Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.worksheetsplanet.com/what-is-an-anticyclone/
Context: Extreme weather in Dubai (floods) and Mumbai (humid heat) was influenced by a northern Indian Ocean anticyclone, highlighting global weather interconnectivity.
Details
- The recent extreme weather events in Dubai and Mumbai, characterised by floods in Dubai and intense humid heat in Mumbai, were influenced by a massive anticyclone over the northern Indian Ocean.
- The anticyclone, along with other local weather phenomena, contributed to both the flooding and heat waves, highlighting the interconnectedness of weather patterns across distant regions.
Anticyclones
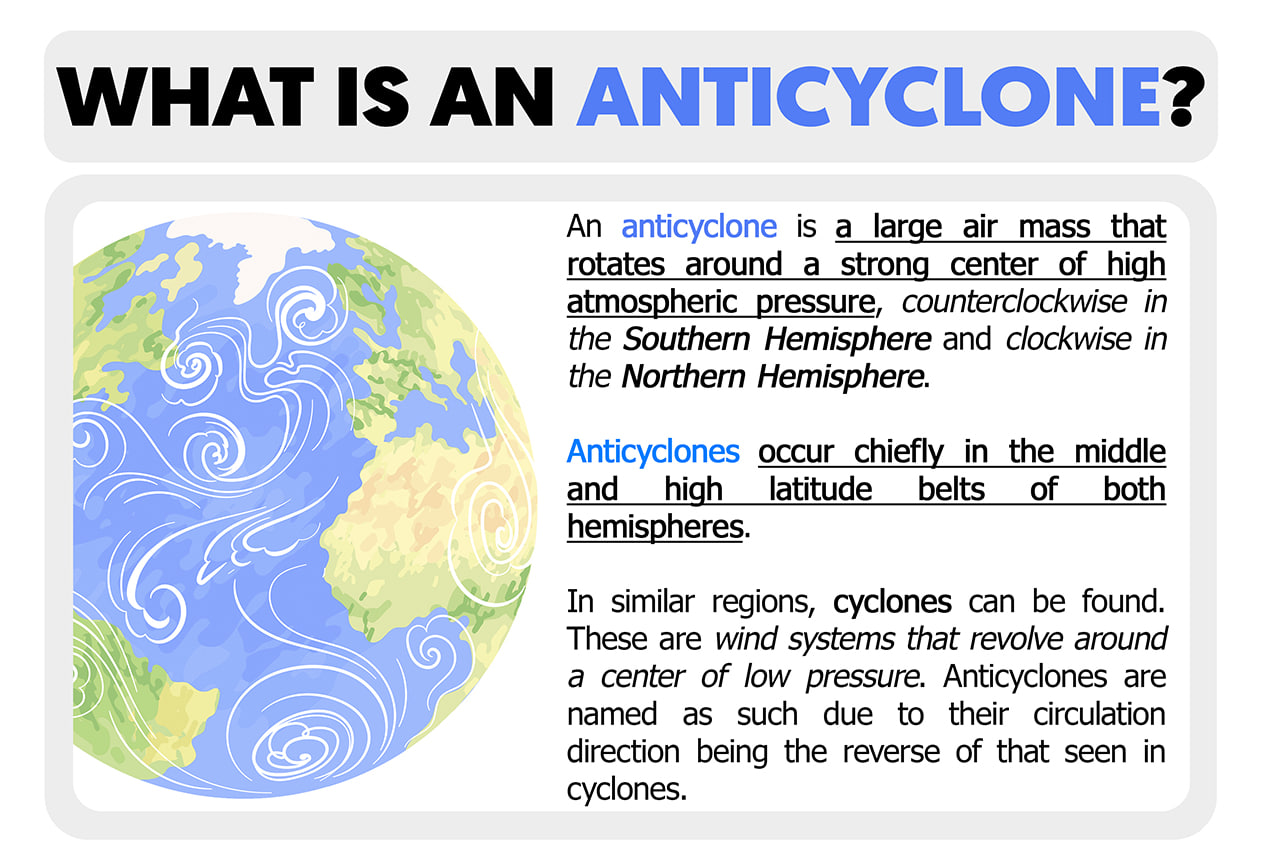
- An anticyclone is a region of high atmospheric pressure characterised by descending air. As the air descends, it warms and inhibits the formation of clouds and precipitation.
- Anticyclones can influence large areas of the atmosphere, affecting weather patterns and conditions over vast regions.
|
An anticyclone is a significant weather phenomenon characterised by a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure.
|
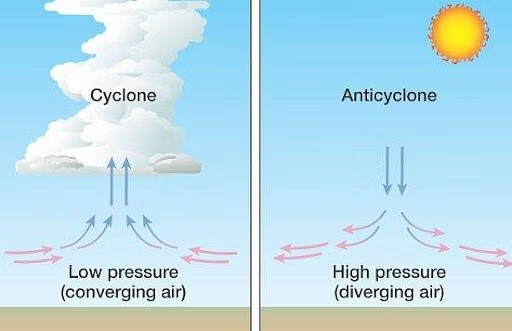
Structure of Anticyclones
- Anticyclones feature descending air, leading to high pressure at the Earth's surface.
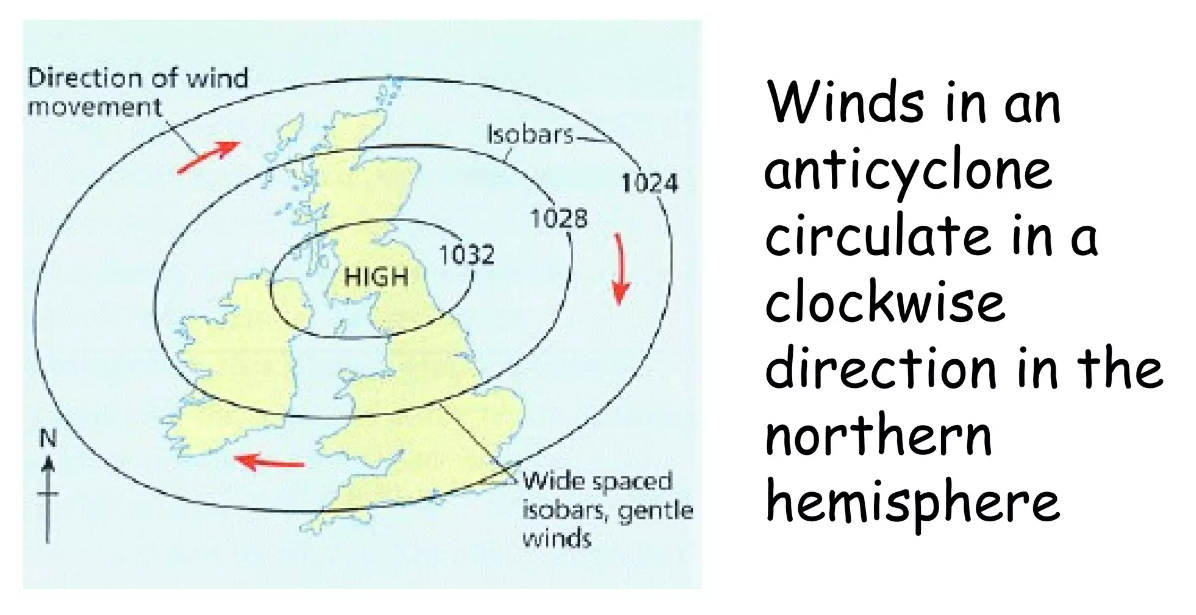
- Winds circulate clockwise around the central region of high pressure in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
- They are associated with clear skies, cooler temperatures, and drier air at the surface.
- Fog formation is common overnight within regions of higher pressure due to subsidence and stable air conditions.
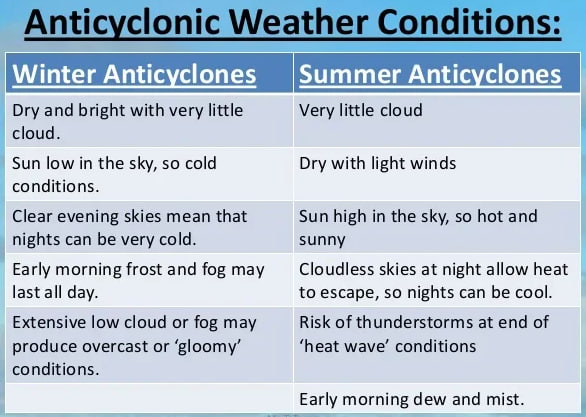
Effects of Anticyclones
- Anticyclones result in light surface winds and subsidence of air, leading to clear skies and rapid temperature changes.
- Subsidence warms air by adiabatic heating, causing temperatures to rise during the day and drop at night.
- When humidity rises overnight, anticyclones can promote fog formation.
- In urban areas, subsidence under high-pressure systems can lead to particulate buildup and haze.
Regional and Global Impact
- Anticyclones contribute to the formation of subtropical ridges, which influence global climate and precipitation patterns.
- They play a role in steering tropical cyclones around their margin and can inhibit free convection and cloud development near their centres.
- Upper-level anticyclones allow for upper-level divergence, leading to surface convergence and potential thunderstorm development.
|
Anticyclonic storms have been observed on other planets like Jupiter and Saturn, powered by different mechanisms compared to Earth-based anticyclones. These extraterrestrial anticyclones highlight the broader understanding of atmospheric dynamics beyond Earth's atmosphere.
|
Mumbai's Humid Heatwave
- Mumbai experienced a humid heatwave as a result of the anticyclone's impact. The descending air from the anticyclone suppressed the development of cooling sea breezes.
- Sea breezes typically help moderate temperatures in coastal areas like Mumbai. However, the presence of the anticyclone prevented this cooling effect, leading to higher-than-usual temperatures and humidity.
- The warm air sweeping in from the northern Arabian Sea, combined with moisture from the pre-monsoon period, contributed to the intense humidity observed in Mumbai.
Dubai's Torrential Rainfall and Flooding
- Dubai and other parts of the United Arab Emirates experienced excessive rainfall and flooding due to the anticyclone system.
- The anticyclone-blocking effect prevented the normal passage of weather systems, such as a western disturbance, which may have otherwise influenced the region.
- Cloud seeding operations conducted by the National Centre of Meteorology of the UAE, along with the presence of dust particles in the atmosphere, likely enhanced the rainfall.
Link Between Extreme Weather Events
- Despite being geographically distant, both Mumbai and Dubai were affected by the periphery of the same massive anticyclone.
- The anticyclone's expansive influence created conditions for extreme weather phenomena, leading to floods in Dubai and oppressive humidity in Mumbai.
|
Why is it important to monitor anticyclones?
●Anticyclones can exacerbate heat waves, increase humidity levels, and contribute to the intensification of storms and rainfall.
●Understanding the influence of anticyclones on regional weather patterns is crucial for predicting and preparing for extreme weather events. This knowledge helps meteorologists and policymakers anticipate and mitigate the impacts of such events.
|
Challenges posed by anticyclones
- Intensification of heat waves: Anticyclones can trap warm air and prevent cooling, leading to prolonged periods of high temperatures.
- Amplification of humidity: Sinking air within anticyclones can cause moisture to accumulate, resulting in muggy and uncomfortable conditions.
- Impact on storm patterns: Anticyclones can disrupt the normal movement of storm systems, potentially leading to unexpected and severe weather events like heavy rainfall and flooding.
|
Meteorological agencies and researchers monitor anticyclones and their interactions with other weather systems using satellite imagery, weather models, and atmospheric data. This monitoring helps forecasters issue timely warnings and advisories to communities likely to be affected by extreme weather conditions.
|
Way Forward to address the challenges associated with anticyclones and their impacts on weather patterns
- Enhance monitoring and research efforts to improve understanding of anticyclone behaviour and interactions with other weather systems.
- Develop advanced forecasting techniques to predict the onset and duration of heat waves, humidity spikes, and storm events associated with anticyclones.
- Implement effective communication strategies to disseminate weather forecasts and warnings, especially in regions prone to extreme weather influenced by anticyclones.

Conclusion
- The recent weather events in Dubai and Mumbai underscore the significant influence of anticyclones on regional weather patterns. As climate change continues to alter atmospheric conditions, the role of anticyclones in driving extreme weather events is likely to become more pronounced. By advancing scientific understanding and implementing proactive measures, communities can better prepare for and respond to the impacts of anticyclones and associated weather phenomena
Source:
Down to Earth
Wikipedia
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements in the context of the anticyclone:
1. Anticyclones are areas of high atmospheric pressure characterised by sinking air and warming temperatures.
2. Anticyclones are associated with clear skies and calm weather conditions.
3. Anticyclones rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
4. Anticyclones are often associated with high temperatures and heatwaves.
How many of the above statements are correct?
A) Only one
B) Only two
C) Only three
D) All four
Answer: C
|



















