Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: aishe.gov.in
Context: The All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) 2021-22, released by the Ministry of Education, provides a comprehensive picture of the higher education landscape in India.
Key findings of the All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) 2021-22
Enrollment Trends
- Overall Enrollment Increase: Total enrollment in higher education increased from approximately 4.14 crore in the previous session to nearly 4.33 crore in 2021-22, marking an increase of around 19 lakh students.
- Female Enrollment Growth: Female enrollment increased from 2.01 crore in 2020-21 to 2.07 crore in 2021-22. The increase in female enrollment from 2014-15 (1.57 crore) to 2021-22 (2.07 crore) accounts for around 50 lakh students.
- Enrollment by Stream: In 2021-22, 57.2 lakh students were enrolled in the science stream, with female students outnumbering male students (29.8 lakh versus 27.4 lakh).
- D. Enrollment: Female Ph.D. enrollment doubled from 0.48 lakh in 2014-15 to 0.99 lakh in 2021-22. The annual increase in female Ph.D. enrollment for the period 2014-15 to 2021-22 is 10.4%.
- Enrollment by Category: The enrollment of Scheduled Tribe (ST) students increased from 16.41 lakh in 2014-15 to 27.1 lakh in 2021-22, marking a 65.2% increase.
- Enrollment in North East States: Total student enrollment in North East States increased from 9.36 lakh in 2014-15 to 12.02 lakh in 2021-22. Female enrollment in North East States (6.07 lakh) surpassed male enrollment (5.95 lakh) in 2021-22.
- Enrollment by Social Category: OBC student enrollment increased by 45% in 2021-22 (1.63 crore) compared to 2014-15 (1.13 crore). Minority student enrollment increased from 21.8 lakh in 2014-15 to 30.1 lakh in 2021-22, with female minority enrollment witnessing a 42.3% increase.
Discipline and Course Level Enrollment
- Undergraduate vs. Postgraduate Enrollment: About 78.9% of total students are enrolled in undergraduate-level courses, while 12.1% are enrolled in postgraduate-level courses.
- Discipline Enrollment: Enrollment is highest in Arts (34.2%) at the undergraduate level, followed by Science (14.8%), Commerce (13.3%), and Engineering & Technology (11.8%). At the postgraduate level, maximum students are enrolled in Social Science (21.1%), followed by Science (14.7%).
- D. Enrollment: Ph.D. enrollment increased by 81.2% to 2.12 lakh in 2021-22 compared to 1.17 lakh in 2014-15.
Institutional and Faculty Trends
- Establishment of Institutions: 341 universities and university-level institutions have been established since 2014-15.
- Female Faculty Increase: Female faculty/teachers increased from 5.69 lakh in 2014-15 to 6.94 lakh in 2021-22, marking a 22% increase.

Implications and Future Directions
- The increase in enrollment, particularly among females and marginalized communities, reflects efforts to improve access to higher education.
- More focus may be needed on diversifying disciplines and promoting STEM education among underrepresented groups.
- Strategies to support Ph.D. enrollment and research output can contribute to academic excellence and innovation.
- Continued investment in infrastructure and faculty development is essential to accommodate the growing student population and ensure quality education.
All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE)
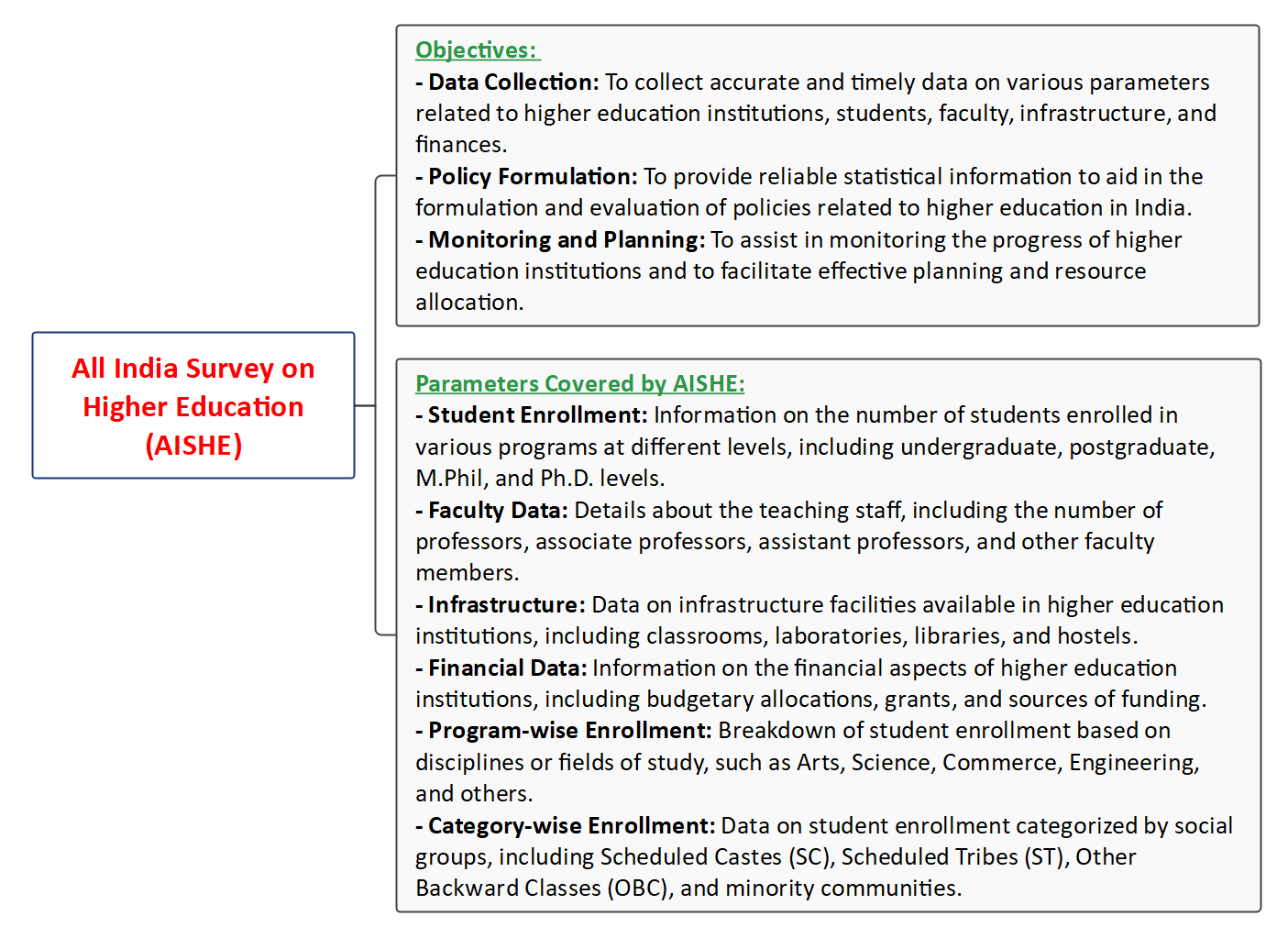
- The All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) is an annual statistical exercise conducted by the Ministry of Education (formerly known as the Ministry of Human Resource Development) in India.
- The survey aims to collect comprehensive data on various aspects of higher education institutions (HEIs) and students in the country.
Methodology
- Coverage: The survey covers all recognized universities, colleges, and institutions providing higher education in India.
- Data Collection: Institutions are required to provide detailed information on various parameters through an online portal developed by the Department of Higher Education.
- Annual Exercise: AISHE is conducted annually to ensure that the data collected is up-to-date and reflective of the current state of higher education in the country.
Significance
- Policy Formulation: The data collected through AISHE serves as a crucial resource for policymakers to formulate and modify policies related to higher education.
- Resource Allocation: The information gathered helps in the allocation of resources and funds based on the needs and requirements of different institutions.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: AISHE enables the government to monitor the growth and development of higher education institutions and evaluate the effectiveness of policies implemented.
- Research and Analysis: Researchers, analysts, and policymakers use AISHE data for in-depth studies, research, and analysis on various aspects of higher education.
Conclusion
- The AISHE is a comprehensive initiative that plays a pivotal role in enhancing the understanding of the higher education landscape in India. The data collected supports evidence-based decision-making and contributes to the overall improvement of the education system in the country.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How can the Indian education system cultivate a culture of innovation, questioning, and critical thinking within its classrooms, encouraging students to challenge assumptions, think independently, and become lifelong learners, rather than rote learners focused on passing exams?
|
















