Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Union Education Minister inaugurated the state-of-the-art Centre for Nanotechnology (CNT) and Centre for Indian Knowledge System (CIKS) at IIT Guwahati.
About
- Centre for Nanotechnology (CNT) aims at meeting future challenges and augment academic partnerships with industry in Nanotechnology.
- The key outcomes expected from the Centre for Nanotechnology include
- nano-enabled healthcare,
- energy harvesting,
- LED prototypes,
- devices and technologies,
- start-ups/ incubation ecosystem,
- high-end R&D outputs,
- capacity building of highly skilled manpower in the area of nanofabrication and
- nanoelectronics, etc.
- Centre for Indian Knowledge System (CIKS) will focus on preserving, documenting and sustaining the knowledge that is unique to India.
- The top priorities include Indian classical music, Yoga, Sanskrit, traditional medicines, temple architecture, ceramic tradition and special agricultural practices of North-East India, herbal plants of north-east as health food and metal work of Assam.
Nanotechnology
- Nanoscience and nanotechnology are the study and application of extremely small things and can be used across all the other science fields, such as chemistry, biology, physics, materials science, and engineering.
- Nanotechnology is the understanding and control of matter at the nanoscale, at dimensions between approximately 1 and 100 nanometers, where unique phenomena enable novel applications.
- In the International System of Units, the prefix "nano" means one-billionth, or 10-9; therefore one nanometer is one-billionth of a meter.
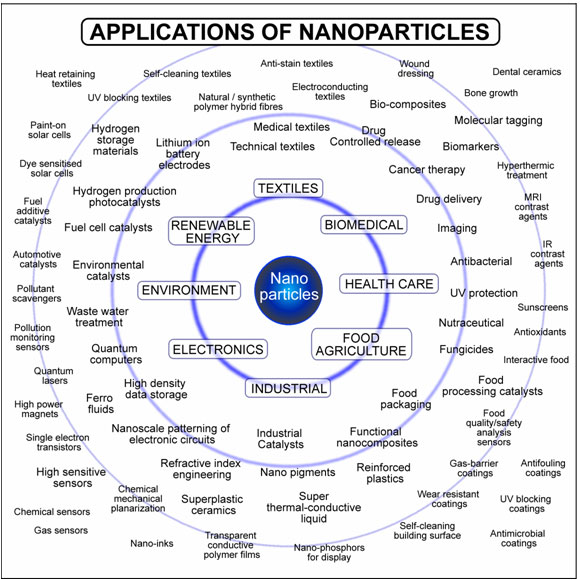
Few examples and applications of Nanotechnology
- Nanotechnology and nanomaterials can be applied in all kinds of industrial sectors. They are usually found in these areas:
Electronics
- Carbon nanotubes are close to replacing silicon as a material for making smaller, faster and more efficient microchips and devices, as well as lighter, more conductive and stronger quantum nanowires. Graphene's properties make it an ideal candidate for the development of flexible touchscreens.
Energy
- A new semiconductor developed by Kyoto University makes it possible to manufacture solar panels that double the amount of sunlight converted into electricity. Nanotechnology also lowers costs, produces stronger and lighter wind turbines, improves fuel efficiency and, thanks to the thermal insulation of some nanocomponents, can save energy.
Biomedicine
- The properties of some nanomaterials make them ideal for improving early diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases or cancer.
- They are able to attack cancer cells selectively without harming other healthy cells.
- Some nanoparticles have also been used to enhance pharmaceutical products such as sunscreen.
Environment
- Air purification with ions, wastewater purification with nanobubbles or nanofiltration systems for heavy metals are some of its environmentally-friendly applications.
- Nanocatalysts are also available to make chemical reactions more efficient and less polluting.
Food
- In this field, nanobiosensors could be used to detect the presence of pathogens in food or nanocomposites to improve food production by increasing mechanical and thermal resistance and decreasing oxygen transfer in packaged products.
Textile
- Nanotechnology makes it possible to develop smart fabrics that don't stain nor wrinkle, as well as stronger, lighter and more durable materials to make motorcycle helmets or sports equipment.
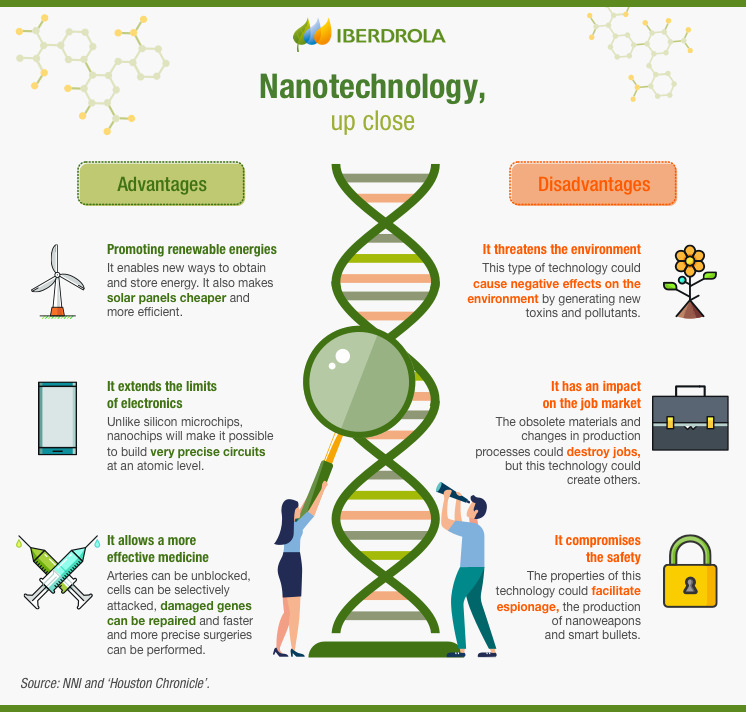
Nanotechnology and India
- Nanotechnology originated in India around 16 years back.
- It is in its early development phase. This new sphere of scientific innovation has a broader scope.
- The three chief divisions of Nanotech are Nanoelectronics, Nanomaterials, and Nano-Biotechnology.
- The implications of Nanotechnology in India can be found in the field of telecommunications, computing, aerospace, solar energy, and environment.
- However, Nanotech’s major contribution can be seen in the computing, communication and, medical field.
- Nanomedicine is the most important field of Nanotechnology.
- The nano level gadgets and materials are used for diagnosing and treatment of diseases.
- Nano-Pharmacology has generated a specific category of smart drugs that affect negligible side effects.
- The use of Nanotech has also helped in the detection of narcotics and fingerprints of the suspected criminals.
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, also known as CSIR has set up 38 laboratories in India dedicated to research in Nanotechnology.
- This technology will be used in diagnostic kits, improved water filters and sensors and drug delivery.
- The research is being conducted on using it to reduce pollution emitted by the vehicles.
- Looking at the progressive prospects Nanotechnology has certainly acquired an essential position in the Indian Economy and Scientific Research Department and it is expected to reach the pinnacle of Development thereby making India a role model for the countries of the world.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Dharmendra-Pradhan-inaugurates-Centres-for-nano-technology-and-Indian-Knowledge-System-at-IIT-Guwahati&id=430046












