Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Scientists have discovered a massive sinkhole off the coast of the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico.
- The giant blue hole is around 900 feet deep and scientists have dubbed it the second deepest blue hole found on the planet.
Details
- Spread over an area of 13,660 square meters, the giant, underwater cavern is located in the Chetumal Bay and has been named Taam Ja’ which means "deep water" in Mayan.
- The submerged blue hole has a nearly circular shape at its surface with steep sides that form a large conic structure covered by biofilms, sediments, limestone, and gypsum ledges.
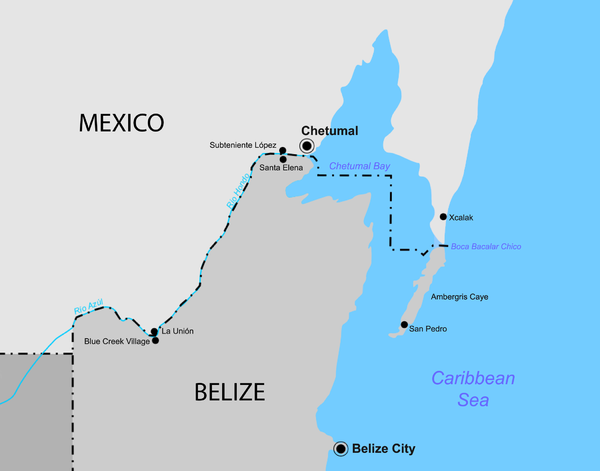
Chetumal Bay
- Chetumal Bay is a large bay of the western Caribbean Sea on the southern coast of the Yucatán Peninsula.
- It is located in northern Belize and south-eastern Mexico.
Blue Hole
- A blue hole is a large marine cavern or sinkhole, which is open to the surface and has developed in a bank or island composed of carbonate bedrock (limestone or coral reef).
- Their existence was discovered in the late 20th century by fishermen and recreational divers.
- Blue holes typically contain tidally influenced water of fresh, marine, or mixed chemistry.
- They extend below sea level for most of their depth and may provide access to submerged cave passages.
- Well-known examples are the Dragon Hole (in the South China Sea) and, in the Caribbean, the Great Blue Hole and Dean's Blue Hole.
Features
Shape and colour
- Blue holes are roughly circular, steep-walled depressions, and so named for the dramatic contrast between the dark blue, deep waters of their depths and the lighter blue of the shallows around them.
- The deep blue color is caused by the high transparency of water and bright white carbonate sand.

Water Circulation
- Their water circulation is poor, and they are commonly anoxic below a certain depth.
Support to sea-life
- Their environment is unfavorable for most sea life, but nonetheless can support large numbers of bacteria.
- Due to the conditions of a blue hole, they are forced to live off of sulfur compounds like hydrogen sulfide, which are toxic to most organisms.
Deepest Blue Hole
- The deepest blue hole in the world at 300.89 meters (987 feet) deep is in the South China Sea and is named the Dragon Hole, or Longdong.

Overall Largest Blue Hole
- The overall largest blue hole (taking into account depth and width) is located 100 kilometers from the coast of Belize.
- The Great Blue Hole is a massive 300 meters wide and 125 meters deep.
Diving Risks
- Despite the beauty and allure of blue holes, they are some of the most dangerous waters to dive.
Nitrogen narcosis is a change in consciousness, neuromuscular function, and behavior brought on by breathing compressed inert gasses. It has also been called depth intoxication, “narks,” and rapture of the deep.
- Nitrogen Narcosis begins to set in at depths below 70 feet and causes disorientation and changes in consciousness.
- Divers experiencing Nitrogen Narcosis may become too confused to swim back into shallower waters, and some unfortunately never make it back to the surface.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which of the following statements are correct with reference to Blue Holes?
a) A blue hole is a large marine cavern or sinkhole, which is open to the surface and has developed in a bank or island composed of carbonate bedrock (limestone or coral reef).
b) The deepest blue hole in the world at 300.89 meters (987 feet) deep is in the South China Sea and is named the Dragon Hole, or Longdong.
c) Blue Holes can support large numbers of bacteria and a huge diversity of organisms/sea-life.
d) Water circulation of Blue Holes is poor, and they are commonly anoxic below a certain depth.
1. a and b only
2. b and c only
3. a, b and d only
4. All of the above.
Correct Answer: Option 3
|

https://www.indiatoday.in/science/story/mysterious-900-foot-deep-blue-hole-discovered-in-mexico-2364463-2023-04-25

















