




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
About ASEAN
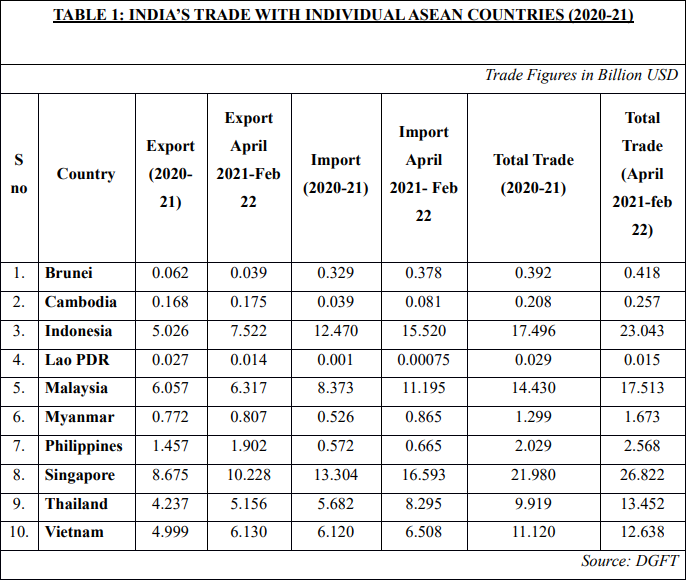
India-ASEAN Relations
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GDQ9S82J5.1&imageview=0








© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved