Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://mybestplace.com/en/article/relampago-del-catatumbo-the-spectacular-phenomenon-of-perennial-lightning
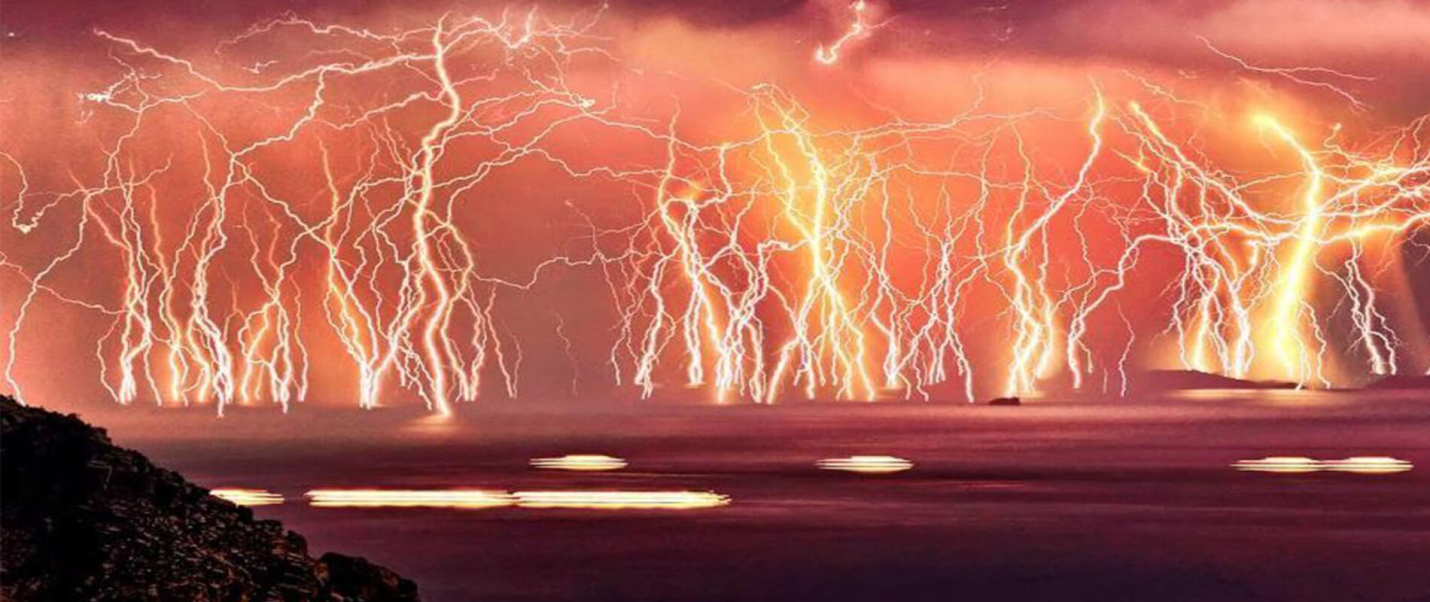
Context: The Catatumbo Lightning in Venezuela occurs almost nightly over Lake Maracaibo due to warm Caribbean air meeting cool mountain air, creating persistent lightning.
Details
- Catatumbo lightning is a unique natural phenomenon that appears in Venezuela, precisely where the Catatumbo River joins Lake Maracaibo. This region is one of the most likely places on Earth to see lightning strikes, with over 300 nights of violent storms every year.
- The Catatumbo lightning is caused by unique atmospheric conditions in the region.
- Warm, moist air from the Caribbean Sea combines with cooler air descending from the Andes Mountains.
- As two opposing air masses collide over Lake Maracaibo, they provide ideal conditions for the creation of electrical charges in the atmosphere.
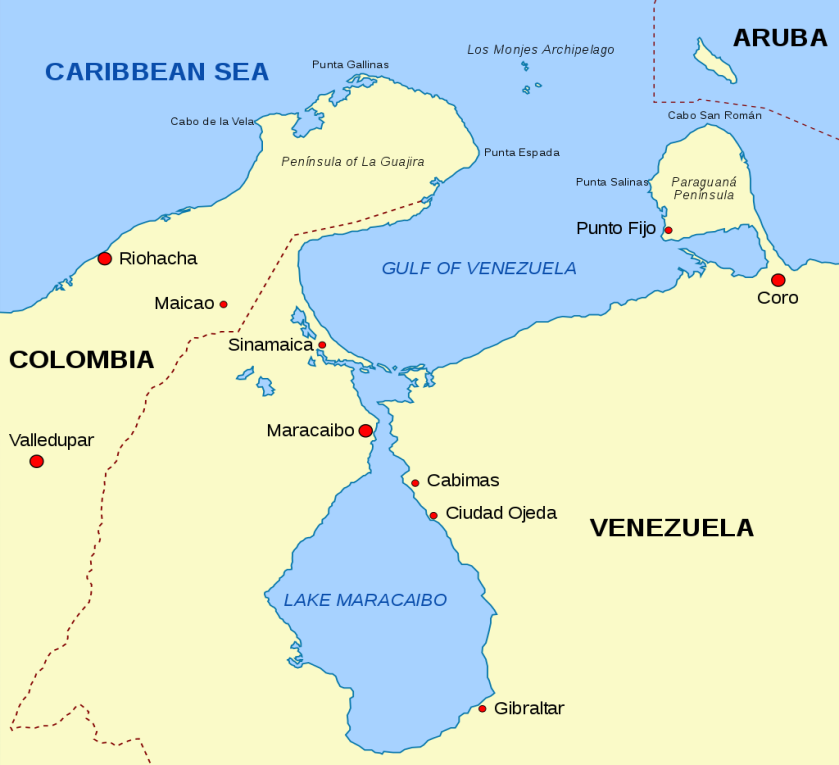
About Lake Maracaibo
- Lake Maracaibo is located in northwestern Venezuela; it is the largest lake in Venezuela.
- Despite its name as a "lake," Lake Maracaibo is hydrologically more similar to a large, brackish bay connected to the Gulf of Venezuela by a narrow spit.
- It is believed to have formed around 36 million years ago in the Andes Mountains. Over time, geological processes and changes in sea level led to the formation of what is now considered Lake Maracaibo.
- The lake is fed by several rivers, with the Catatumbo River being the most significant. These freshwater inflows contribute to the brackish nature of the lake, where freshwater mixes with seawater from the Gulf of Venezuela.
- The northern section of Lake Maracaibo is situated along a geological fault that is rich in oil and gas resources. This area is Venezuela's primary oil-producing region, with extensive oil extraction and production activities taking place in and around the lake.
- Lake Maracaibo faces environmental challenges, including eutrophication caused by oil pollution. Eutrophication occurs when excess nutrients, such as from oil and other pollutants, lead to increased algae growth, decreased oxygen levels, and ecological imbalances in the water body.
- It is a vital region for fishing and agriculture in Venezuela. The lake supports diverse fish species and sustains fishing communities that depend on its resources for their livelihoods.
|
Lake Maracaibo is renowned for the Catatumbo lightning phenomenon, which occurs predominantly in the northwestern part of the lake. This lightning is one of the most frequent and intense in the world, often occurring nightly for around 300 days a year. The atmospheric conditions over the lake, influenced by its geography and climatic factors, create the ideal conditions for this unique natural spectacle.
|
About Catatumbo lightning
- Catatumbo lightning, also known as Relámpago del Catatumbo, is a fascinating atmospheric phenomenon that occurs over and around Lake Maracaibo in Venezuela.
- It occurs for approximately 140 to 160 nights per year, lasting for about nine hours each night. During this time, lightning flashes occur at a rate ranging from 16 to 40 times per minute, making it one of the most intense lightning displays globally.
- It is believed to result from the convergence of warm air masses from the Caribbean Sea with cooler air masses descending from the surrounding mountains. This collision of air masses leads to the formation of storm clouds at an altitude exceeding 1 kilometre.
- Several theories have been proposed to explain the phenomenon.
- One hypothesis suggests that methane emissions from the swamps and extensive oil deposits in the region contribute to the lightning.
- Other studies have explored the influence of atmospheric variables like the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), Caribbean Low-Level Jet, and convective available potential energy (CAPE) on Catatumbo lightning.

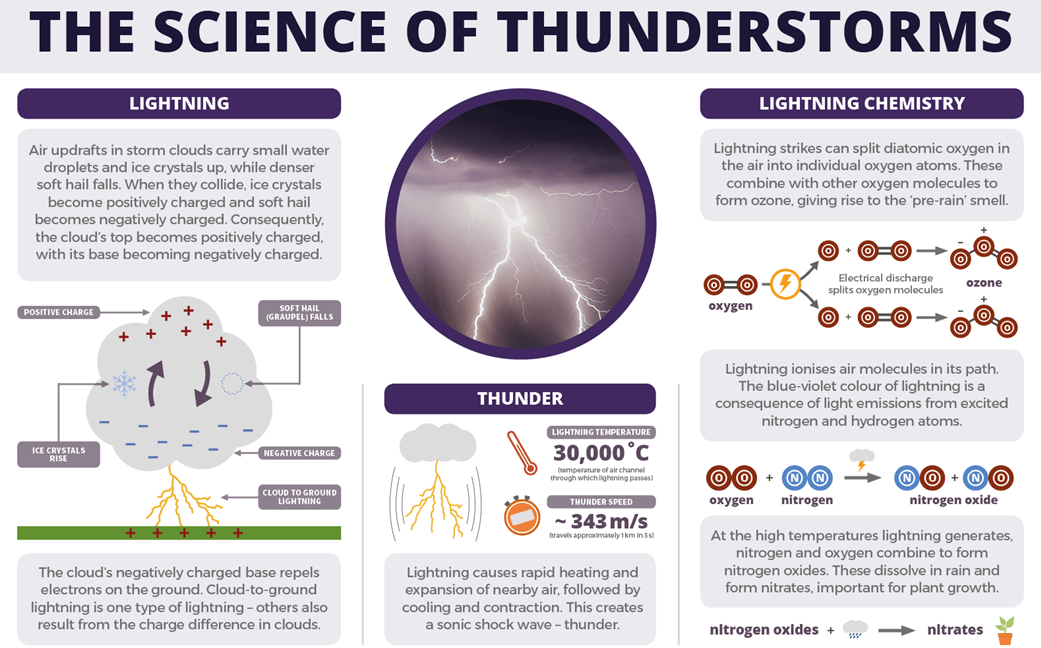
Thunderstorm
- A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or lightning storm, is a meteorological phenomenon characterized by the presence of lightning and its accompanying sound, thunder.
Key features and characteristics of thunderstorms
- Thunderstorms develop when warm, moist air rises rapidly in an unstable atmosphere. This upward movement of air can be triggered by various factors, such as daytime heating, frontal boundaries, orographic lifting (air forced upwards by terrain), or convergence of air masses.
- Thunderstorms are associated with cumulonimbus clouds, which are tall, dense clouds capable of reaching heights of over 20 kilometres. These clouds form through the rapid upward convection of warm air, leading to condensation and cloud formation.
- Lightning is a discharge of electricity that occurs within a thunderstorm. It is caused by the buildup and release of electrical charge within the clouds or between the clouds and the ground. Thunder is the sound produced by the rapid expansion of air heated by the lightning discharge.
- Thunderstorms often produce heavy rainfall, which can lead to localized flooding. The intensity and duration of rain vary depending on the strength and duration of the thunderstorm.
- Thunderstorms can generate strong surface winds, especially near the downdraft region of the storm. These winds can be gusty and may cause damage, particularly in severe thunderstorms.
- In intense thunderstorms, hailstones may form when strong updrafts carry raindrops upward into extremely cold regions of the cloud where they freeze and accumulate layers of ice before falling to the ground.
- Some thunderstorms become severe, exhibiting particularly intense characteristics such as large hail, damaging winds (often exceeding 50 knots or 93 km/h), and tornadoes. These severe storms pose significant risks to life and property.
Source:
Atlas Obscura
Wikipedia
Wikipedia
Wikipedia
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. 1. What is the primary cause of the Catatumbo Lightning phenomenon in Venezuela?
A) Collision of warm Caribbean air with cool mountain air
B) Volcanic activity beneath Lake Maracaibo
C) Earth's geomagnetic field disturbances
D) High concentrations of atmospheric ozone
Answer: A
|














