Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Chennai-based space-tech startup Agnikul Cosmos has made strides in India's private space sector with the development of its rocket, Agnibaan.
- This innovative suborbital space vehicle demonstrates the potential of 3D printing technology in aerospace manufacturing, making Agnikul the second Indian space-tech company to achieve such a feat.
Details
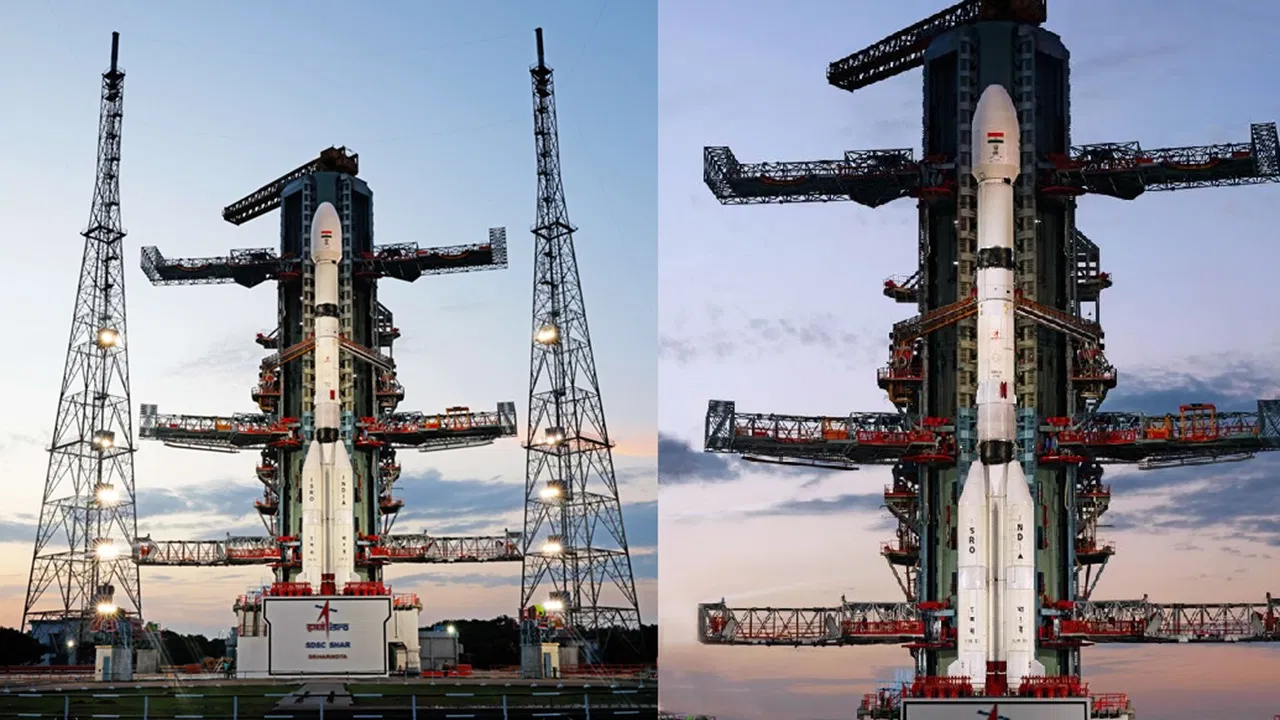
Agnikul's Suborbital Tech Demonstrator (SorTeD)
- Vehicle Overview: Agnikul's SorTeD, named Agnibaan, is a single-stage launch vehicle equipped with the company's proprietary Agnilet engine.
- Vertical Lift-Off: Agnibaan launches vertically and follows a predetermined trajectory during its suborbital space flight.
- Payload Capacity: Agnibaan can carry payloads of up to 100 kg to low Earth orbit (LEO) at altitudes of up to 700 km.
- Physical Dimensions: The vehicle stands 18 m tall, has a diameter of 1.3 m, and a liftoff mass of 14,000 kg.
- Payload Envelope: The payload bay measures 2m x 1.5m and can accommodate one or more satellites.

The Agnilet Engine
- Key Features: Agnilet is an entirely 3D-printed, single-piece, 6 kN semi-cryogenic engine developed by Agnikul.
- Propellants: The engine utilizes a combination of liquid kerosene and supercold liquid oxygen as propellants.
- Testing and Validation: Agnilet engine underwent successful testing at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre in Thiruvananthapuram.
3D Printing's Role in Aerospace
- Speeding Up R&D: Srinath Ravichandran, Agnikul's co-founder and CEO, emphasized 3D printing's ability to rapidly produce complex and customized designs, facilitating faster research and development.
- Iterative Development: Iterative design iterations are possible due to 3D printing's flexibility, allowing designers to refine their prototypes efficiently.
- Challenges and Scalability: While 3D printing accelerates design and prototyping, it may not be as scalable as traditional manufacturing techniques.
Private Sector's Role in Indian Space Industry
- Opening to Private Participation: The establishment of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) in 2020 paved the way for greater private sector engagement in India's space activities.
- Resource Allocation: Private involvement in routine activities frees up resources for ISRO to focus on research, development, interplanetary exploration, and strategic missions.
- Commercial Ventures: Indian space industry has ventured into satellite launch services, weather satellites, and communication satellites, allowing ISRO to concentrate on exploration and scientific missions.

Conclusion
Agnikul Cosmos' Agnibaan showcases the potential of 3D printing in aerospace innovation and exemplifies India's growing prowess in the private space sector. As the private space industry matures, it complements ISRO's efforts in expanding the country's space-based applications, services, and exploration endeavors. The collaboration between ISRO and private players, as seen with Agnikul, not only accelerates technological advancements but also paves the way for India to establish itself as a significant player in the global space economy.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Examine the role of 3D printing technology in aerospace innovation and its impact on research and development. How does the collaboration between the private sector and ISRO contribute to India's space exploration objectives? (250 Words)
|
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-sci-tech/private-rockets-3d-printed-engines-8898688/