



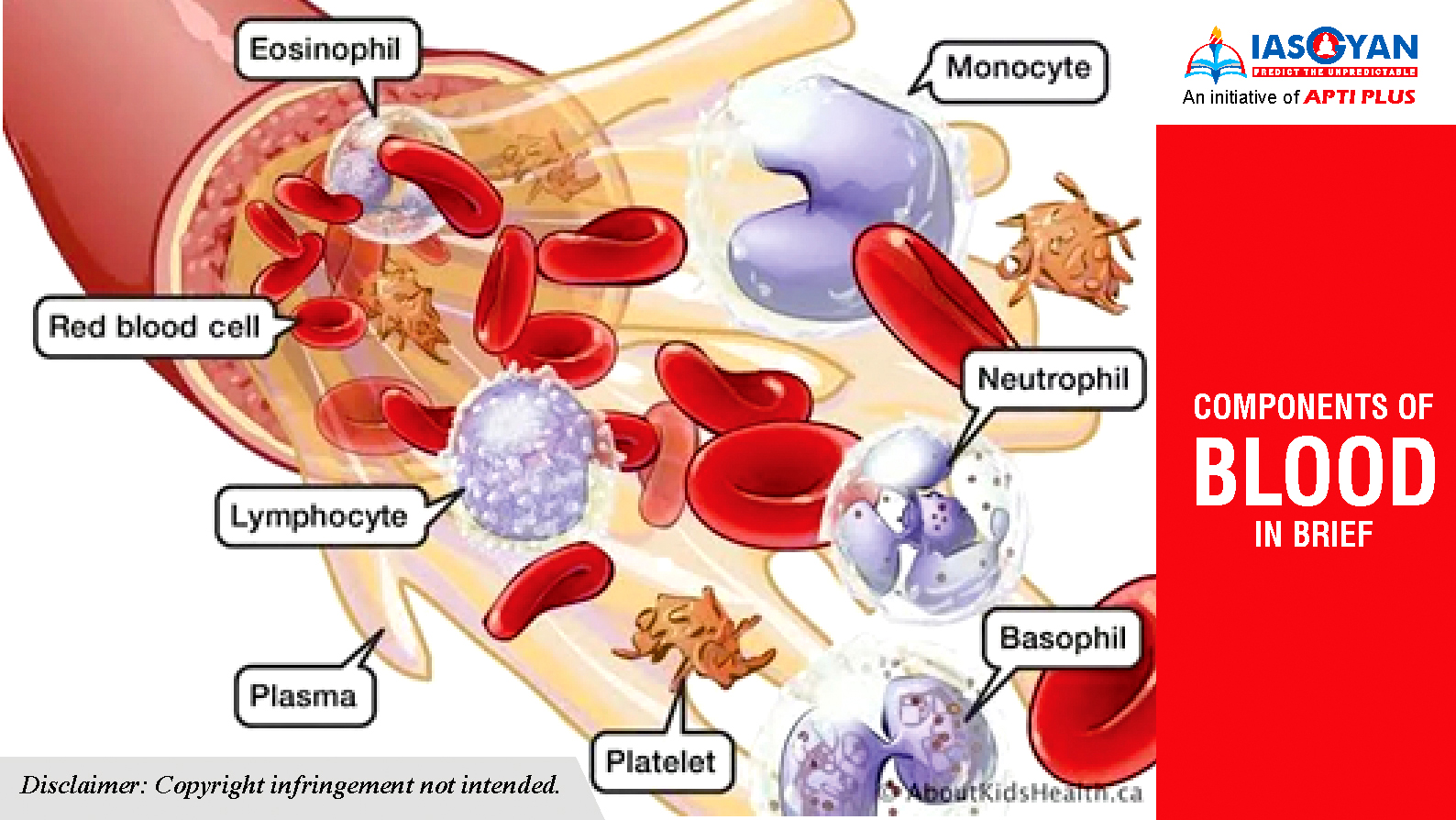
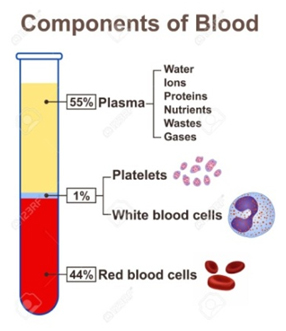
 Plasma
Plasma
7.png)
White Blood Cells

Platelets
Red Blood Cells
|
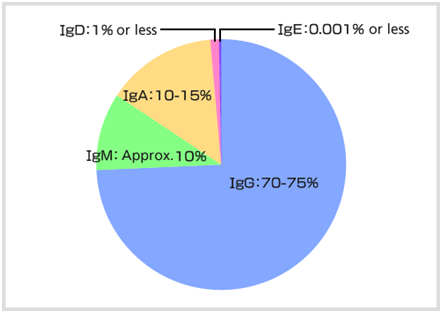
IgG |
It is the only antibody that can pass through the placenta, and IgG transferred from the mother's body protects a newborn until a week after birth. IgG widely distributed to the blood and tissue, and protects the body. |
|
|
IgM |
IgM has a key role in the initial immune system. It is distributed to the blood. |
|
|
IgA |
It is distributed to serum, nasal discharge, saliva, breast milk and bowel fluid. |
|
|
IgD |
IgD is present on the surface of B cells and plays a role in the induction of antibody production. |
|
|
IgE |
IgE is related to immunity reactions to parasites, and has recently become known as a key factor of allergies such as pollinosis. |
© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved