




Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://phys.org/news/2016-02-animals-oxygen.html
Context: Researchers have identified anoxic marine basins as potential sites for large-scale carbon sequestration by depositing plant biomass in oxygen-deprived zones on the seafloor, offering an effective strategy with minimal impact on marine life.
Details
Why Anoxic Basins?
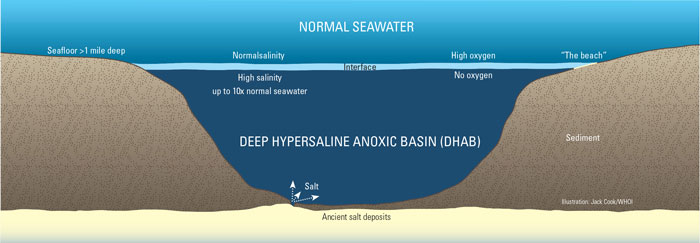
About Anoxic Basins
|
Feature |
Details |
Example |
|
Definition |
Bodies of water devoid of dissolved oxygen (O2) |
Black Sea, Cariaco Trench, Baltic Sea |
|
Formation |
Stratification: Density differences (salt or temperature) create layers, impeding vertical mixing and oxygen replenishment. Organic matter decomposition: Microbes consume oxygen while breaking down organic matter, depleting levels. Limited circulation: Restricted flow from surrounding oxygenated waters. |
Deep, enclosed basins with limited connections to open ocean |
|
Types |
Permanent: Anoxia persists year-round. Temporary: Anoxia occurs seasonally or during specific events. |
Black Sea (permanent), Baltic Sea (seasonal) |
|
Characteristics |
Low oxygen: < 0.2 mg/L or undetectable O2. High hydrogen sulfide (H2S): Produced by microbes under anoxic conditions, creating a rotten egg smell. Extreme conditions: Salinity, temperature, pH can vary depending on basin. Unique microbial communities: Adapted to anoxic environments, utilizing alternative electron acceptors (e.g., nitrate, sulfate) for respiration. |
Black Sea: Hypersaline, anoxic throughout. Cariaco Trench: Anoxic bottom layer, high H2S. |
|
Ecological impact |
Limited animal life: Most animals cannot survive without oxygen. Chemosynthetic communities: Microbes thrive, forming the base of the food chain. Nutrient cycling: Play a role in global cycles of carbon, nitrogen, and other elements. |
Black Sea: Dominated by microbial communities. Cariaco Trench: Supports unique chemosynthetic organisms. |
|
Potential implications |
Climate change: May be affected by warming temperatures and increased stratification. Carbon sequestration: Could be used for storing captured CO2, but concerns exist about potential environmental consequences. Resource exploration: Anoxic sediments may contain valuable minerals, but extraction raises environmental concerns. |
Studies ongoing to assess impact of climate change and potential uses. |
Conclusion
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of anoxic marine sediments? A) High concentration of hydrogen sulfide B) Presence of chemosynthetic bacteria C) Abundance of macroscopic animals D) Decomposition of organic matter Answer: C Explanation: Anoxic environments lack sufficient oxygen for most animals to survive. While chemosynthetic bacteria thrive in these conditions, macroscopic animals are typically absent. |







© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved