Description
Copyright infringement not intended
In News:
- The National Health Authority (NHA) introduced a new system to measure and grade hospital performance under the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) Scheme.
- The main objective behind the decision is to shift the focus of measuring the performance of hospitals from the volume of services provided to the value of healthcare services.
- The National Health Authority said that “the authority is implementing various measures to ensure that the beneficiaries of the PM-JAY scheme receive both cashless healthcare benefits and high-quality care at every empanelled hospital. These measures include;
- Standardizing the cost of treatment under the scheme.
- Adding new and advanced treatment procedures.
- Incentivize best-performing hospitals that provide quality care to patients.
Details:
- The National Health Authority under the new initiative has introduced the concept of ‘value-based care’, where payment will be based on the outcome and service providers will be rewarded according to the quality of the treatment delivered.
- Under the new initiative, the performance of the empanelled hospitals will be measured based on 5 indicators:
- Beneficiary Satisfaction
- Hospital Readmission Rate
- The extent of Out-of-Pocket Expenditure
- Confirmed Grievances
- Improvement in patient’s Health-Related Quality of Life
- The performance of the hospitals will be released on a website dashboard so that the beneficiaries could make an informed decision.
- The hospital's performance will determine the financial incentive to be received by the hospital, and also create a demand for quality treatment for beneficiaries under PMJAY.
- The service providers will be rewarded for helping the patients in improving their overall health.
- It will reduce the effects of the disease on the population in the long term.
- The new initiative is expected to be a win-win situation for all concerned stakeholders from patients to healthcare providers, payers and suppliers.
- The Patients will get better health outcomes and higher satisfaction from the services they receive.
- Service Providers will get better care efficiencies.
- Payers will be able to maximize the health benefits generated by the spending.
- Significance
- A healthier population with fewer claims will translate into less drain on payers’ premium pools and investments.
- Service providers and Suppliers would be benefited from positive patient outcomes and reduced costs.
- It will improve the healthcare system by incentivizing and encouraging healthcare providers to focus more on delivering patient-centric services.
.jpeg)
Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY):
- The scheme was launched in 2018 to achieve the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- PM-JAY was earlier known as the National Health Protection Scheme (NHPS) before being rechristened. It subsumed the then-existing Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana (RSBY) which had been launched in 2008.
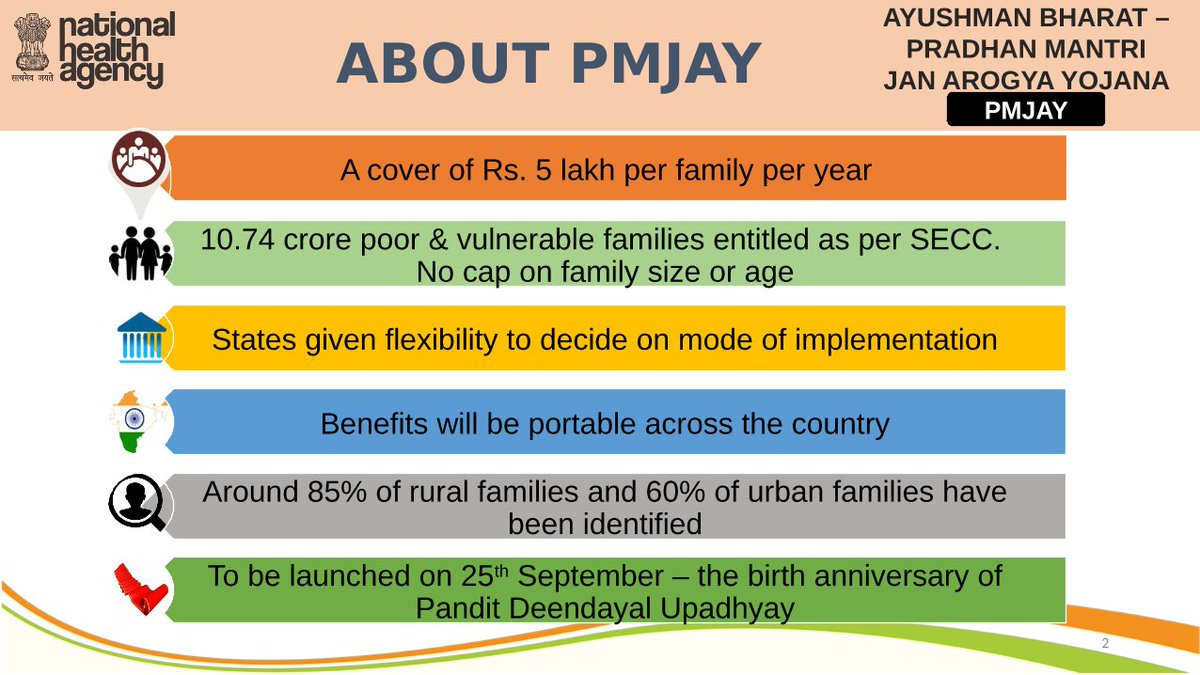
- It is the largest health assurance scheme in the world, which aims at providing a health cover of Rs. 5 lakhs per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization to over 10.74 crores poor and vulnerable families (approximately 50 crores beneficiaries) that form the bottom 40% of the Indian population.
- There are no restrictions on the number of family members, age, or gender.
-
- Households included are based on the deprivation and occupational standards of the Rural and Urban Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011 (SECC 2011).
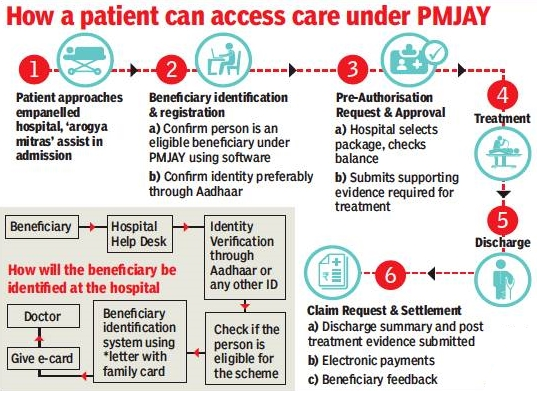
- It provides the point of service, the beneficiaries in the hospital, with cashless access to medical services.
- The program has expanded its reach to 33 states/regions in the Union, making the lives of beneficiaries easier while receiving treatment.
- Under the program, more than one crore of treatment is available to beneficiaries. More than half of the total number of beneficiaries who receive benefits under this system are female.
Copyright infringement not intended
National Health Authority (NHA):
- National Health Authority (NHA) is responsible for implementing “Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana” and has been entrusted with the role of designing a strategy, building technological infrastructure and implementing “National Digital Health Mission” to create a National Digital Health Eco-system.
- Functions of NHA under PM-JAY
- Formulation of various operational guidelines related to PM-JAY.
- Determine the central ceiling for premium per family per year to be provided to the States/UTs and review it from time to time.
- Develop and enforce standards for treatment protocols, quality protocols, minimum documentation protocols, data sharing protocols, data privacy and security protocols, fraud prevention and control including penal provisions, etc.
- Develop mechanisms for strategic purchasing of health care services through PM-JAY, to get the best return on Government’s investment.
- Set up effective and efficient mechanisms to pay the health care providers.
- Set up systems and processes for the convergence of PM-JAY with other health insurance/assurance schemes.
- Work closely with Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority on the development and implementation of Health Insurance Regulations targeting insurance companies, Third Party Administrators, hospitals and other stakeholders.
- Effective implementation of PM-JAY across the country and its regular monitoring including taking course corrections actions, as and when required.
- Coordination with various State Governments on regular basis for the implementation of PM-JAY.
- Capacity building of State Health Agencies and other stakeholders continuously.
- Carrying out awareness activities for informing beneficiaries and other stakeholders about the scheme.
- Grievance redressal for all the stakeholders at various levels.
- Set up an efficient monitoring system for the scheme.
- Take decisions related to the implementation of the scheme, recruitment rules and hiring of staff, disbursement of grant-in-aid to the States and issue relevant directions from time to time, as required.
- And all other activities as assigned by the Government of India from time to time.
Steps taken by the Government to reform the Health Sector:
- Promotion of Institutional deliveries through Cash incentives under Janani Suraksha Yojana.
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram: Free ante-natal Check-ups, Postnatal Care and treatment of Sick infants till one year of age.
- Providing Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child and Adolescent Health Services, the establishment of Special Newborn Care Units.
- Home Based Newborn Care is being provided by ASHAs.
- MAA for improving breastfeeding practices.
- Pradhan Mantri Dialysis Program.
- Mission Indradhnaush: Expanding full immunization Coverage, the introduction of new vaccines.
- PM Swasthya Suraksha Yojana for strengthening the tertiary health Sector.
- POSHAN Abhiyaan to address Malnutrition.
- Iron and folic acid Supplementation for the Prevention of Anaemia, home visits by ASHAs to promote breastfeeding and promote the use of ORS and Zinc for the management of diarrhoea in children.
- Medical Devices Rules, 2017: Transparent regulatory System, ensuring the Safety and quality of medical devices Allowed 100% FDI in the medical devices Sector to Promote Make in India.
- National Health Resource Repository: Create a reliable, unified registry of the Country’s healthcare resources showing the distribution pattern of health facilities and Services between Cities and rural areas - ISRO is a Technology Partner for providing data Security.
- Allowed 100% FDI in the Medical devices Sector to promote Make in India.
- Kayakalp initiative to Promote Cleanliness, hygiene and infection control practices in public health facilities.

https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1889730















