Description
Copyright infringement is not intended
Context: A study report, titled ‘Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage Policy Framework and its Deployment Mechanism in India’, was released.
Details:
- The report explores the importance of Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage as an emission reduction strategy to achieve deep decarbonization from the hard-to-abate sectors.
- The report outlines broad level policy interventions needed across various sectors for its application.
- As, India has updated its NDC targets for achieving 50% of its total installed capacity from non-fossil-based energy sources, 45% reduction in emission intensity by 2030 and taking steps towards achieving Net Zero by 2070, the role of Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS) becomes important as reduction strategy to achieve decarbonization from the hard-to abate sectors.
- CCUS can enable the production of clean products while still utilizing our rich endowments of coal, reducing imports and thus leading to an Atmanirbhar Indian economy
- CCUS projects will also lead to a significant employment generation. It estimates that about 750 mtpa of carbon capture by 2050 can create employment opportunities of about 8-10 million on full time equivalent (FTE) basis in a phased manner.
- India’s dependency on the fossil-based Energy Resources is likely to continue in future, hence CCUS policy in Indian Context is needed.
- The report indicates that CCUS can provide a wide variety of opportunities to convert the captured CO2 to different value-added products like green urea, food and beverage form application, building materials (concrete and aggregates), chemicals (methanol and ethanol), polymers (including bio-plastics) and enhanced oil recovery (EOR) with wide market opportunities in India, thus contributing substantially to a circular economy.
- Indian Scientists under Mission Innovation program, have discovered a strategy to synthesize novel solid adsorbents for CO2 capture and utilization.
NCERT BOOK - https://www.iasgyan.in/ig-uploads/images/ncert_amazon_(1).jpg
Need for such technologies:
- Mitigate global warming by reducing CO2 emissions.
- Existing technologies are not economical viable
- Existing critical materials fails to capture and utilize CO2 completely.
What is carbon sequestration?
- Carbon dioxide is the most commonly produced greenhouse gas.
- Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- It is one method of reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere with the goal of reducing global climate change.
- Aim: stabilizing the amounts of the greenhouse gas concentration in the atmosphere and reducing the human ‘carbon footprint’.
- Carbon sequestration is both a natural and artificial process by which carbon dioxide is removed from the Earth’s atmosphere and then stored in liquid or solid form.
Types of Carbon Sequestration
- Biological Carbon Sequestration: storage of carbon dioxide in vegetation like grasslands and forests, as well as in soils and oceans.
- In oceans: Naturally, oceans absorb about 25% of the carbon dioxide emitted through human activities each year.
- In forests: plant-rich landscapes like forests, rangelands and grasslands absorb about 25% of the global carbon emissions. When the trees, branches and leaves die and fall to the ground, they release the carbon they had stored into the soil.
- In soils: carbon can be sequestered in soil by plants through photosynthesis. Soil can also store carbon as carbonates.
- In grasslands: grasslands and rangelands are more reliable areas of storing carbon than forests due to the rapid wildfires and deforestation affecting forests.
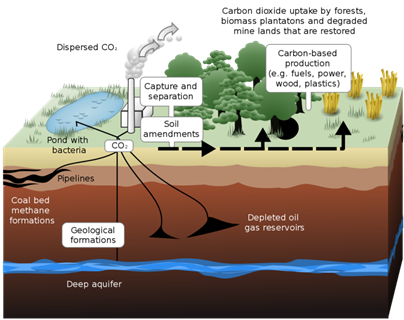
- Geological Carbon Sequestration: This is where carbon dioxide is stored in underground geologic formations, such as in rocks. Industrial sources of carbon dioxide such as steel or cement production companies or energy-related sources like power plants or natural gas processing facilities will release their carbon dioxide, which is then injected into porous rocks for long-term storage.
- Technological Carbon Sequestration: This is a relatively new way of capturing and storing carbon dioxide. This method uses innovative technologies for removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Graphene production: Technology is being used to produce graphene from carbon dioxide as its raw material. Graphene can be used as a viable resource and solution in reducing carbon’s emissions from the atmosphere.
- Engineered molecules: engineering molecules can act as filters and only attract the element they are engineered to seek.
- Direct air capture (DAC): this is a means of capturing carbon dioxide from the air using advanced technology plants. It is an effective technological method of sequestrating carbon but it is energy-intensive.
- Industrial Carbon Sequestration: This is not a widely renowned method, that can capture the carbon in three ways a. Pre-combustion: the carbon is captured in power plants before the fuel is burned. The aim is to remove the carbon from coal before it is burned. The coal is reacted with oxygen to produce synthesis gas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gases.
- Post-combustion: carbon is removed from a power station’s output after the fuel has been burned. This means waste gases are captured and scrubbed clean of their carbon dioxide before they travel up smokestacks.
- Oxyfuel or oxy-combustion: the point is to burn fuel in more oxygen and the process traps the entire output from the smokestacks and stores it all. Pure oxygen is blown into the furnaces to purify the exhaust, so the fuel burns completely, producing relatively pure steam and carbon dioxide gas.
Examples of Carbon Sequestration
- Photosynthesis: This is the process where plants and trees absorb and store carbon dioxide during growth, releasing oxygen in turn.
- Century Plant: This is the single biggest carbon capture and storage plant in the world.
How Does Carbon Sequestration help the Environment?
- Forests and vegetation have been identified to be key players in capturing and storing carbon dioxide, capturing about 25% of all carbon emissions.
- It helps reduce global warming
- It reduces ocean acidification
- Helping mitigate carbon dioxide emission
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1879865
Array
(
[0] => daily-current-affairs/carbon-capture-utilisation-technologies-26
[1] => daily-current-affairs
[2] => carbon-capture-utilisation-technologies-26
)
















