Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context: India has been unanimously elected as the chair of the Standing Committee on Integrated Pest Management (IPM) of the Asia Pacific Plant Protection Commission (APPPC) for the biennium 2023-24. The election took place during the 32nd Session of the APPPC held in Bangkok, Thailand.
Details
- India has been actively involved in APPPC activities and has contributed to the development and implementation of several regional standards for phytosanitary measures. India has also hosted several workshops and training programmes on IPM, pest risk analysis, and pesticide management for the benefit of other member countries.
Asia Pacific Plant Protection Commission (APPPC)
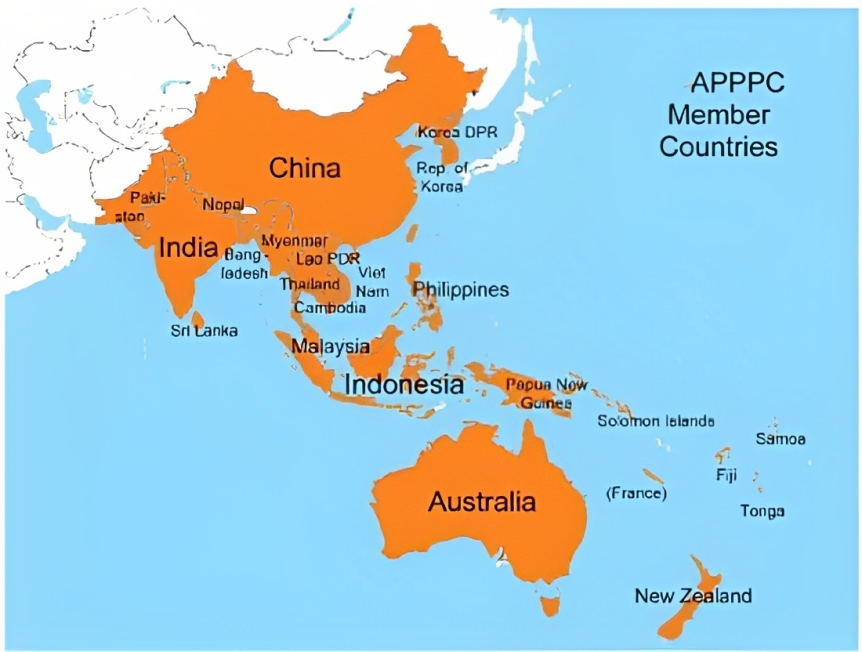
- APPPC is an intergovernmental organization that aims to promote cooperation and coordination in plant protection among its 25 member countries.
- It was established in 1956 under the auspices of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and is one of the nine regional plant protection organizations recognized by the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC).
Features that distinguish APPPC from other regional plant protection organizations
- It covers a vast and diverse geographical area, spanning from Afghanistan to New Zealand and from Mongolia to Fiji.
- It has a broad mandate that encompasses not only plant health, but also plant production and trade, invasive alien species, biological control, pesticide management, and environmental protection.
- It operates through a network of national plant protection organizations (NPPOs), regional and international organizations, research institutes, universities, and other stakeholders.
Some of its achievements include:
- Developing and adopting regional standards for phytosanitary measures (RSPMs) that guide various plant health issues such as pest risk analysis, pest surveillance, pest reporting, pest-free areas, and phytosanitary certification.
- Facilitating the exchange of information and expertise on plant protection through various platforms such as newsletters, websites, databases, workshops, training courses, and technical consultations.
- Supporting the implementation of the IPPC and its related instruments such as the International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (ISPMs), the Phytosanitary Capacity Evaluation (PCE) tool, and the ePhyto system.
- Promoting regional cooperation and collaboration on plant protection issues such as fruit fly management, coconut lethal yellowing disease control, fall armyworm surveillance and management, and invasive alien species prevention and management.
- Enhancing the capacity of NPPOs and other stakeholders to address plant protection challenges through various projects and programs funded by FAO, donor countries, and other partners.
Challenges that hinder its effectiveness and efficiency
- Limited financial and human resources constrain its ability to deliver its services and activities.
- The diverse needs and priorities of its member countries require tailored and flexible approaches.
- Rapid changes in the plant protection landscape due to globalization, climate change, urbanization, and emerging pests and diseases.
- Lack of awareness and recognition of its role and functions among some stakeholders.
The APPPC needs to adopt a strategic and proactive approach that focuses on:
- Mobilizing more resources from various sources to support its core functions and activities.
- Strengthening its governance structure and operational mechanisms to ensure transparency, accountability, and responsiveness.
- Improving its communication and advocacy strategies to raise its profile and visibility among stakeholders.
- Building stronger partnerships with regional and international organizations, research institutes, universities, civil society organizations, private sector entities, and other relevant actors.
- Innovating its products and services to meet the changing needs and expectations of its member countries.
The APPPC has the potential to play a more prominent role in addressing the current and future plant protection challenges in the region. However, it also needs to adapt to the changing environment and enhance its capacity and performance. By doing so, it can contribute more effectively to achieving food security, environmental sustainability, and economic development in the Asia Pacific region.
|
Standing Committee on Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- The Standing Committee on IPM is one of the four technical committees of the APPPC that provides guidance and recommendations on various aspects of IPM, such as;
- Pest surveillance
- Pest risk analysis
- Pest management strategies
- Pesticide management
- Regional and international standards for phytosanitary measures
|
Conclusion
- As the chair of the committee, India will play a key role in coordinating and supporting plant protection activities in the region with a strong information exchange programme, a regional standard development programme, and inputs into an international standard-setting and regional pesticide programme. India will also take a leadership role in integrated pest management (IPM) programmes and build local capacities in member countries.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is/are the key objectives of the Asia Pacific Plant Protection Commission (APPPC)?
A) Setting standards for phytosanitary measures
B) Setting standards for pesticide residues
C) Setting standards for plant breeding
D) Setting standards for plant biotechnology
How many of the above statements are correct?
A) Only 1
B) Only 2
C) Only 3
D) All
Answer: A
Explanation: According to the FAO website, the key objective of the APPPC is setting standards for phytosanitary measures.
|

https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1933446
















