Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Bolivia recently said it had broken diplomatic ties with Israel because of its attacks on the Gaza Strip.
About
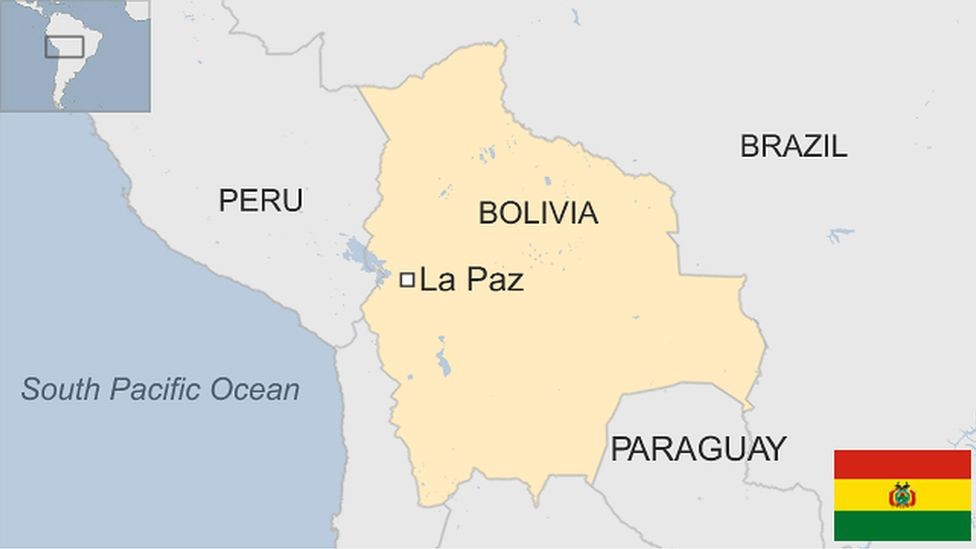
- Bolivia is a landlocked country in western-central South America. Its official name is the Plurinational State of Bolivia.
- It is named after the revolutionary Simon Bolivar.
- The country is located in the steep Andes Mountains, with a highland plateau and lowland lowlands in the Amazon basin.
- The Andean Mountain range encompasses one-third of the country.
- Bordering Countries: It shares borders with Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay, and Peru.
- Sucre is the constitutional capital, but La Paz is the seat of government and executive capital.
- Bolivia and Peru share ownership of Lago Titicaca, the world's highest navigable lake for big vessels, at 12,500 feet above sea level.
History
- During the 15th and 16th centuries, an ancient civilization known as the Inca ruled the region.
- Spanish conquistadors (or 'conquerors') arrived from Europe in 1538 and took control of the country.
- It declared independence from Spanish authority in 1825.
- Much of its following history has been characterized by coups and countercoups, with the most recent coup taking place in 1978.
- The establishment of democratic civilian rule began in 1982.
.jpg)
Government
- The government is a republic, and the new constitution defines Bolivia as a "Social Unitarian State."
- The president is the chief of state and the head of government.
- Currency: Bolivian boliviano
- Official Language: It has 37 official languages, including Spanish.
- Bolivia has a mixed economic system that includes a variety of private freedoms combined with centralized economic planning and government regulation.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Discuss the socio-political and economic challenges facing Bolivia in the 21st century. (150 words)
|













