Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu held a telephone discussion on the escalating threats to maritime security in the Red Sea because of the actions of Houthi militants of Yemen.
- The conversation came soon after the Pentagon announced an international mission to counter the growing number of attacks against Israel-bound international traffic.
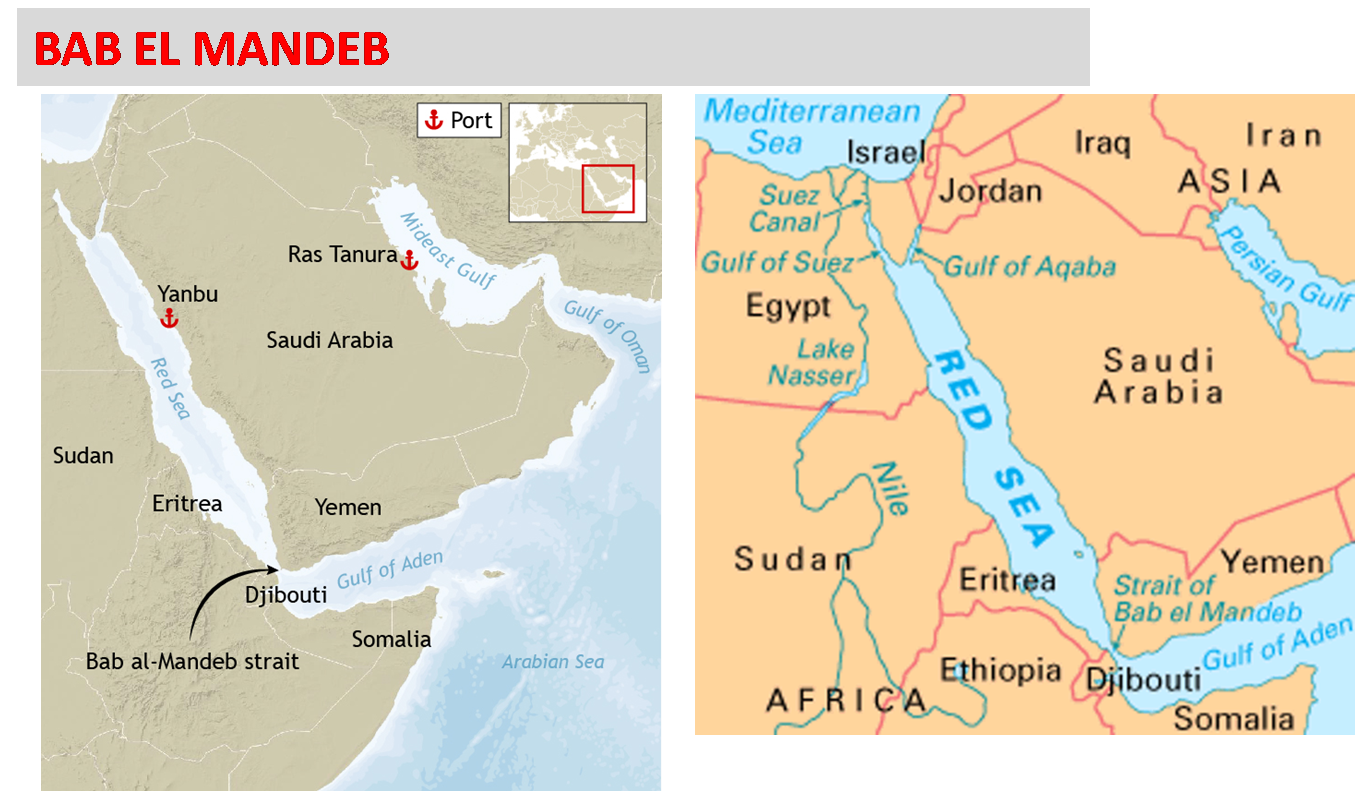
About Bab al-Mandab Strait
- It is a strait that connects the Red Sea (northwest) with the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean (southeast).
- It is located between Arabia (northeast) and Africa (southwest).
- It is an important strategic connection in the marine commerce route connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean via the Red Sea and the Suez Canal.
- It is one of the world's most important seaborne commodity shipping routes, primarily for crude oil and petroleum.
- Yemen borders it on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea border it on the African coast.
The following are the most important facts regarding the Red Sea:
- It is a semi-enclosed inlet (or extension) of the Indian Ocean located between the African and Asian continents. It has one of the hottest waters on the planet.
- The Sinai Peninsula divides the northern Red Sea into the Gulfs of Aqaba and Suez, where it connects to the Mediterranean Sea via the famed Suez Canal.
- Yemen and Saudi Arabia share a border with the Red Sea to the east.
- Egypt borders it to the north and west, and Sudan, Eritrea, and Djibouti border it to the west.

What are straits?
- A strait is a naturally created, narrow, and usually navigable stream that joins two bodies of water.
- It is most typically a body of water that connects two geographical masses.
- Some straits are impassable because they are too shallow, or because of an impassable reef or archipelago.
How do straits form?
- Straits are feasible as a result of the narrow-shaped isthmus fracture.
- It connects many bodies of water. Straits, according to folklore, form as a result of plate tectonic action. For example, tectonic action in Africa generated the Strait of Gibraltar.
- It's a breakdown of the Gibraltar Isthmus. Human action, on the other hand, generates straits known as canals.
- It directs water flow for home and commercial purposes. Suez Canal, completed in 1869, is one such strait.
- It acts as a watershed between the Mediterranean and the Red Sea.
- Originally built for commerce, it now functions as a waterway connecting Europe and Asia.
- Without a watershed, one would have to cross into Africa to deliver products, which lengthens the voyage time.
- As a result, specific straits are built to boost commercial activity.
- Straits can also form when bodies of water flood.
- Straits can also emerge as a result of erosion and landslides.
- The Bosporus is a waterway that connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea.
- Bosporus formed naturally as a result of weathering and erosion.
- The Bosporus is important to geologists because it is the only physical barrier between Europe and Asia.
What is the significance of straits?
- Straits play a vital part in commercial shipping's seaborne trade.
- They are very essential in
- For millennia, the straits have been vital to human culture.
- They are crucial in economic and military affairs.
- Commercial shipping uses the world's major straits to go from one exclusive zone or sea to another.
- The Straits of Hormuz are very significant both commercially and strategically. Many ships use the straits as passable routes.
- The Strait of Hormuz, for example, is critical because it transports one-third of the world's oil commerce.
- Straits are also used to generate tidal power using turbines. Cook's Strait in New Zealand, for example, generates 5.6 GW of energy.
- The Strait has an important function in serving as a route through which ocean currents move, aiding in the mortification of the climate in that area.
- As a result, straits play an important role in both physical and human geography.
Distinctions between the Gulf and the Strait
- Gulfs and Straits are regarded as geographical features on the earth's surface. The aquatic body includes both gulfs and straits.
- The term "gulf" refers to a deep inlet within the sea with a limited opening.
- The term "gulf" refers to the portion of the ocean that penetrates the land. It can differ in shape, depth, and size.
- A strait is a narrow canal that connects to a larger body of water. Because the connector connects two watersheds, it is formed by an isthmus fracture. Generally, straits form as a result of tectonic movements.
- The gulf and Straits of Hormuz are both man-made and natural; they serve economic purposes.
- The Gulf of Mexico and Oman have served as economic hubs for transportation and trade.
- The Gulf of Mexico is the largest gulf and is used for recreational, commercial, and sporting purposes.
- The Suez Canal is the world's greatest man-made strait for trade and transit.
Gulf
- The gulf is a sea portion that penetrates within the land.
- It connects both land and sea.
- The gulf is usually formed naturally.
- The Gulf is very helpful for harbouring ships.
- Sometimes, it is also considered a large bay.
- eg: Gulf of Mannar, Persian Gulf
Strait
- Straits are narrow watersheds that act as a connector between two huge water bodies.
- It is a connector of water bodies only.
- It is mostly man-made, like canals.
- They are very small and cannot be used for harboring purposes.
- They are very narrow and are used as canals.
- eg: Hormuz straits, Malacca strait

Conclusion
- The Gulf and straits are important geological structures formed by biological activity.
- However, the differences can be detected by their size, shape, and depth, among other things.
- The gulf is a sea section that penetrates the mainland, whereas straits are enclosed on all sides by water.
- The Gulf of Mexico has a tiny mouth, and the strait as a whole is narrow. Both are used in business and commerce.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
| List-I (Strait) |
List-II (Water Body) |
| A.Strait of Hormuz |
1.Java Sea |
| B.Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb |
2.Andaman Sea |
| C.Strait of Malacca |
3.Red Sea |
| D.Strait of Sunda |
4.Gulf of Persia |
Code:
A) A-4 B-2 C-3 D-1
B) A-1 B-3 C-2 D-4
C) A-1 B-2 C-3 D-4
D) A-4 B-3 C-2 D-1
Answer: D
|











