



Introduction
What are monoclonal antibodies?
|
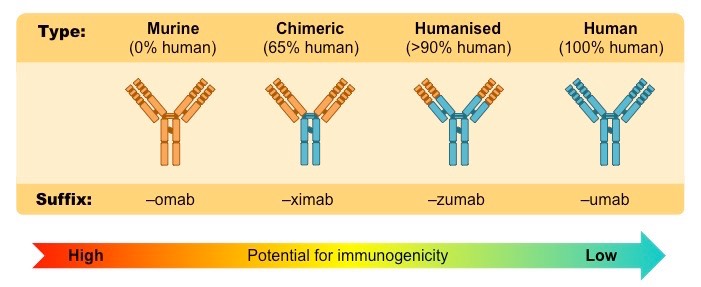
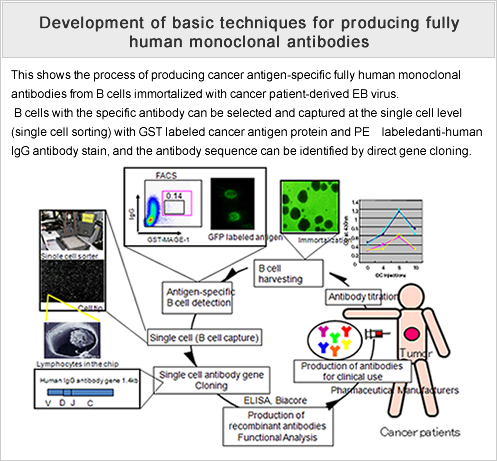
In a nutshell, Monoclonal antibodies are man-made proteins that act like human antibodies in the immune system. There are 4 different ways they can be made and are named based on what they are made of.
Murine: These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in -omab. Chimeric: These proteins are a combination of part mouse and part human and the names of the treatments end in -ximab. Humanized: These are made from small parts of mouse proteins attached to human proteins and the names of the treatments end in -zumab Human: These are fully human proteins and the names of the treatments end in -umab. |
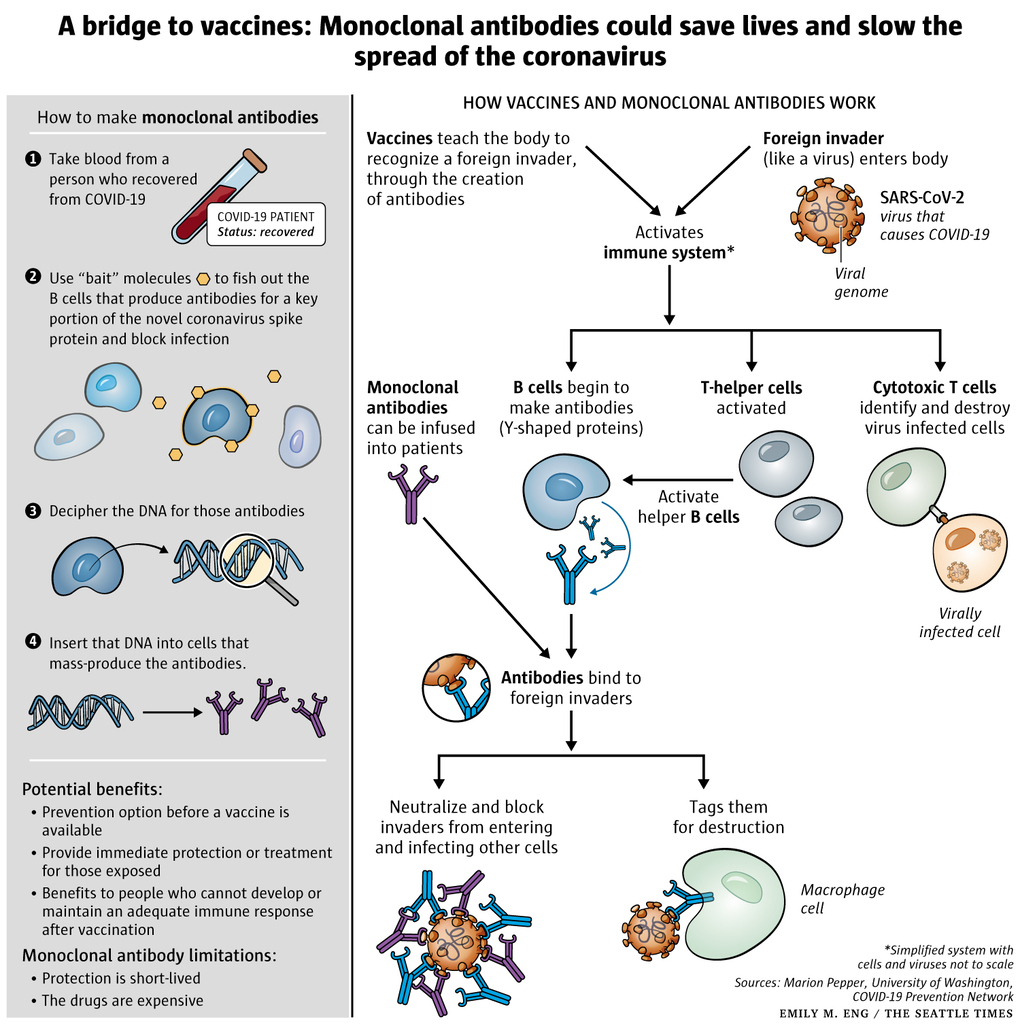
What does the new study show?
Is this therapy available in India?

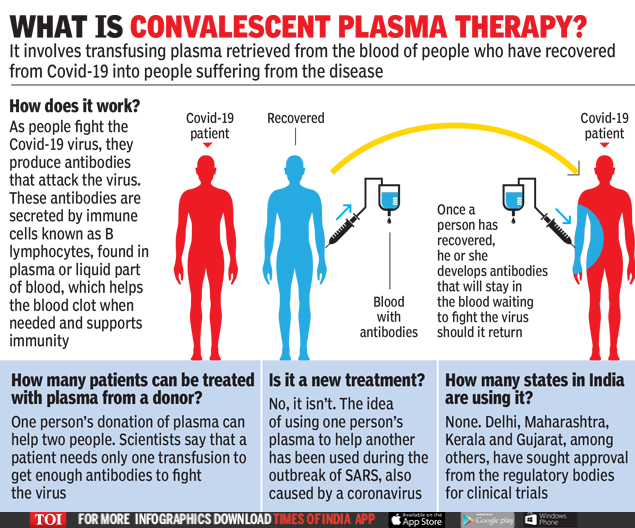
Monoclonal Antibodies and Convalescent Plasma Therapy

© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved