




|
Indus Valley Civilization |
Features |
|
Period |
Bronze Age |
|
Date |
3300 BC – 1300 BC |
|
Geographical Range |
Indus River Basin; NW India & Eastern Pakistan |
|
Preceded by |
Mehrgarh |
|
Succeeded by |
Painted Grey Ware Culture |
|
Noted for |
Urban planning, baked brick houses, elaborate drainage systems, water supply systems, clusters of large non-residential buildings, and new techniques in handicraft (carnelian products, seal carving) and metallurgy (copper, bronze, lead, and tin) |
|
Status |
UNESCO World Heritage Site |

4.png)
|
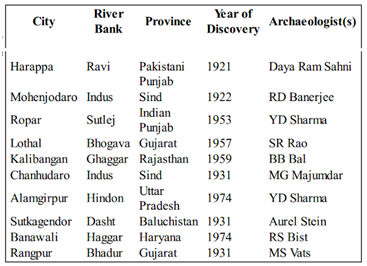
Harappa |
Cemetery H & R37; Coffin burial; Phallus worship; Mother goddess, Bullock Carts, Single Roomed Barracks, Granaries, Sandstone Steatite of a youth with muscular body, Bronze Image of a Dog Attacking a Deer, Sandstone Girl Dancer, Reserved slip ware of Mesopotamian Type |
|
Mohenjo-Daro |
Prepared garments, Pashupati seal, Bronze statue of a dancing girl, Ivory weight balance, The Great Bath, The Great Granary, Priest king statue (of steatite), human skeleton huddled together |
|
Kalibangan |
Lower fortified town, Fire Altar, Boustrophedon style writing, Wooden drainage, Copper ox, Evidence of earthquake, Wooden plough, Camel’s bone, 6 types of pottery |
|
Lothal |
Dockyard, Port Town, Evidence of Rice, Fire Altar, Ivory weight balance, Copper dog. |
|
Rangpur |
Evidence of Rice |
|
Surkotada |
Horse bone, stone covered grave, Human ashes |
|
Chanhudaro |
Bangle factory, Ink pot, only city without citadel, Carts with seated driver, Small Pot Shell Ornament Makers Factory, Metal Workers Factory, Bead Making Factory Shell Ornament Makers Factory |
|
Balakot |
Bangle Factory |
|
Daimabad |
Bronze Buffalo, Copper Rhinoceros, Copper Elephant |
|
Amri |
Remains of Rhinoceros |
|
Ropar |
Dog buried with humans, steatite seal, oval pit burials. |
|
Banawali |
Oval shaped settlement, only city with radial streets, toy plough |
|
Dholavira |
Only site to be divided into three parts, giant water reservoir, unique water harnessing system, Dam, Embankments, stadium, rock – cut architecture |
|
Balakot |
Shell Ornament makers Factory |
|
Rakhigarhi |
Skeletons of a 4,500-old woman, Clay plough |
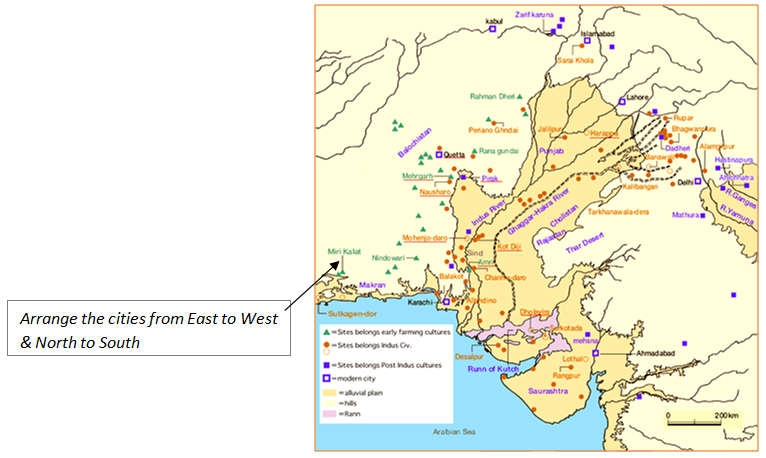
Note: Indus Valley Script has not yet been deciphered. 70% of the city is yet to be excavated.
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved