Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- The Antarctic Sea ice (South Pole) reached its lowest level ever recorded in the summer of 2022, a study by the National Centre for Polar and Oceanic Research (NCPOR revealed.
Findings of the Study:
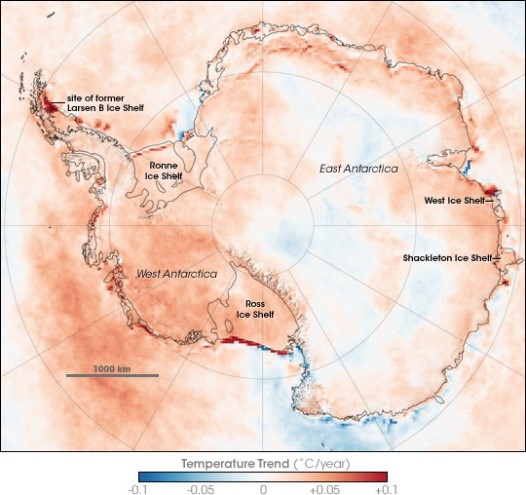
- Records reveal that the sea ice extent (SIE) reached a record low of 2.16 × 1,000,000 km2 in February 2022, which was 43% lower than the mean extent of the previous February months since the satellite era.
- The Weddell Sea, Ross Sea, and Bellingshausen/Amundsen Seas (ABS) sectors experienced the maximum sea ice change on a regional scale.
- The Antarctic Sea ice retreat from September 2021 was close to the minimum sea ice extent (SIE) records since 1979, with the lowest in February 2022.
- Antarctic SIE is showing a sustained loss from 2016, and this could be a start of sea ice loss reported in the Arctic over the satellite period. In Antarctica, sea ice forms and grows freely in cold waters without land barriers. Thus, sea ice becomes thinner and weak, which can be easily drifted by the strong winds, especially in the regions of the Amundsen Sea.
- The ocean-atmospheric interaction has a significant effect on the sea ice. Studies suggested that if the Antarctic sea ice loss continues to decline at this rate over the next few years, then it will equate to the rate of sea ice loss over 30 years in the Arctic, thus resulting in various global warming events.
Factors responsible
- The atmospheric precursors that triggered the record low ice extent around Antarctica that revealed two weather events -- the positive polarity of Southern Annular Mode (SAM) that helped bring warmer air from higher latitudes towards the pole and the intensification of the low-pressure center in the Amundsen Sea (ASL).
|
Southern Annular Mode (SAM)
The Southern Annular Mode, or SAM, also known as the Antarctic Oscillation (AAO), is a mode of variability which can affect rainfall in southern Australia. The SAM refers to the north/south movement of the strong westerly winds that dominate the middle to higher latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. In a positive SAM event, the belt of strong westerly winds contracts towards Antarctica. This results in weaker-than-normal westerly winds and higher pressures over southern Australia, restricting the penetration of cold fronts inland.
|
.jpeg)
National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research:
- The National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, (NCPOR) formerly known as the National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR) is an Indian research and development institution, situated in Vasco da Gama, Goa.
- It is an autonomous Institution of the Department of Ocean Development (DOD),Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It is responsible for administering the Indian Antarctic Programme and maintains the Indian government's Antarctic research stations, Bharati and Maitri.
- NCPOR was established as NCAOR on 25 May 1998.
- NCPOR is known for its participation in global experiments, hosting of international conferences and in the leadership of international committees concerned with Antarctic science.
- At present, NCPOR is an agency working under the Ministry of Earth Sciences,Government of India since 2006.
- NCPOR complex is a home to a special low-temperature laboratory and is setting up a National Antarctic Data Centre and a Polar Museum.
The NCPOR operates in different fields or tasks:
Note: In 2016, it established a high altitude research station in Himalaya called Himansh. The station is situated above 13500 feet (> 4000 m) at a remote region in Spiti, Himachal Pradesh.

https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/others/antarctica-weather-patterns-changing-leading-to-record-loss-of-ice-ncpor-study-101674816761716.html
Array
(
[0] => daily-current-affairs/changing-antarctica-weather-pattern
[1] => daily-current-affairs
[2] => changing-antarctica-weather-pattern
)
















