Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled the "Bharat 6G Vision Statement".
- India is gearing up to roll out high-speed 6G communication services by 2030.
Must Read Article: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/the-evolution-of-5g-technology
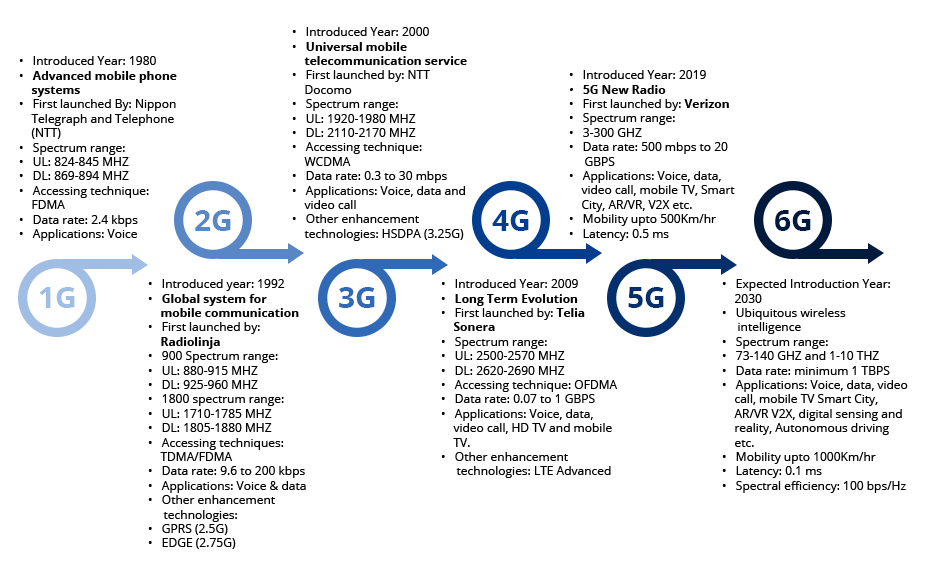
What is 6G?
- 6G, or the sixth-generation telecom network, is the cell phone technology that will provide internet speed of up to 1 terabyte (TB) per second with "ultra-low latency".
Latency is the time it takes for data to pass from one point on a network to another.
- It will ensure smooth machine-to-machine and machine-to-human interactions and boost the development of virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Must Read Article on AR and VR: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/augmented-and-virtual-reality
.jpeg)
How is 6G different from 5G?
- Under the 5G technology, the average speed range lies between 40 to 1,100 Mbps, potentially hitting maximum speeds of 10,000 Mbps through technologies such as millimetre-wave spectrum and beamforming.
- According to the document, 6G will offer ultra-low latency with speeds up to 1 Tbps.
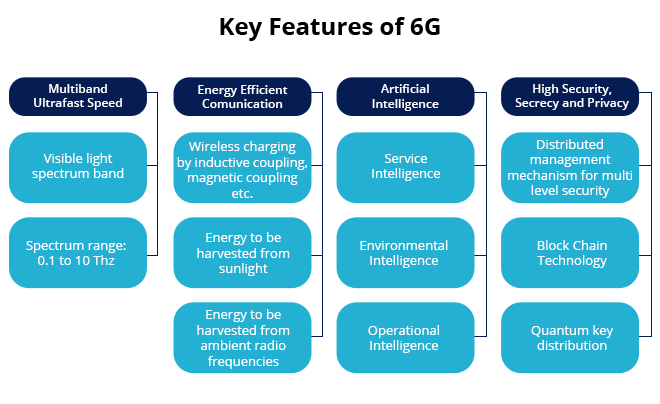
Why is 6G necessary?
- The primary focus of 6G is to support the 4th Industrial Revolution by building a bridge between human, machine, and environmental nodes.
- In addition to surpassing 5G, 6G will have a range of unique features to establish next-generation wireless communication networks for linked devices by using machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI).
- This will also benefit emerging technologies like smart cities, driverless cars, virtual reality, and augmented reality, in addition to smartphone and mobile network users.
- It will combine and correlate different technologies, like deep learning with big data analytics.
Read about 4th Industrial Revolution: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/industry-40
What will change with 6G?
- 6G mobile communication technology is expected to improve and enable access to required information, resources, and services.
- Its deployment is expected to reduce differences in regional and social infrastructure and economic opportunities.
- Thus, it promises a way to slow down rural migration to cities and metro-led urbanisation.
- 6G will play an important role in filling the gap in the availability of e-services between urban and rural communities. This will subsequently fulfill the UN's SDGs and tremendously contribute to improving the quality and opportunities of human life.
- The main use cases of the 6G network will include remote-controlled factories, constantly communicating self-driven cars and smart wearables.
How is India planning to develop and launch 6G?
- The Centre will implement the 6G project in two phases.
- In the first phase, it will provide support to explore new ideas and pathways. With the government's support, these ideas will then be used to develop use cases, intellectual properties (IPs) and testbeds.
- In the second phase, these IPs, prototypes and testbeds will be commercialised.

How much money has been set aside for the development of 6G?
- An apex council has also been appointed to oversee the 6G project and to ensure standardisation, adequate funding and a conducive environment, among other things.
- The statement recommended the creation of a corpus of Rs 10,000 crore to facilitate various funding instruments such as grants, loans, VC funds, fund of funds, etc., over the next ten years.
Is there any caution?
- While 6G promises growth, it will simultaneously have to be balanced with sustainability as most 6G supporting communication devices will be battery-powered and can have a significant carbon footprint.
Which other countries are focussing on the 6G network?
- South Korea has unveiled its 6G research and development plan with an investment of Rs 1,200 crore till 2025.
- Dedicated research centres have been set up in the country and are working closely with the Korean Intellectual Property Office.
- In Europe, the European 6G Vision has identified key features of this network and is currently conducting a research project named Hexa-X. It will end this year.
- In Japan, the Integrated Optical and Wireless Network (IOWN) Forum has published its Vision 2030 white paper for 6G. The paper laid out key technology directions for infrastructure evolution in four dimensions: cognitive capacity, responsiveness, scalability, and energy efficiency.

|
MAINS PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. 6G is not simply an incremental upgrade of wireless, the cloud, or the Internet but the fusion of all of these for the re-imagination of a fully automated life that is built on planet-scale automation. How is India planning to develop and launch 6G? What are the key features of 6G technology? Discuss. Shed light on the challenges associated with Technology.
|

https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/tech-news-technology/bharat-6g-project-india-plans-to-roll-out-high-speed-internet-by-2030-8513471/














