Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Context: The Bodoland Territorial Council (BTC) of Assam is to start its Mission Happiness programme throughout the Bodoland Territorial Area (BTR).
Details
- The Bodoland Territorial Council (BTC) government will begin implementing its Mission Happiness in April over the 9,000 sq. km (BTR).
- After consulting with various groups of individuals to understand and evaluate the causes of their "anger, frustration, and dissatisfaction," all stakeholders were included in the development of the course material.
- Former radicals, government officials, political leaders, members of civil society, delegates from various ethnic, linguistic, and religious groups, as well as the "downtrodden individuals at the bottom of the barometer of happiness" are among the contributors.
.jpeg)
Bodoland Territorial Council (BTC)
- The Bodoland Territorial Council (BTC) was created under the 6th Schedule of the Indian Constitution following the Memorandum of Settlement between the Bodoland Liberation Tiger Force (BLTF), the Government of India, and the Government of Assam.
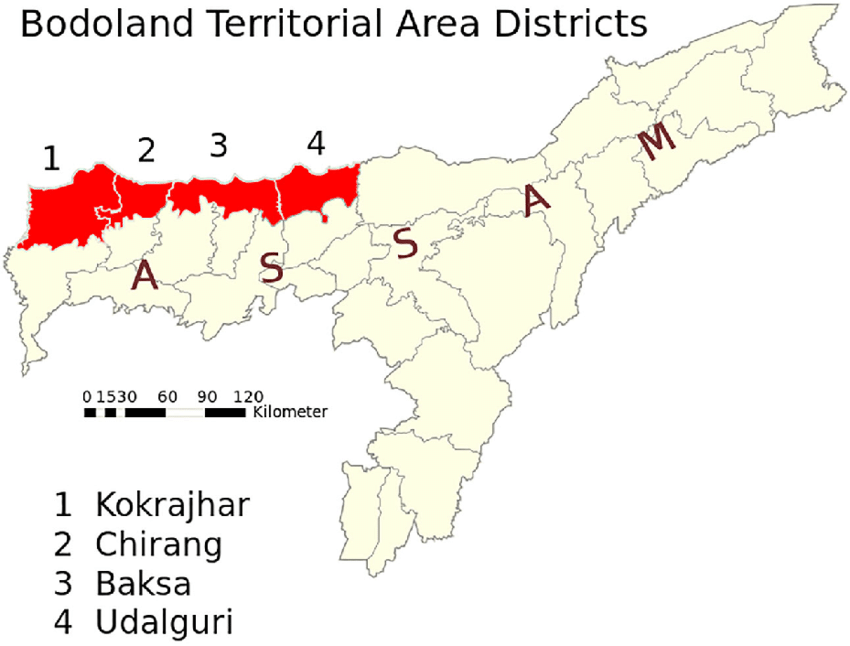
- It is an autonomous region within Assam. It consists of four districts (Kokrajhar, Chirang, Baksa, and Udalguri) that are situated by the foothills of Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh on the north bank of the Brahmaputra river.
- The BTC is made up of 40 elected members and an additional six that the Assam Governor appoints.
- A Speaker leads the Bodoland Territorial Council, while a Chief Executive Member chairs the executive committee.
- The BTC region is located within India's least developed zone on the map. The people's main source of livelihood is the agro-economy. There are few industrialization and other employment opportunities.
- Power and Function
- The Bodoland Territorial Council's executive and legislative authority derives from the provisions of the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution as well as the 2003 and 2020 Bodoland Peace Agreements.
- The Bodoland Territorial Council has the authority to levy taxes, fees, and tolls on a variety of items, including land, buildings, animals, vehicles, boats, goods entering the region, transportation by ferry or bridge, sanitation, employment, and income, as well as general taxes for the upkeep of roads and schools.

Autonomous District Councils
- According to Article 244, the administration of the tribal areas in the four northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram is covered by the sixth schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- The Indian Constitution's 6th Schedule permits the creation of autonomous administrative units that have been granted autonomy within their respective states.
- The State Governor has the authority to modify the boundaries of the autonomous districts, including changing their names.
- In terms of their administration, the 6th Scheduled Areas fall under the State's executive authority.
- Some autonomous districts and autonomous regions are exempt from the laws of the Parliament or the state legislature, or they do so with specific modifications and restrictions.
- These Autonomous Councils have been given extensive civil and criminal judicial powers, including the ability to set up village courts, among other things. The relevant High Court has jurisdiction over these councils.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which of the Following States are covered under the 6th Schedule of the Indian Constitution?
1. Meghalaya
2. Manipur
3. Mizoram
4. Meghalaya
5. Arunachal Pradesh
Choose the correct code.
(A) 1, 2 and 3 only
(B) 1 and 3 only
(C) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(D) 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
Answer: B
Explanation:
Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram are covered under the sixth schedule of the Indian Constitution.
|

https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/30152/OPS/G3KB1NNGF.1.png?cropFromPage=true











