Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context - The Union Government has reviewed the progress of work under the Aspirational District Programme (ADP).
Details
- The Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions has chaired a meeting at Baramulla in Jammu & Kashmir to review the progress of work under the Aspirational District Programme (ADP).
- He stated that the main aim of the Programme is to focus on improving people’s ability to participate fully in the developmental economy.
Aspirational District Programme (ADP)
- The Union Government launched the ‘Transformation of Aspirational Districts’ programme in 2018.
- The overall objective of the programme;
- Convergence of Central & State Schemes.
- Collaboration of Central, State level ‘Prabhari’ Officers and District Collectors.
- Competition among districts with a spirit of mass Movement.
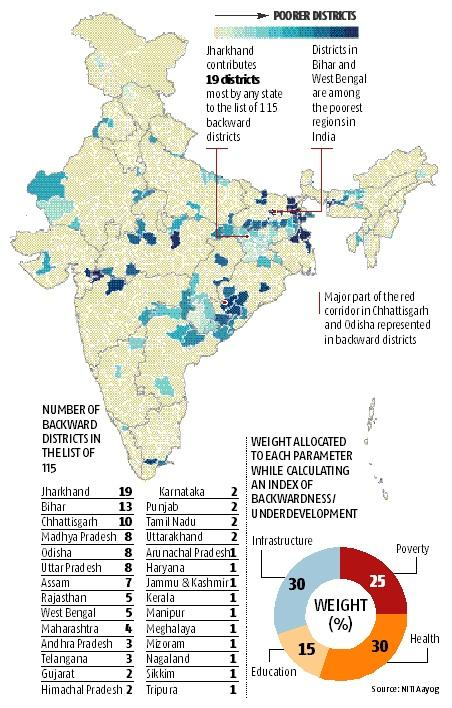
- 115 districts were transparently identified from 28 states by a committee of Senior Officers to the Government of India, in consultation with State Officials using a composite index.
- The Composite index included data from the Socio-Economic Caste Census, Key health and education sector performance and the basic infrastructure of the State.
- The NITI Aayog coordinates and manages the programme with support from Central Ministries and the State Governments.
- NITI Aayog is supervising the initiative in 30 districts.
- Various central ministries oversee 50 districts.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs focuses on 35 Left Wing Extremism (LWE) affected districts.
- The Officers at the level of Joint Secretary or Additional Secretary are nominated to become the ‘Central Prabhari Officers’ of each district.
- States have appointed Prabhari officers.
- An Empowered Committee under the NITI Aayog will help in the convergence of various government schemes and efforts.
- NITI Aayog release the Delta ranking for Aspirational Districts to assess the performance across 5 developmental areas;
- Health and Nutrition
- Education
- Agriculture and Water Resources
- Financial Inclusion and Skill Development
- Basic Infrastructure
Copyright infringement not intended
NITI Aayog
- Planning Commission Inspired by the USSR/Soviet Model, Prime Minister established a Planning Commission in 1950 to design the five-year Plans for India.
- In 2015, it was replaced by a new organization named National Institution for Transforming India (NITI)
- Promote Cooperative Federalism
- Governing Council of NITI Aayog has Lieutenant Governors of Union Territories and State Chief Ministers.
- NITI Aayog Constituted a Committee of State Chief Ministers to examine important issues.
- Promote Competitive Federalism
- NITI Aayog has Prepared online dashboards to rank the States on various indicators of development Such as;
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) India Index.
- Health Index.
- School Education Quality Index.
- Digital Transformation Index.
- Launched Aspirational District Programs for monitoring the Progress of backward districts.
- NITI Aayog has not been given the mandate or Powers to impose Policies on States.
- NITI Aayog is a think tank or an advisory body.
- The Powers for allocation of funds have not been given to the NITI Aayog. The Powers are with Finance Ministry.
- As a ‘think-tank’, Niti Aayog has helped the government In framing various Policies on;
- Clean energy
- Methanol based economy
- Infrastructure human development etc.
- The model acts on agricultural land leasing, livestock Selling etc.
- NITI Aayog regularly organizes Seminars, Workshops, and Conferences.
- NITI initiated Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) to help Startups. NITI is developing National Program on Artificial Intelligence.
- NITI’s approach is modernized, forward-looking, and less bureaucratic; NITI Aayog is playing an important role as a think tank for Economic growth, Human development and Good governance in India.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1819894














