Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended
Details
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, IPCC, highlights that The Arctic sea ice is decreasing day by day.
- If global emissions will continue to increase and led to temperatures beyond 4.5°C, the first sea-ice free summer will happen much before 2050.
- It is expected that the Arctic will be free of ice-free by 2081-2100 if such temperature rise continue.
- From the time when satellite started monitoring and recording the Arctic, Every year the rate of loss of ice has been around 13%.
Must read article:
https://iasgyan.in/blogs/all-about-intergovernmental-panel-on-climate-changeipcc
Findings of Report
- Even if the collective efforts to sharply reduce carbon emissions are taken, there are still chances that there would a loss of Arctic ice.
- Nature study confirms that the situation, where temperature-rise was restricted to 1.5°C or 2°C of pre-industrial level, provides no guarantee of saving of Arctic sea in summer.
- With current trend of Greenhouse gas emissions first such summer would be as early as in the 2030s.
Cause of Ice melting
- Anthropogenic factors contributed to 90% of the melting ice problem., the rest 10 % of it caused by natural variability.
- The climate models of IPCC underestimates the pace of melting.
- If the actual conditions are taken into account and model is tweaked, the first ice-free Augusts and Octobers is likely by 2080 if emission increases temperatures above 4.5°C.
.jpeg)
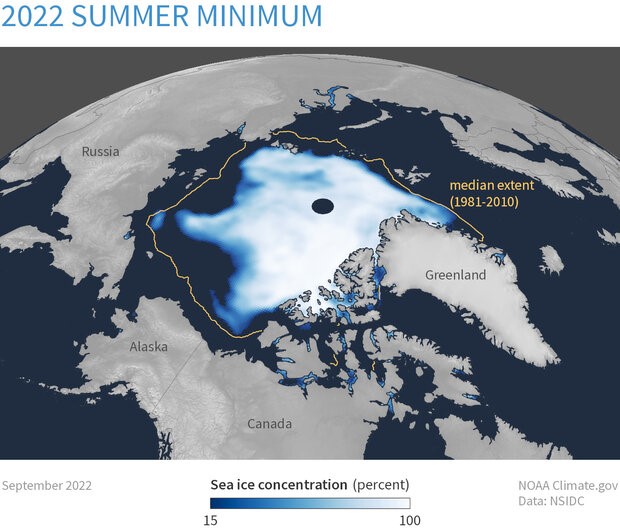
Sea Ice
- Sea ice, massive sheets of ice, is frozen seawater which floats on the ocean surface.
- It is present in both the Arctic and the Antarctic in each hemisphere's, mostly in the polar ice packs of planet’s polar regions.
- However ice melts and sea ice retreats in the summer, but does not completely disappear.
Thickness of Artic sea ice vary with seasons
- Sea ice of the Arctic region influences global climate significantly and contributes to changes in Arctic sea temperature.
- By mid-September Sea ice is thinnest because normally melts during this time due to its long exposure to sunlight. The size of ice is generally half of what is present in winters.
- In winters winter there is a dip in temperatures leading to the expansion and thickening of sea ice. It continues till March and envelops most of the Arctic sea.
Sea ice and its Impact on Planet
- Sea ice is an integral part of the Arctic Ocean and an important indicator of climate change.
Global warming and significance for climate
- Sea ice has high Albedo, the fraction of light that a surface reflects, thus reflects more sunlight back to space. Hence it is vital for maintaining the earth’s heat budget and help in keeping Polar Regions, covered in white snow, cool.
- It also a barrier between the cold air above and the relatively warmer water below thus keeping the air cool.
- These ice sheets help in reduced frequency and intensity of intense heatwaves
- When it melts, the cooling effect of Arctic region is reduced, and a loop between ocean warming and loss of sea ice is created which heighten the melting of ice.
- One side effect of such sea ice is polar jet stream and extreme winters.
- However melting sea ice weakens the polar jet streams and led to increasing instances of heatwaves.
- Polar jet stream is a high-pressure wind that circles the Arctic region. It can disrupt the normal living condition in the north of northern hemisphere as it is destabilized by warmer air, which can dip south, bringing bitter cold with it.
Impact on Marine Life
- Changes in sea ice affects presence of sea ice for hunting.
- Hence biodiversity is impacted and Marine animal like polar bears and walruses are severely affected.
- It makes food availability, breeding, and migrating difficult for them thus threatening survival.
Impact on local population
- Reduced ice cover affects indigenous Arctic communities’ life style. Some of such communities are - the Yup’ik, Iñupiat, and Inuit, the EPA notes.
- Glacial melt of the Greenland ice, if it melts entirely, can increase global sea levels by as much as 20 feet.
- Average sea level threatens coastal cities and small island nations. It accentuates the danger of coastal flooding, storm surge, and other frequent dangerous weather events.
Impact on Trade
- Due to opening up of shipping lanes and easy accessibility of Arctic region, it provides a commercial and economic opportunity in trade and exploitation of natural resources.
- However threat of global competition in trade and Arctic resources may prove detrimental to environment and biodiversity as it lead to more emission, pollution and temperature rise.
Way Ahead
- To enhance the protection and stabilization of Arctic summer sea ice, carbon emissions need to be reduced
- Net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050.
- Methane emission reductions.
- Decrease in greenhouse gas
- Behaviourial changes should be promoted -
- Using electricity and water wisely to cut down energy.
- Limiting resource consumption and hence less greenhouse gas burden on climate.
- Promotion to energy produced by renewable sources of energy.

Must read article:
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/arctic-ice
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
With a special reference to arctic ice discuss the significance of sea ice to the planet. Also suggest the measures/efforts to keep melting of sea ice in limit. (150 words)
|
https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/39218/OPS/GODBBFIL0.1.png?cropFromPage=true
















