Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: razorpay.com
Context: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has proposed to introduce Card-on-File Tokenization (CoFT) as a measure to enhance convenience for cardholders. This initiative aims to provide cardholders with an easier way to create and link tokens to their existing accounts when using various e-commerce applications.
Key Highlights
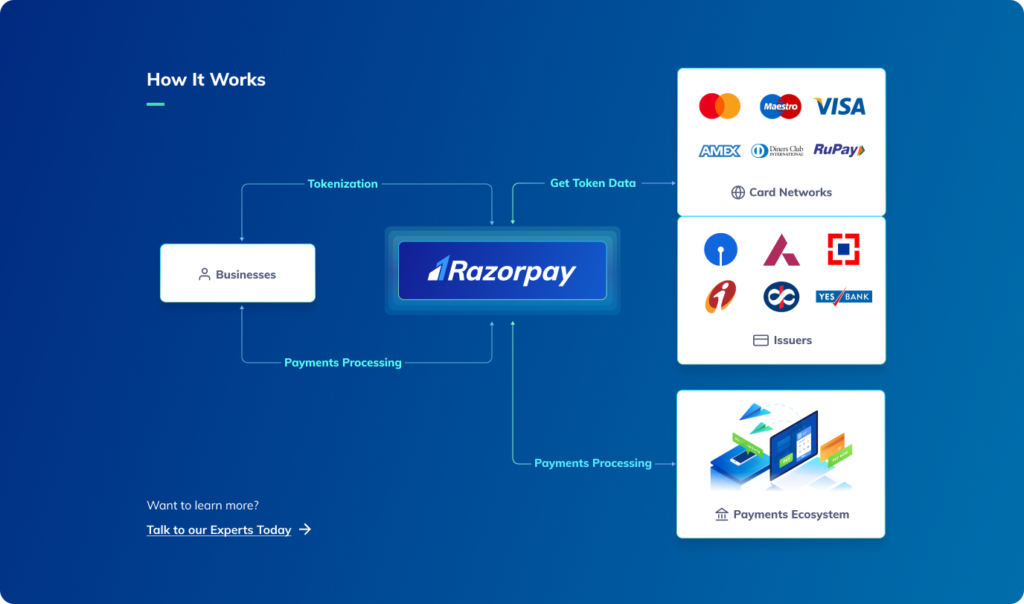
- Tokenization is a process where actual card details are replaced with a unique alternate code called a token. When a consumer uses a tokenized card for a transaction, the actual card details are not shared with the merchant, which enhances security.
- The RBI's proposal suggests that the process of creating and managing these tokens will be carried out directly at the issuer bank level. This means that the banks that issue credit or debit cards will be responsible for implementing and managing the tokenization process.
- In addition to the CoFT proposal, the RBI has also extended the Payments Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) Scheme by two years, until December 31, 2025. The PIDF scheme aims to increase the number of payment touchpoints across India, promoting digital payments at the grassroots level.
- The PIDF scheme's coverage will be expanded to include beneficiaries of the PM Vishwakarma Scheme and to deploy emerging modes of payment acceptance, such as soundbox and Aadhaar-enabled biometric payment acceptance devices.
- Industry experts have lauded the RBI's initiative to introduce CoFT, considering it a game-changer for both cardholders and the financial industry. It enhances convenience and security, reducing the friction associated with digital transactions.
Card-on-File Tokenisation (CoFT) offers several advantages
- Enhanced Security: With tokenization, sensitive card information is not shared with merchants during transactions. This significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud, enhancing the security of digital payments.
- Convenience: Cardholders no longer need to enter their card details for every transaction. Once the card is tokenized, the token can be used for multiple transactions without exposing the actual card information, making the payment process more convenient for users.
- Reduced Friction: The process of entering card details for each transaction can be cumbersome and time-consuming. Tokenization reduces this friction associated with digital transactions, leading to a smoother payment experience for consumers.
- Promotion of Digital Payments: By enhancing the security and convenience of digital transactions, the RBI's initiative encourages more people to adopt digital payment methods. This aligns with the government's efforts to promote a cashless economy and financial inclusion.
- Innovation in Payment Methods: The RBI's move to extend the Payments Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) Scheme and include emerging modes of payment acceptance, such as soundbox and Aadhaar-enabled biometric payment acceptance devices, fosters innovation in the payment industry. This diversification of payment methods caters to a wider range of consumers and merchants.

Conclusion
- RBI's Card-on-File Tokenization enhances India's digital payment landscape, ensuring security, convenience, and trust for consumers. By replacing sensitive card data with tokens, this initiative simplifies transactions, encourages financial inclusion, and accelerates the nation's transition to a secure cashless economy.

Must Read Articles:
Card Tokenization: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/card-tokenization
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is Card-on-File Tokenization, and how does it enhance the security of online transactions? Provide examples of industries or scenarios where Card-on-File Tokenization is particularly beneficial.
|
















