Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Burkina Faso's security and intelligence services foiled a coup attempt, according to the country's military government.
Details
- Burkina Faso, a landlocked country in West Africa, is a nation of rich cultural diversity and natural beauty.
Geography and Demographics
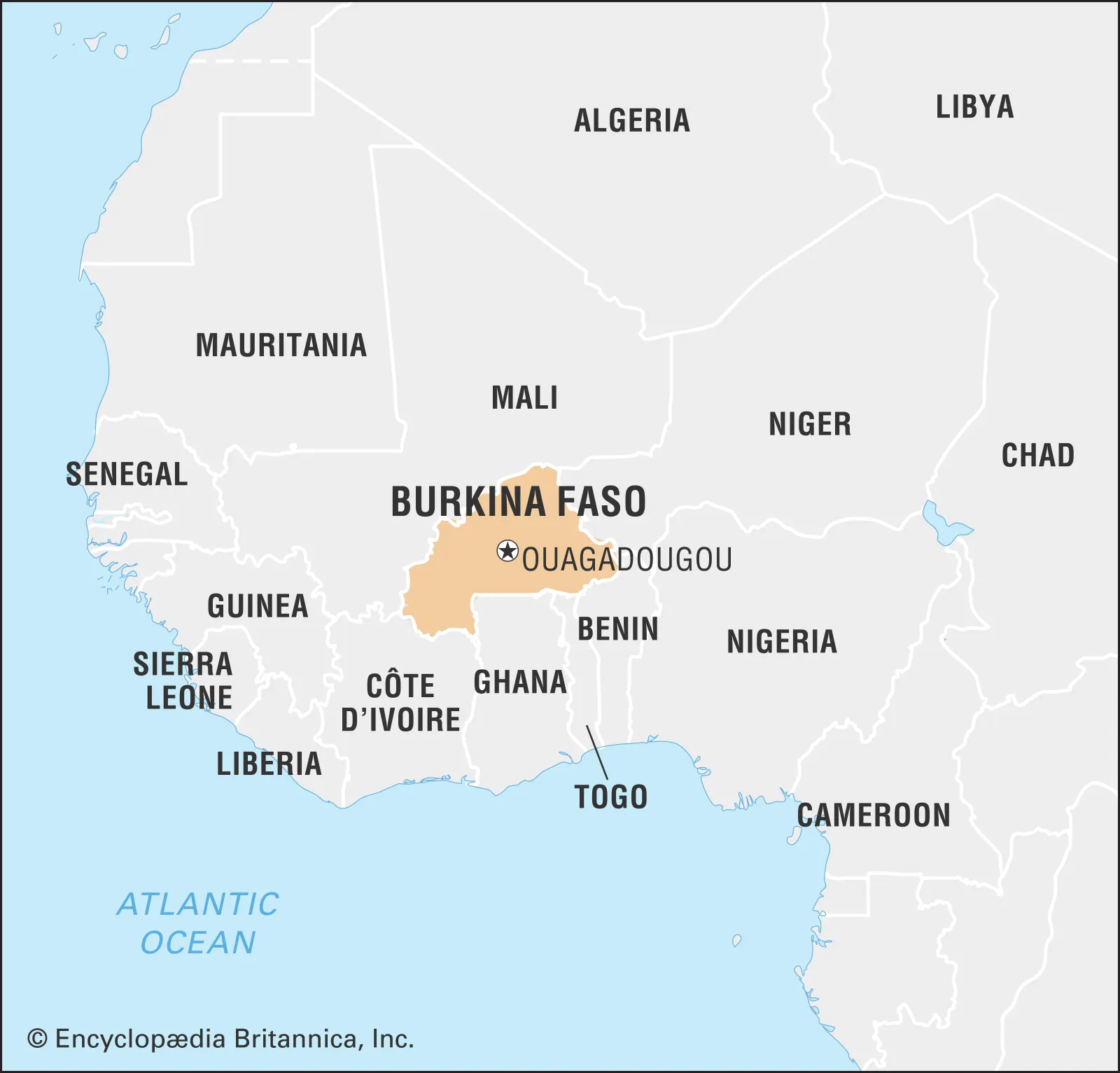
- Location: Burkina Faso is situated in West Africa, bordered by six countries: Mali to the north, Niger to the east, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Cote d'Ivoire to the southwest.
- Capital: Ouagadougou.
- Population: Approximately 21 million people, with diverse ethnic groups, including Mossi, Fulani, Mande, and others.
Historical Significance
- Colonial Legacy: Burkina Faso, formerly known as Upper Volta, gained independence from French colonial rule in 1960.
- Thomas Sankara: The country's most iconic figure is Thomas Sankara, who served as its president from 1983 to 1987. Sankara was a charismatic leader known for his progressive policies and emphasis on self-reliance. He was assassinated in a coup, and his legacy still resonates in Burkina Faso and beyond.

Culture and Society
- Languages: French is the official language, but many ethnic groups have their own languages. Moore, Dioula, and Fulfulde are widely spoken.
- Art and Music: Burkina Faso boasts a vibrant cultural scene, with traditional music, dance, and art playing a significant role in daily life.
- Cuisine: Millet and sorghum are staple crops, and dishes often feature sauces with ingredients like peanuts and okra. Street food is popular and includes dishes like "tô," a millet or sorghum-based porridge.
Economy
- Agriculture: The majority of the population is engaged in subsistence agriculture, growing crops such as millet, sorghum, maize, and cotton. Livestock farming is also prevalent.
- Mining: Burkina Faso has a growing mining industry, particularly in gold production. However, this sector faces challenges related to security and environmental concerns.
- Economic Challenges: The country faces economic challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and limited access to education and healthcare.
Challenges
- Security: Burkina Faso has experienced increasing security challenges, including terrorism and violent conflicts. The northern and eastern regions have been particularly affected.
- Political Instability: The country has faced periods of political unrest and military coups.
- Human Development: Burkina Faso grapples with issues related to human development, including healthcare access, education, and gender inequality.
.jpg)
Conclusion
Burkina Faso, with its cultural richness and natural beauty, is a nation striving for progress and stability. While it faces a range of challenges, its people and leaders continue to work towards a brighter future, guided by their cultural heritage and the legacy of leaders like Thomas Sankara.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa. Which countries border Burkina Faso?
a. Mali, Niger, Benin, Togo, and Ghana
b. Algeria, Libya, Chad, Sudan, and Nigeria
c. Senegal, Guinea, Cote d'Ivoire, Liberia, and Sierra Leone
d. Morocco, Western Sahara, Mauritania, Mali, and Algeria
Answer: a
|











