Court-judges&id=465785
Anniversary of the Quit India Movement
Context:
- BJP MPs demonstrated in front of the Mahatma Gandhi Statue in Parliament complex on the occasion of the 81st Anniversary of the Quit India Movement.
Details:
- The members were raising slogans like "Corruption Quit India", "Appeasement Quit India" and "Nepotism Quit India.".
- Parliamentary Affairs Minister Prahlad Joshi said in remembrance of the Quit India Movement, BJP MPs are holding programmes against social evils.
About Quit India Movement:
- Quit India Movement, also known as the “Bharat Chodo Andolan”, was launched by Mahatma Gandhi on August 8, 1942.
- The movement was a mass movement that was launched at the Bombay session of the All India Congress Committee (AICC). Gandhiji gave the clarion call of ‘Do or Die’ to the countrymen for a decisive fight against British rule.
Significance of the movement:
- The Quit India Movement also called the 'August Movement' or 'August Kranti' played a crucial role in India's struggle for independence, representing a turning point in the nation's history.
- This movement was a declaration of India's unwavering determination to an immediate end to British rule in India and for the British to "Quit India."
- It sparked widespread civil disobedience, non-cooperation, and acts of defiance against British authorities.
- The movement saw a mass mobilisation of Indians from all walks of life across the country, in the fight for independence, which culminated in the nation's independence on August 15, 1947.
- The Quit India Movement did not achieve its immediate goal of forcing the British to leave India. However, it did have a significant impact on the course of India's independence struggle.
- The movement helped to galvanize Indian public opinion in favor of independence, and it showed the British that the Indian people were determined to achieve their freedom.
- The Quit India Movement was a significant and watershed moment in the struggle for freedom from British colonialism and it had a lasting impact on Indian politics and society.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=On-occasion-of-81st-Anniversary-of-Quit-India-Movement-BJP-MPs-demonstrates-in-front-of-Mahatma-Gandhi-Statue&id=465792

Non-confidence Motion
Context:
- The much-awaited debate on the no-confidence motion against the Narendra Modi government began today with both the opposition parties and the ruling NDA coalition putting forward their arguments for and against the motion
Details:
- Initiating the debate, Congress Deputy Leader in Lok Sabha, Gaurav Gogoi, who moved the motion, accused Prime Minister Modi of taking a "vow of silence" on issues such as the ethnic violence in Manipur and Chinese incursions and said opposition parties were forced to bring a no-confidence motion against the government to make him speak up.
- Gogoi also put forward three demands, saying the opposition wanted Modi to visit Manipur, lead an all-party delegation to the north-eastern state and make sincere efforts to restore peace by meeting various organisations there.
About No-Confidence Motion:
- A Council of Ministers is collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha and it remains in office till it enjoys the confidence of the majority of the members in Lok Sabha. Thus, a motion of no-confidence is moved to remove the council of ministers and thus oust the government from office.
- While Article 75 of the Indian Constitution specifies that the council of ministers shall be collectively responsible to the House of the People – there is no mention of a no-confidence motion.
- All it indicates is that the majority of Lok Sabha members must be with the Prime Minister and his Cabinet.
- Article 118 of the Constitution permits each house of Parliament to make its own rules for the conduct of business. Rule 198 of the Lok Sabha specifies the procedure for a motion of no-confidence.
- Any member may give written notice before 10 am; the Speaker will read the motion of no-confidence in the House and ask all those favoring the motion to rise.
- If there are 50 MPs in favor, the Speaker could allot a date for discussing the motion – but this has to be within 10 days. However, this cannot be done in conditions of din or confusion in the House.
Conditions of a no-confidence motion:
- A no-confidence motion can be moved only in the Lok Sabha (or state assembly as the case may be). It cannot be moved in the Rajya Sabha (or state legislative council);
- It is moved against the entire Council of Ministers including the Prime Minister and not individual ministers or private members; and,
- It needs the support of at least 50 members when introduced in the Lok Sabha.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Review-of-Parliament-Proceedings&id=465774







