Description
Copyright infringement not intended
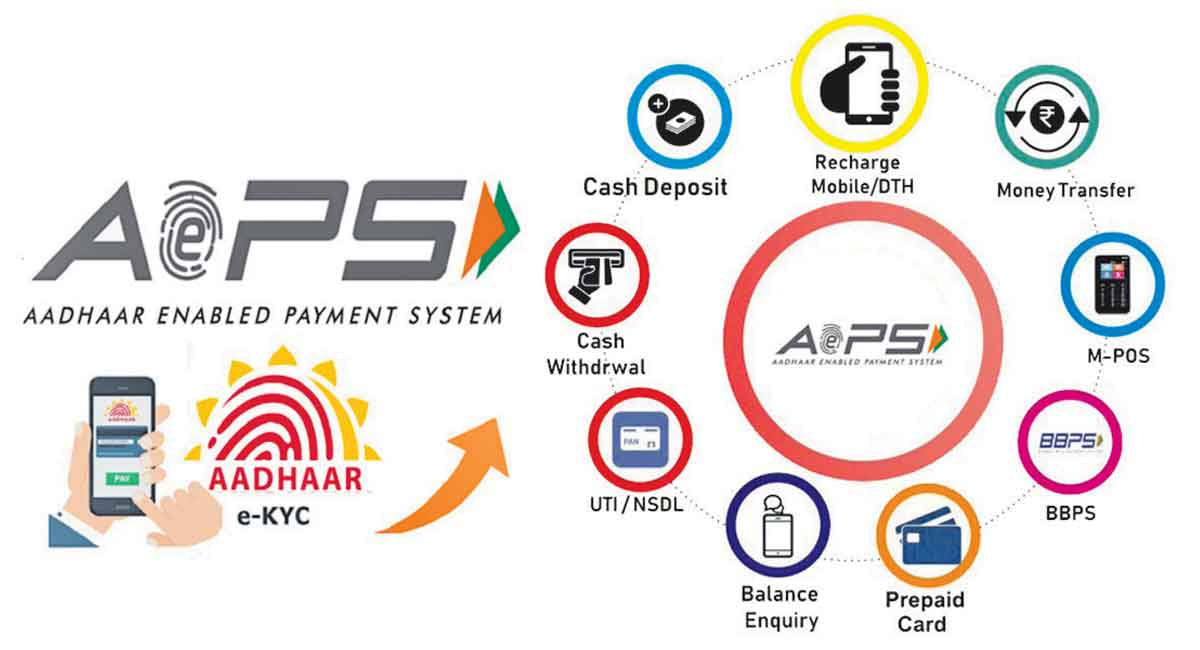
Context: Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS) is a bank-led model that allows online interoperable financial transactions at Point-of-Sale (PoS) devices and micro ATMs of any bank using Aadhaar authentication.
Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS)
About
- AePS is a bank-led model that is developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), which is the umbrella organization for all retail payment systems in India.
- It allows interoperability among different banks and enables people to use any bank's micro-ATM or PoS device to access their bank account.
- It facilitates the delivery of government benefits and subsidies directly to the beneficiaries bank accounts through Aadhaar.
- It is a simple, secure and convenient way to make payments, especially for those who do not have access to smartphones, the Internet or formal banking channels.
- It removes the need for OTPs, bank accounts and other financial details.
Benefits of AePS
- It is available 24x7 and across the country.
- It is free of cost for customers.
- It is interoperable among different banks and service providers.
- It is fast and easy to use.
- It promotes financial inclusion and digital literacy.
Balance enquiry
- You can check your account balance using your Aadhaar number and biometric authentication at any AePS-enabled PoS device or micro ATM.
Cash withdrawal
- You can withdraw cash from your Aadhaar-linked bank account using your Aadhaar number and biometric authentication at any AePS-enabled PoS device or micro ATM.
Cash deposit
- You can deposit cash into your Aadhaar-linked bank account using your Aadhaar number and biometric authentication at any AePS-enabled PoS device or micro ATM.
Fund transfer
- You can transfer funds from your Aadhaar-linked bank account to another Aadhaar-linked bank account using your Aadhaar number and biometric authentication at any AePS-enabled PoS device or micro ATM.
Bill payment
- You can pay utility bills such as electricity, water, gas, etc. using your Aadhaar number and biometric authentication at any AePS-enabled PoS device or micro ATM.

How to use AePS
- An Aadhaar number that is linked to a bank account.
- A bank name that provides AePS service.
- A micro-ATM or PoS device that supports AePS service.
- A fingerprint or iris scan for biometric authentication.
Steps to use AePS
- Visit any micro-ATM or PoS device that supports AePS service.
- Provide the Aadhaar number and bank name to the business correspondent (BC) or merchant.
- Choose the type of transaction (balance enquiry, cash withdrawal, cash deposit, fund transfer, etc.).
- Scan fingerprint or iris for biometric authentication.
- Receive a confirmation receipt for the transaction.
Significance
- It is simple, secure and convenient to use as it does not require any card, PIN or password.
- It is inclusive and accessible as it covers rural and remote areas where banking infrastructure is limited or absent.
- It is cost-effective and efficient as it reduces the operational and transactional costs for both banks and customers.
- It is transparent and accountable as it eliminates fraud and leakage of funds by using biometric authentication.
Challenges
Transaction failures
- The AePS is prone to transaction failures due to various reasons, such as biometric mismatches, network connectivity issues, system errors, or interoperability problems among different banks and service providers.
- These failures cause inconvenience and frustration to customers who need to access or remit cash urgently, especially during the COVID-19 crisis when many government schemes rely on AePS for cash transfers.
Lack of awareness and financial literacy
- Many customers are not aware of the benefits and features of AePS, or how to use it safely and effectively. They may also lack the financial literacy to understand the terms and conditions, fees, and risks involved in using AePS.
- This may lead to misuse, fraud, or exploitation by unscrupulous agents or business correspondents who may charge excessive fees, provide false information, or manipulate transactions.
Inadequate infrastructure and regulation
- The AePS requires adequate infrastructure and regulation to ensure its smooth functioning and customer protection.
- This includes reliable biometric devices, network connectivity, power supply, security systems, grievance redressal mechanisms, and quality standards for service providers. However, these are often lacking or inconsistent across different regions and contexts, affecting the quality and accessibility of AePS services.

Steps need to be taken
Improving the technical and operational aspects of AePS
- Reducing the transaction failure rates by improving the biometric authentication process, ensuring network connectivity and system compatibility, resolving interoperability issues among banks and service providers, and upgrading the hardware and software of AePS devices.
- Ensuring adequate security measures to prevent data breaches, frauds, or cyberattacks on AePS transactions.
Increasing the awareness and financial literacy of customers
- Educating and sensitizing customers about the benefits and features of AePS, how to use it properly and safely, what are the fees and risks involved, and what are their rights and responsibilities as AePS users.
- Providing clear and transparent information about AePS services, terms and conditions, grievance redressal mechanisms, and customer feedback channels.
Strengthening the infrastructure and regulation of AePS
- Ensuring adequate availability and accessibility of AePS devices, network connectivity, power supply, and other infrastructure across different regions and contexts.
- Establishing and enforcing quality standards, guidelines, norms, and regulations for AePS service providers, agents, business correspondents, banks, NPCI, and other stakeholders involved in AePS transactions.
Conclusion
- The Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AePS) is a bank-led model which allows online financial transactions at Point-of-Sale (PoS) devices and micro ATMs of any bank using Aadhaar authentication. The model removes the need for OTPs, bank accounts and other financial details. It allows fund transfers using only the bank name, Aadhaar number, and fingerprint captured during Aadhaar enrolment.
- It is a promising initiative that can enable financial inclusion and digitalization in India. However, it requires concerted efforts from various stakeholders to overcome the challenges it faces and realize its full potential.
Must Read Articles:
Aadhaar: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/aadhar-card
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AePS) for India's financial inclusion and digitalization goals? How can the system be improved to address the existing loopholes and challenges?
|

https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/36485/OPS/GCVB82IPE.1+GOJB831M6.1.html













