Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- Since the explosive Hindenburg Research report that alleged that Adani had committed “stock manipulation and fraud over a period of decades”, Adani Group companies’ stocks have been in free fall, routinely hitting the lower circuits.
What are Circuit Breakers?
- The term "circuit breaker refers" to an emergency-use regulatory measure that temporarily halts tradingon an exchange. Circuit breakers attempt to curb in panic-selling.
- Circuit breakers function automatically by stopping trading when prices hit predefined levels in exchanges.
Purpose
- A circuit breaker in a stock market is a system by which stock exchanges prevent excessive fluctuation of a stock or index. In other words, it is a measure to curb excess volatility in the share price of an equity.
- Since, stock markets are extremely volatile, circuit breaker helps in keeping a check on market manipulation by big investors or brokerage houses.
.jpeg)
Implementation in India:
- In June 2001, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) implemented index-based market-wide circuit breakers.
- Circuit breakers are triggered to prevent markets from crashing due to panic-induced sale of stocks.
- Circuit breakers temporarily halt trading and thus stop the sell-off.
- Effectively, circuit-breakers cap how much the value of a stock can fall in a single day/trading session and in doing so, create a more stable market overall.
Working of index-based market-wide circuit breaker system in India:
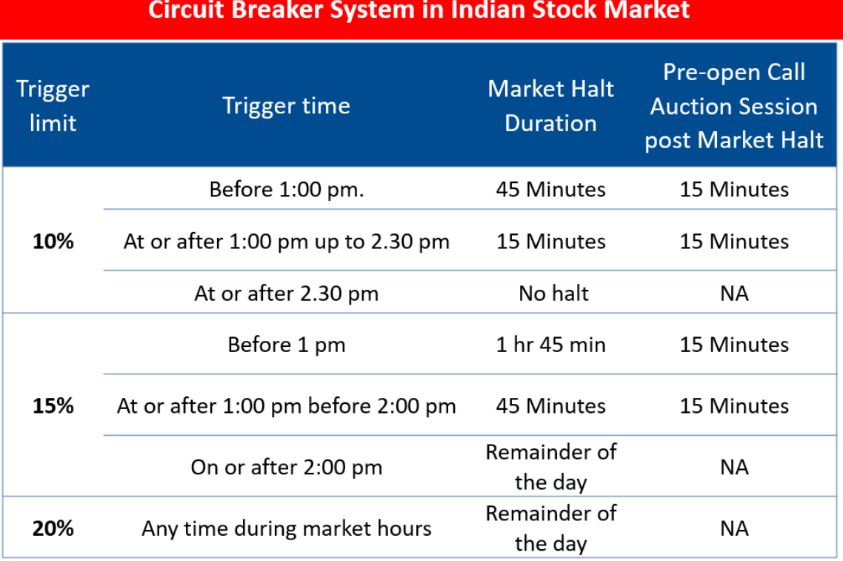
- Index-based market-wide circuit breaker system applies at three stages of the index movement, at 10, 15 and 20 per cent. When triggered, these circuit breakers bring about a coordinated trading halt in all equity and equity derivative markets nationwide.
- For instance, if the S&P BSE Sensex were to fall
- More than 10 per cent before 1 pm on a given day, circuit breakers would be triggered for a period of 45 minutes;
- In case it fell more than 15 percent on or after 2 pm, circuit breakers would be triggered for the remainder of the day and
- In case it fell more than 20 percent at any time of the day, the trading would be halted for the remainder of the day.
- The Stock Exchange computes the Index circuit breaker limits on a daily basis based on the previous day’s closing level of the index rounded off to the nearest tick size.
Types of Circuit Breaker:
Circuit breaker are of two types:
- Upper Circuit
- Lower Circuit
Upper Circuit:
- These are upper limits defined by stock exchanges on share price of stocks. A stock is not allowed to appreciate more than 20% in a single day with respect to its previous closing price.
- For example: Suppose, TCS closed at Rs.100 on the previous day. Then upper circuit level becomes Rs.120 for TCS. So, on the next day, the maximum value at which the share can trade will be Rs.120
Lower Circuit:
- Similar to upper circuit, lower circuit level determines the lowest price at which a stock could trade for that day.
- For example: If TCS had closed at Rs.100 on the previous day, its lower circuit level would become Rs.80 and would not be allowed to trade at a price lower than 80 for that particular day.

Note: Circuit breakers are applied in spot market only, for F&O (Future and Options) stocks there are no such restrictions.
|
Mains Model Question
Q. What is Circuit Breaker in Stock Market? Explain the working of Index-Based Market-Wide Circuit Breaker System in India.
|

https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/circuit-breaker-8420164/















