Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.indiatoday.in/india-today-insight/story/why-its-important-to-get-screened-for-cancer-2453621-2023-10-25
Context: Global cancer burden increased by 20 million new cases in 2022, with lung cancer being the most common, followed by breast, colorectal, prostate, and stomach cancers.
Key Highlights
Global Cancer Burden (2022)
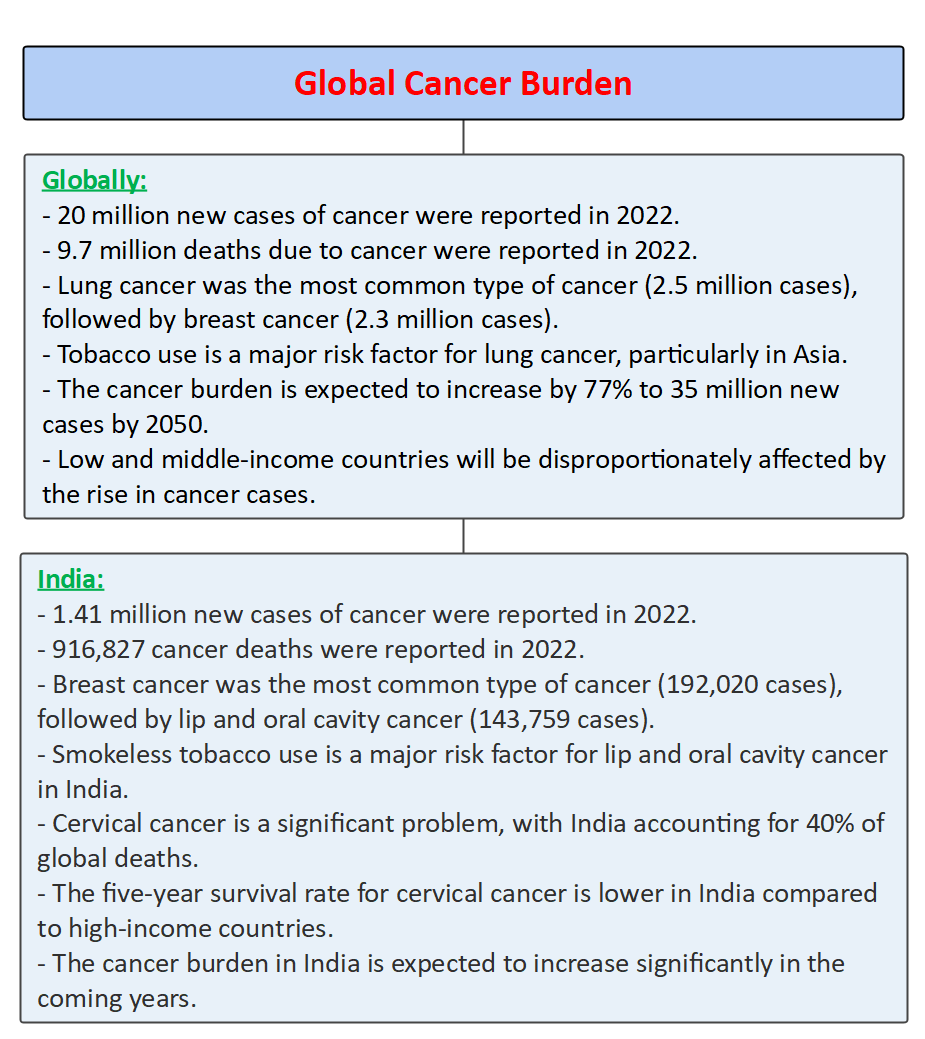
- In 2022, the global burden of cancer increased by 20 million new cases.
- Globally, about 9.7 million deaths due to cancer were reported in 2022.
- Globally, lung cancer was the most common, followed by female breast, colorectal, prostate, and stomach cancers.
- Women in lower Human Development Index (HDI) countries are 50% less likely to be diagnosed with breast cancer but have a higher risk of dying due to late diagnosis and inadequate access to quality treatment.
- Countries with the highest Human Development Index (HDI) are expected to have an additional 4.8 million new cases predicted in 2050 compared to figures reported in 2022.
- The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) projected a 77% increase in the global cancer burden by 2050, reaching 35 million new cases, due to multiple risk factors such as tobacco, alcohol, obesity, and air pollution.
- The proportional increase in incidence is most striking in low HDI countries (142% increase) and medium HDI countries (99% increase). Cancer mortality in these countries is projected to almost double in 2050.

Cancer Burden in India (2022)
- India reported 1.41 million new cancer cases in 2022.
- Breast cancer had the highest proportion, with 192,020 new cases, accounting for 13.6% of all patients and over 26% in women.
- After breast cancer, other prevalent cancers in India included lip and oral cavity, cervix and uterine, lung, and oesophagal cancers.
- India reported 916,827 cancer deaths in 2022, with 470,055 in men and 446,772 in women.
- India accounted for 40% of global deaths due to cervical cancer, with a five-year survival rate of 51.7%. Government efforts to encourage vaccination for girls aged 9-14 aim to prevent cervical cancer.
Cancer in Asia and India
- In Asia, tobacco usage contributed to lung cancer being the most common type.
- In India, lip, oral cavity, lung, and oesophagus cancer were the leading types for men, and breast, cervix, uterine, and ovarian cancer for women.
- A study highlighted that India accounted for a significant portion of global deaths and new cases of lip and oral cavity cancer in 2019, attributed to the widespread consumption of smokeless tobacco (SMT) in South Asian countries.
Conclusion
- The global and regional trends in cancer incidence and mortality, the impact of various risk factors, and the disparities in cancer burden based on socioeconomic factors. It underscores the need for concerted global efforts to address risk factors, improve prevention and early detection, and ensure access to quality treatment, particularly in countries with fewer resources.
Must Read Articles:
REPORT ON CANCER: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/report-on-cancer
LANCET COMMISSION REPORT ON GENDER INEQUITY IN CANCER CARE: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/lancet-commission-report-on-gender-inequity-in-cancer-care
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is the role of the food industry, the pharmaceutical industry, and other industries in shaping the environments that contribute to lifestyle diseases? What are their ethical responsibilities in addressing this issue?
|

















