Description
Copyright infringement is not intended
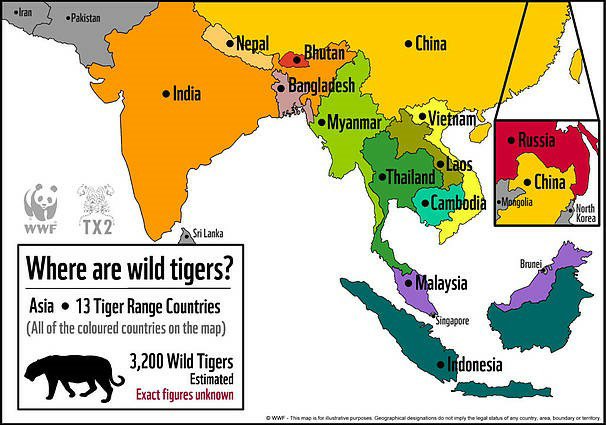
Context: India 4th Asia Ministerial Conference on Tiger Conservation adopted the Kuala Lumpur Joint Statement.
Organised by: The Government of Malaysia and Global Tiger Forum (GTF)
Key highlights of the conference:
- Asked for formalising collaboration and sharing intelligence information among law enforcement agencies to combat wildlife poaching and trafficking.
- Will implement a South East Asia Tiger Recovery Plan, focused on where tiger poaching and trafficking are acute.
India’s achievements:
- India has doubled the tiger population in 2018 itself, 4 years ahead of the targeted year 2022.
- The budgetary allocation for tiger conservation has increased from Rs 185 crore in 2014 to Rs 300 crore in 2022.
- 14 Tiger Reserves in India have already been awarded with international CA|TS accreditation and efforts are on to bring in more Tiger Reserves under CA|TS accreditation.

The 14 tiger reserves, which have been accredited are
- Manas, Kaziranga and Orang in Assam
- Satpura, Kanha and Panna in Madhya Pradesh
- Pench in Maharashtra
- Valmiki Tiger Reserve in Bihar
- Dudhwa in Uttar Pradesh
- Sunderbans in West Bengal
- Parambikulam in Kerala
- Bandipur Tiger Reserve of Karnataka and
- Mudumalai and Anamalai Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu
Why to conserve Tigers?
- Tigers, the top predators in ecosystem, are vital in regulating and perpetuating ecological processes.
- Conservation of top carnivore guarantees the wellbeing of forested ecosystems, the biodiversity as well as water and climate security.
- It is as an umbrella species for majority of the ecosystem in the Indian sub-continent.
Key challenges to tiger conservation
- rise in organised poaching driven by an international demand for tiger body parts and products
- depletion of tiger prey and
- habitat loss
Global Tiger Forum
- It is the only inter- governmental international body established with members from willing countries to embark on a global campaign to protect the Tiger.
- India is one of the Founding members of the intergovernmental platform of Tiger Range Countries ( Nepal, Bhutan, Vietnam, Bangladesh, Cambodia, India and Myanmar).
- It calls upon Range Countries to prepare and update their National Action Plans for Tiger conservation.
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1791473
















