




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
A new concept has emerged i.e Everything as a Service (XaaS) means anything can now be a service with the help of cloud computing and remote accessing. Where cloud computing technologies provide different kinds of services over the web networks. In Everything as a Service, various tools and technologies, and services are provided to users as a service. Before XaaS and cloud services, companies had to buy licensed products and install them. They had to buy all securities on their site and provide infrastructure for business purposes. With XaaS, business is simplified as they have to pay for what they need. This Everything as a Service is also known as Anything as a Service. Everything-as-a-Service (XaaS) simply denotes the increasing servitization of technology.
XaaS is a collective term that refers to the delivery of anything as a service. It encompasses the many products, tools and technologies that vendors deliver to users as a service over a network -- typically, the internet -- as an alternative to providing them locally or on-site to an enterprise.
This umbrella term refers to service offerings that are accessed as needed and financed using a pay-as-you-go cloud computing pricing model. XaaS offerings can scale up or down as needed with IT services delivered on demand by a managed service provider.
Examples of XaaS:
As XaaS stands for “Everything as a service”, There are many examples. There are many varieties of cloud computing models like:
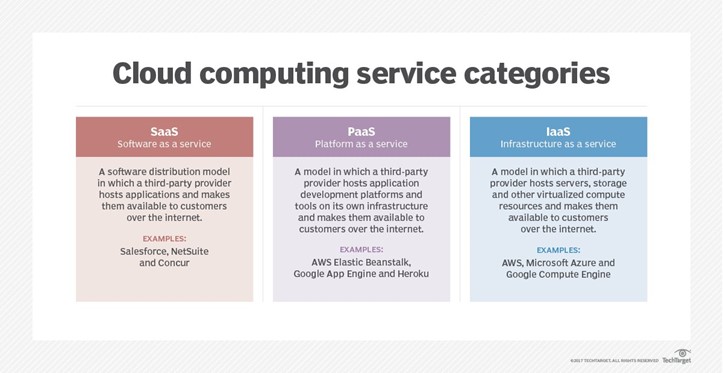
SaaS:
SaaS provides many software applications like Google Apps, and Microsoft Office 365.
PaaS:
PaaS providers deliver hardware and software tools to users over the internet. PaaS offerings, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk, Apache Stratos, Google App Engine and Salesforce's Heroku and Salesforce Platform, typically provide preconfigured virtual machines and other resources for application development and testing.
IaaS
IaaS is a model where a cloud provider provides IT infrastructure, such as storage, server and networking resources, over the internet to customers on a subscription basis . Examples of IaaS offerings include AWS Elastic Compute Cloud, Google Compute Engine and Microsoft Azure.
Everything as a Service (XaaS) Model Examples:
Hardware as a Service (HaaS)
Managed Service Providers (MSP) provide and install some hardware on the customer’s site on demand. The customer uses the hardware according to service level agreements. This model is very similar to IaaS as computing resources present at MSP’s site are provided to users substituted for physical hardware.
Communication as a Service (CaaS)
This model comprises solutions for different communication like IM, VoIP, and video conferencing applications which are hosted in the provider’s cloud. Such a method is cost-effective and reduces time expenses.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
DaaS provider mainly manages storing, security, and backing up user data for desktop apps. And a client can also work on PCs using third-party servers.
Security as a Service (SECaaS)
In this method, the provider integrates security services with the company’s infrastructure through the internet which includes anti-virus software, authentication, encryption, etc.
Healthcare as a Service (HaaS)
The healthcare industry has opted for the model HaaS service through electronic medical records (EMR). IoT and other technologies have enhanced medical services like online consultations, health monitoring 24/7, medical service at the doorstep e.g. lab sample collection from home, etc.
Transport as a Service (TaaS)
Nowadays, there are numerous apps that help in mobility and transport in modern society. The model is both convenient and ecological friendly e.g. Uber taxi services is planning to test flying taxis and self-driving planes in the future.
Benefits in XaaS
Cost Saving
When an organization uses XaaS then it helps in cost-cutting and simplifies IT deployments.
Scalability
XaaS can easily handle the growing amount of work by providing the required resources/service.
Accessibility
It helps in easy accessing and improving accessibility as long as the internet connection is there.
Faster Implementation
It provides faster implementation time to various activities of the organization.
Quick Modification
It provides updates for modification as well as undergoes quick updating by providing quality services.
Better Security
It contains improved security controls and is configured to the exact requirements of the business.
Boost innovation
While XaaS is used it Streamlines the operations and frees up resources for innovation.
Flexibility
XaaS provides flexibility by using cloud services and multiple advanced approaches.
Relevance
With constantly evolving technology and software, XaaS allows small businesses to stay relevant to market and client demands as new products become available.
Higher levels of cybersecurity
Small businesses and enterprises are a favoured target of hackers and cybercriminals. 28% of the breaches in 2019 Involved small business victims. Many businesses opt for lower cost cybersecurity measures that offer less protection. By using XaaS, one can have better security without exorbitant costs.
Disadvantages in XaaS
Internet Breakage
Internet breaks sometimes for XaaS service providers where there can also be issues in internet reliability, provisioning, and managing the infrastructure resources.
Slowdown
When too many clients are using the same resources at the same time, the system can slow down.
Difficult in Troubleshoot
XaaS can be a solution for IT staff in day-to-day operational headaches, but if anywhere problem occurs it is harder to troubleshoot it as in XaaS multiple services are included with various technologies and tools.
Change brings problems
If a XaaS provider discontinues a service or alters it gives an impact on XaaS users.
Not scalable
Smaller XaaS providers may sometimes fail to scale up according to user demand, leading to latency, data storage, bandwidth, and information retrieval.
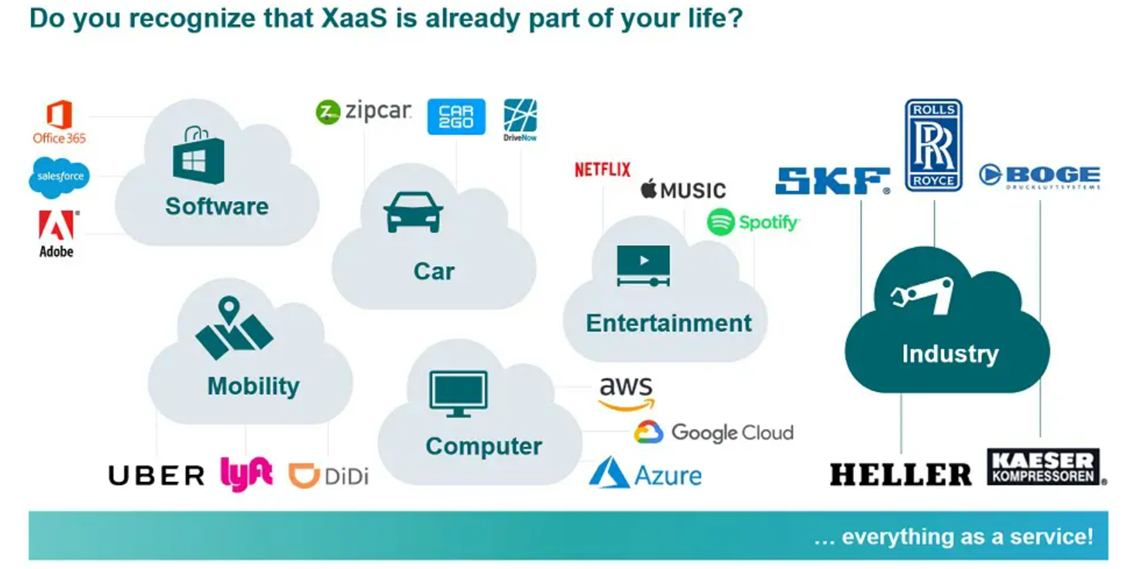
What are the XaaS examples?
XaaS is a very wide-ranging term. Some of those mentioned already are self-explanatory, but let’s look at some other examples of the service.
Hardware as a Service (HaaS)
This is similar to the way in which a business might lease vehicles instead of purchasing outright. The provider owns the hardware and installs it on the client’s site. This allows clients to utilise hardware they may not be able to afford to purchase, and is especially beneficial to small and medium-sized businesses.
Communication as a Service (CaaS)
Communication is one of the most vital tools for many businesses. By using CaaS solutions, it allows a business to access a variety of communication tools and applications as needed. These can include VoIP technology, virtual conferencing tools, and more. The business pays only for a subscription, sometimes based on the time they use these tools, making it highly cost-effective.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
There are times when your staff may need to compute tasks that are beyond their PC or laptop’s abilities. DaaS allows them to access greater computing capacity from a third-party server.
Healthcare as a Service (HaaS)
The healthcare sector is becoming increasingly digitised. By integrating HaaS into your practice or your hospital, you allow for easier sharing of crucial information, online consultations, prescription deliveries, and other vital services. It can also contribute to measuring any ROI for your healthcare business.
XaaS Business Model Explained
XaaS is a business strategy in which businesses can create smart, intelligent platforms, packages, and entitlements. These XaaS business models are deployable for different products, services, and technologies. XaaS facilitates enterprises to adopt a service-oriented business model, which boosts a company’s value by diminishing asset ownership expenditures, allowing management to focus on entrepreneurial prospects, attaining access to cutting-edge technology, and divesting activities with low value-creation prospects. XaaS is functional across multiple dimensions, a few of which are discussed below.
XaaS Model for Products
Managed Service Providers (MSP) own certain equipment/products and provision this on-demand at customers’ premises. Customers employ these products per service level agreements. Computing resources are located at MSP’s location and allocated to consumers per their consumption needs. This pay-as-you-go approach is akin to a utility-based offering. The XaaS Model for Products is extensively delivered across two models:
Servitization: When a company or customer pays for a service rather than buying the equipment or seeks to bundle its service offerings into a single package, this is referred to as servitization. XaaS is built on the premise of being able to take on any IT or business activity, turn it into a product, and then add countless services to it. The hybrid approach to product and service offerings enables firms to deliver more value than siloed solutions.
Smart and Connected Products: Smart and connected products are physical items with smart components (such as sensors) and connectivity components. They enable data exchange and analysis, unlocking value-addition for producers and end-users. Smart, linked products offer exponentially expanding prospects for new functionality, substantially greater reliability, significantly higher product usage, and capabilities that cross and go beyond traditional product boundaries. This product evolution also alters value chains, requiring businesses to rethink and retool practically everything they do internally.
XaaS Model for Services
Enterprises concentrate on delivering an engaging consumer experience and personalized services. This has transformed the way traditional services, as well as modern-day services, are being made available via an innovative service provider. Consequently, new companies (even existing companies are transforming their business models) are venturing into the new areas of useful day-to-day services aimed at making people’s lives more comfortable and easier. Examples include Ride Share Companies, Food Delivery Apps, Essentials Delivery Apps, Courier Delivery Apps, Smart Buildings and Homes, Agriculture and Industrial Management, and Smart Cities.
The number of XaaS model-based services is projected to extend dramatically. Consumers envision value-added services to deliver more than just basic services, such as smartness, connectivity, reliability, technical assistance, ease of use, and hassle-free navigation experience. These novel and beneficial ventures are made possible by smart, linked devices powered by cloud-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
The future for XaaS
XaaS is a conceptual model consisting of all possible services and products that can be provided over networks. At the moment, there is no full implementation of this model. Pushing for XaaS is an ideal benchmark and one of the main strategies for leading global cloud companies such as Microsoft and Google.
The future of Everything-as-a-Service seems to be bright due to emerging technologies and the proliferation of the e-Commerce market. The combination of cloud computing and ubiquitous, high-bandwidth, global internet access bodes well for XaaS growth. The XaaS market is projected to grow to $2.4 trillion in 2029 from $437 billion in 2021, according to a Fortune Business Insights report.
The convergence of 5G -- and, in the future, 6G -- edge computing, big data, artificial intelligence, automation, machine learning and the internet of things have contributed to the move to the XaaS model and the cloud in general.
The XaaS model is the fastest-growing model to unlock market growth and has transcended a strategic need for enterprises that aspire to remain competitive. XaaS models require maturity, organizational preparedness, harmonizing talent profiles across business processes, and timely process automation to construct a thriving business.
© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved