



The Civil Services Examination comprises two successive stages:
Preliminary Examination is meant to serve as a screening test only. Only those candidates who are declared by the Commission to have qualified in the Preliminary Examination in the year will be eligible for admission to the Civil Services (Main) Examination of that year provided they are otherwise eligible for admission to the Civil Services (Main) Examination.
The Civil Services (Main) Examination will consist of a Written Examination and an Interview/Personality Test. The Written Examination will consist of 9 papers of conventional
essay type out of which two papers will be of qualifying in nature. Marks obtained for all the
compulsory papers (Paper-I to Paper-VII) and Marks obtained in Interview/Personality Test will be counted for ranking.
Candidates who obtain such minimum qualifying marks in the written part of the Civil Services (Main) Examination as may be fixed by the Commission at their discretion, shall be summoned by them for an Interview/Personality Test. The number of candidates to be summoned for Interview/Personality Test will be about twice of the number of vacancies to be filled. The Interview/Personality Test will carry 275 marks (with no minimum qualifying marks).
Candidates will be allotted to the various Services keeping in view their ranks in the examination and the preferences expressed by them for the various Services and posts.
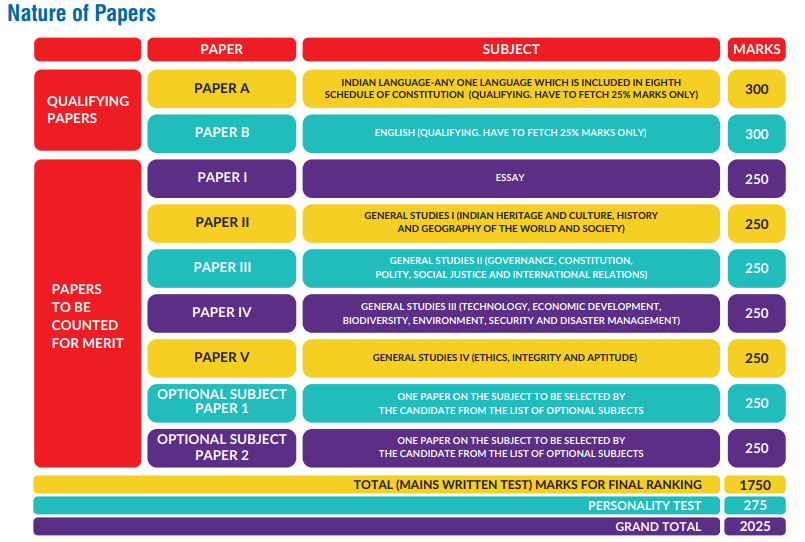
(i) The papers on Indian languages and English (Paper A and paper B) will be of Matriculation or equivalent standard and will be of qualifying nature. The marks obtained in these papers will not be counted for ranking.
(ii) Evaluation of the papers, namely, 'Essay', 'General Studies' and Optional Subject of all the candidates would be done simultaneously along with evaluation of their qualifying papers on ‘Indian Languages’ and ‘English’ but the papers on Éssay', General Studies and Optional Subject of only such candidates will be taken cognizance who attain 25% marks in ‘Indian Language’ and 25% in English as minimum qualifying standards in these qualifying papers.
(iii) The paper A on Indian Language will not, however, be compulsory for candidates hailing
from the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Sikkim.
(iv) The paper A on Indian Language will not, however, be compulsory for Candidates belonging to Persons with Benchmark Disability (only Hearing Impairment sub-category) provided that they have been granted such exemption from 2nd or 3rd language courses by the concerned education Board/University. The candidate needs to provide an undertaking/self-declaration in this regard in order to claim such an exemption to the Commission.
(v) Marks obtained by the candidates for the Paper I-VII only will be counted for merit ranking. However, the Commission will have the discretion to fix qualifying marks in any or all of these papers.
(vi) For the Language medium/literature of languages, the scripts to be used by the candidates will be as under
Language Script
For Santhali language, question paper will be printed in Devanagari script; but candidates will be free to answer either in Devanagari script or in Olchiki.
List of optional subjects for Main Examination:
(i) Agriculture
(ii) Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science
(iii) Anthropology
(iv) Botany
(v) Chemistry
(vi) Civil Engineering
(vii) Commerce and Accountancy
(viii) Economics
(ix) Electrical Engineering
(x) Geography
(xi) Geology
(xii) History
(xiii) Law
(xiv) Management
(xv) Mathematics
(xvi) Mechanical Engineering
(xvii) Medical Science
(xviii) Philosophy
(xix) Physics
(xx) Political Science and International Relations
(xxi) Psychology
(xxii) Public Administration
(xxiii) Sociology
(xxiv) Statistics
(xxv) Zoology
(xxvi) Literature of any one of the following languages:
Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili,
Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu and English.
Note:
(i) The question papers for the examination will be of conventional (essay) type.
(ii) Each paper will be of three hours duration.
(iii) Candidates will have the option to answer all the question papers, except the Qualifying
Language Papers, Paper-A and Paper-B, in any one of the languages included in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India or in English. Notwithstanding this, the Candidate will have the choice to write the Optional Papers in English also if candidates opt to write Paper I-V except the Qualifying Language Papers, Paper-A and Paper-B, in any one of the language included in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India.
(iv) Candidates exercising the option to answer Papers in any one of the languages included in the Eight Schedule to the Constitution of India mentioned above may, if they so desire, give English version within brackets of only the description of the technical terms, if any, in addition to the version in the language opted by them. Candidates should, however, note that if they misuse the above rule, a deduction will be made on this account from the total marks otherwise accruing to them and in extreme cases; their script(s) will not be valued for being in an unauthorized medium.
(v) Candidates should note that if any irrelevant matter/signages/marks etc. are found written in the answer script(s), which would not be related to any question/answer and/or would be having the potential to disclose the candidate’s identity, the Commission will impose a penalty of deduction of marks from the total marks otherwise accruing to the candidate or will not evaluate the said script(s) on this account.
(vi) The question papers (other than the literature of language papers) will be set in Hindi and English only.
The main Examination is intended to assess the overall intellectual traits and depth of understanding of candidates rather than merely the range of their information and memory.
The nature and standard of questions in the General Studies papers (Paper II to Paper V) will
be such that a well-educated person will be able to answer them without any specialized study. The questions will be such as to test a candidate’s general awareness of a variety of subjects, which will have relevance for a career in Civil Services. The questions are likely to test the candidate’s basic understanding of all relevant issues, and ability to analyze, and take a view on conflicting socio-economic goals, objectives and demands. The candidates must give relevant, meaningful and succinct answers.
The scope of the syllabus for optional subject papers (Paper VI and Paper VII) for the examination is broadly of the honours degree 1evel i.e. a level higher than the bachelors’ degree and lower than the masters’ degree. In the case of Engineering, Medical Science and law, the level corresponds to the bachelors’ degree.
Syllabi of the papers included in the scheme of Civil Services (Main) Examination are given as follows:
QUALIFYING PAPERS ON INDIAN LANGUAGES AND ENGLISH
The aim of the paper is to test the candidates' ability to read and understand serious discursive prose, and to express ideas clearly and correctly, in English and Indian language concerned.
The pattern of questions would be broadly as follows:
(i) Comprehension of given passages.
(ii) Precis Writing.
(iii) Usage and Vocabulary.
(iv) Short Essays.
Indian Languages:
(i) comprehension of given passages.
(ii) Precis Writing.
(iii) Usage and Vocabulary.
(iv) Short Essays.
(v) Translation from English to the Indian Language and vice-versa.
Note 1: The papers on Indian Languages and English will be of Matriculation or equivalent standard and will be of qualifying nature only. The marks obtained in these papers will not be counted for ranking.
Note 2: The candidates will have to answer the English and Indian Languages papers in English and the respective Indian language (except where translation is involved).
Essay: Candidates may be required to write essays on multiple topics. They will be expected to keep closely to the subject of the essay to arrange their ideas in orderly fashion, and to write
concisely. Credit will be given for effective and exact expression.
General Studies‐I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the World and Society.
General Studies‐ II: Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International relations.
General Studies‐III: Technology, Economic Development, Bio diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management
General Studies‐ IV: Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
This paper will include questions to test the candidates’ attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity, probity in public life and his problem solving approach to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilise the case study approach to determine these aspects.
The following broad areas will be covered:
Optional Subject Papers I & II: Candidate may choose any optional subject from amongst the List of Optional Subjects given.
© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved