




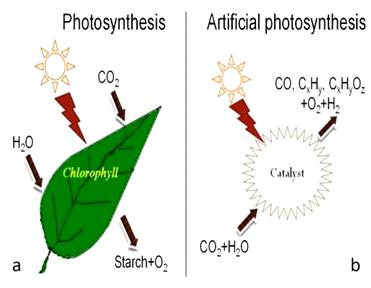
Artificial photosynthesis (AP) harnesses solar energy and converts the captured carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide (CO), which can be used as a fuel for internal combustion engines.
|
What is photosynthesis? Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants use sunlight to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water. The process combines 6 molecules of carbon dioxide and 6 molecules of water to produce one molecule of glucose and 6 oxygen molecules. The glucose is stored in the plant as starch and cellulose which are simply long chain glucose molecules (known as polysaccharides) as a source of food for the plant to survive and grow. The oxygen that is produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis is what most animals rely on to breath, so the process plants and trees fulfill on our behalf is critical to our survival. Artificial Photosynthesis In Artificial Photosynthesis we replicate the photosynthetic process completed by plants Steps
|
Mechanism
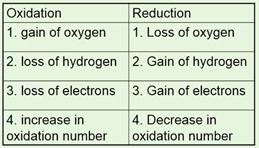
Redox Reactions
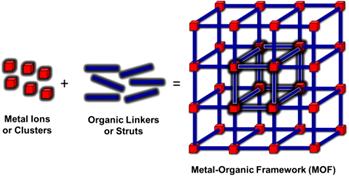
© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved