Description
In News
- NASA’s Cassini spacecraft has detected an unusually high concentration of methane, along with carbon dioxide and dihydrogen, in the moons of Saturn by flying through their plumes.
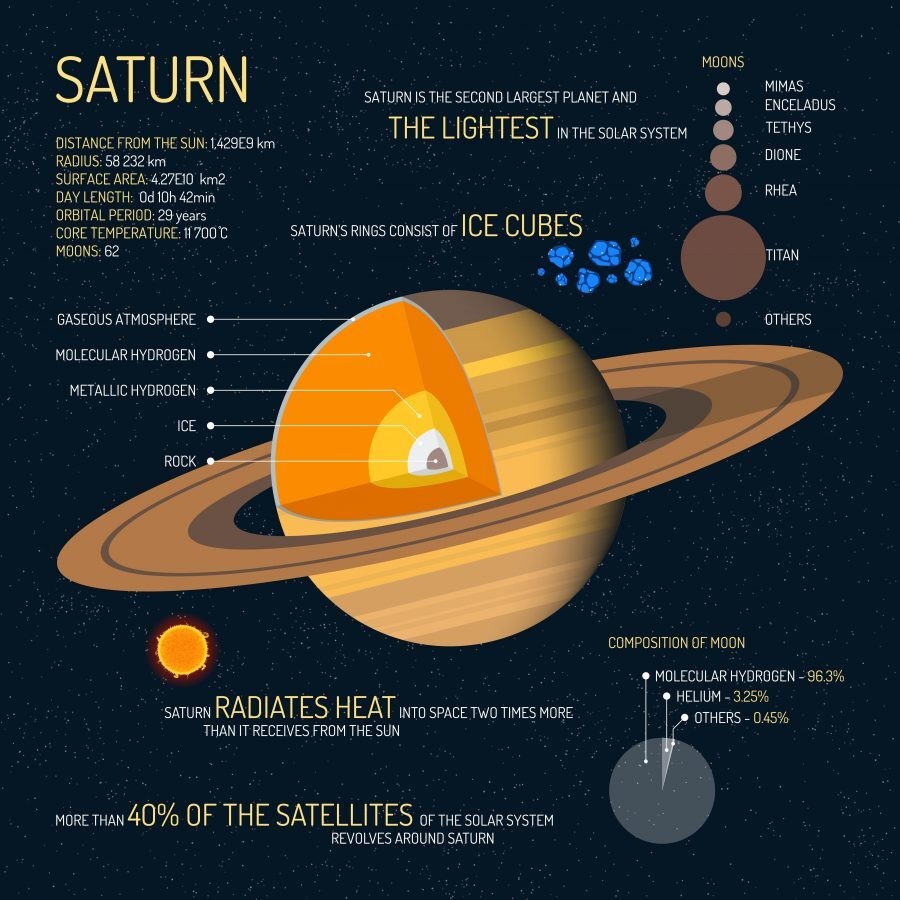
Moons of Saturn
- Saturn has 82 moons with confirmed orbits that are not embedded in its rings.
- Particularly notable among Saturn's moons are:
- Titan, the second-largest moon in the Solar System (after Jupiter's Ganymede), with a nitrogen-rich Earth-like atmosphere and a landscape featuring dry river networks and hydrocarbon lakes,
- Enceladus, which emits jets of gas and dust from its south-polar region, and
- Lapetus, with its contrasting black and white hemispheres.
Findings by Cassini
- The spacecraft has found that Titan has methane in its atmosphere and Enceladus has a liquid ocean with erupting plumes of gas and water.
Processes of Methane Formation
- Methane could be formed by the chemical breakdown of organic matter present in Enceladus’ core.
- Hydrothermal processes could help the formation of carbon dioxide and methane.
- On Earth, hydrothermal vents on seafloors are known to release methane, but this happens at a very slow rate.
- Possibility of Micro organisms called Methanogens.
Note: Searching for such microbes at Enceladus’ seafloor would require extremely challenging deep-dive missions that are not in sight for several decades.
Cassini
- Cassini, is a collaboration among NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, including its rings and natural satellites.
- The Flagship-class robotic spacecraft comprised both NASA's Cassini space probe and ESA's Huygens lander, which landed on Saturn's largest moon, Titan in 1997.
- Cassini was the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter its orbit.
|
Methanogens of Earth
Microorganisms called methanogens are capable of generating methane as a metabolic byproduct. They do not require oxygen to live and are widely distributed in nature. They are found in swamps, dead organic matter, and even in the human gut. They are known to survive in high temperatures and simulation studies have shown that they can live in Martian conditions. Methanogens have been widely studied to understand if they can be a contributor to global warming.
|
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/plumes-on-enceladus-possibility-of-life-on-saturns-moon-explained-7395434/














