Description
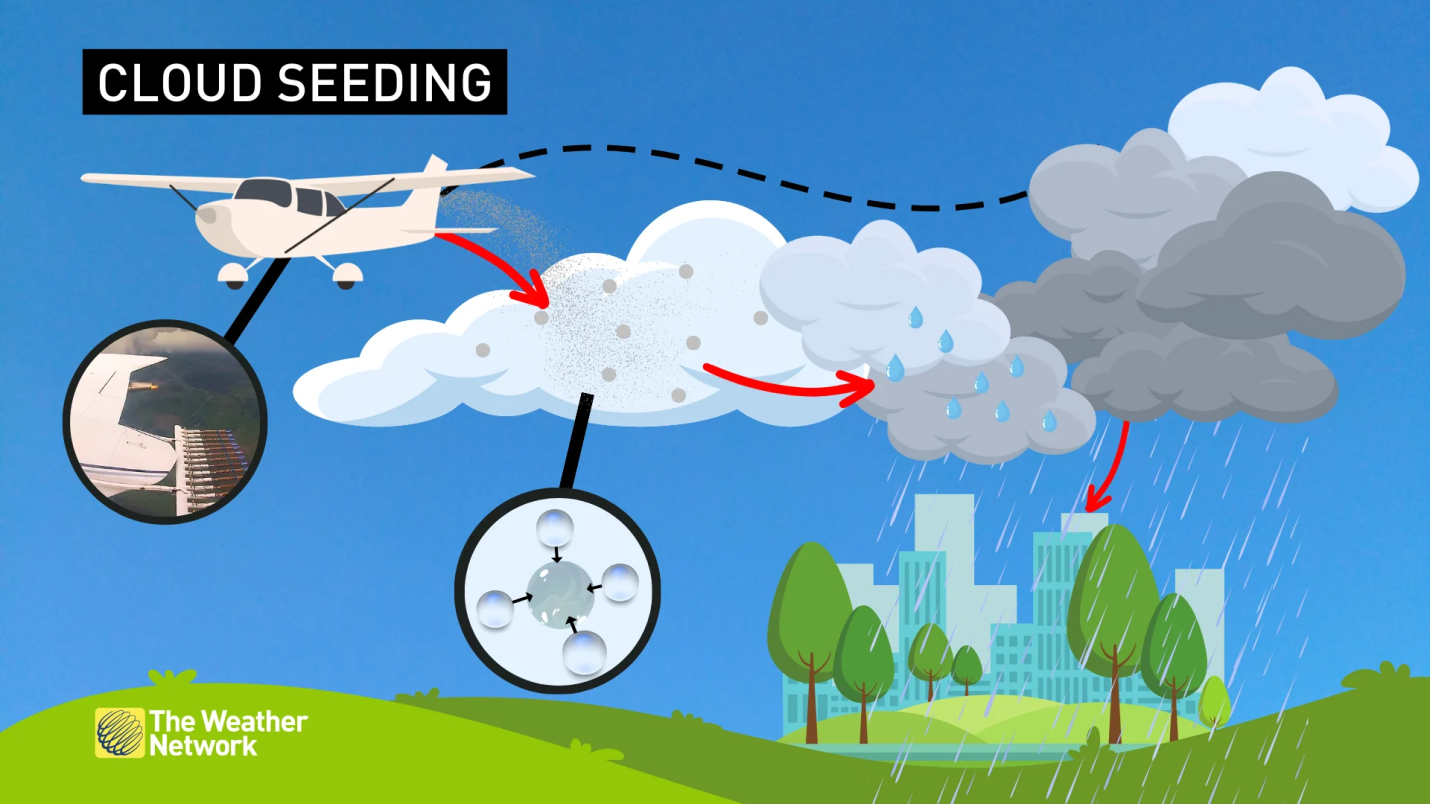
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.theweathernetwork.com/en/news/science/explainers/what-is-cloud-seeding-weather-modification-to-create-rain-snow
Context: The recent forest fires in Uttarakhand drew attention from the Supreme Court, which highlighted the significance of preventive measures rather than relying on rain gods or cloud-seeding to extinguish the fires.
Cloud Seeding
- Cloud seeding is a process of artificially modifying clouds to enhance precipitation by introducing substances known as seeding agents into them.
- The goal of cloud seeding is to encourage the formation of raindrops or ice crystals within clouds, ultimately leading to increased rainfall.
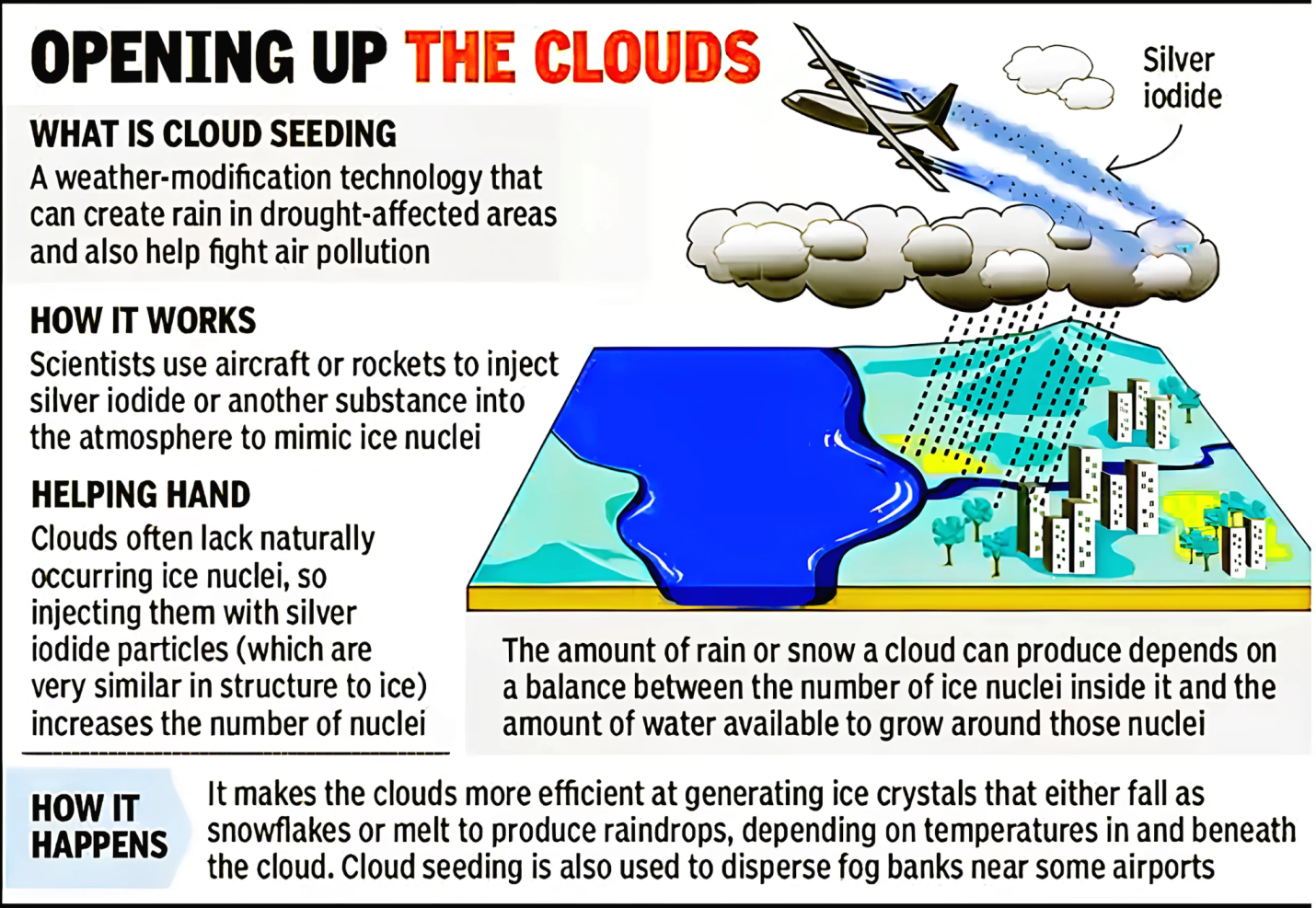
Purpose of Cloud Seeding
- Increasing Precipitation: By promoting the formation of rain or snow, cloud seeding aims to augment natural precipitation and enhance water availability for various purposes such as agriculture, drinking water supply, and ecosystem support.
- Mitigating Weather Hazards: Cloud seeding can also be used to reduce the intensity of severe weather events, such as hailstorms, by modifying cloud dynamics to produce smaller ice particles that are less likely to form damaging hailstones.
Seeding Agents
Cloud seeding involves the deployment of specific substances into clouds, which act as nuclei for condensation or ice crystal formation. Commonly used seeding agents include:
- Silver Iodide: This compound has a crystalline structure similar to ice and is effective in promoting the formation of ice crystals within supercooled clouds (clouds with temperatures below freezing).
- Solid Carbon Dioxide (Dry Ice): Dry ice can rapidly cool the surrounding air, leading to the formation of ice crystals or enhancing the growth of existing ice particles in clouds.
- Salt Crystals (e.g., Sodium Chloride or Calcium Chloride): In warmer clouds, salt particles can induce the growth of water droplets, facilitating the formation of raindrops.
Methods of Cloud Seeding
- Aircraft Seeding: Seeding agents are dispersed into clouds from aeroplanes flying at specific altitudes within or near cloud formations.
- Ground-Based Seeding: Seeding agents are released from ground-based generators or devices positioned on elevated locations to interact with passing clouds.
- Rocket or Cannon Seeding: In some cases, rockets or cannons are used to deliver seeding agents into clouds from the ground.
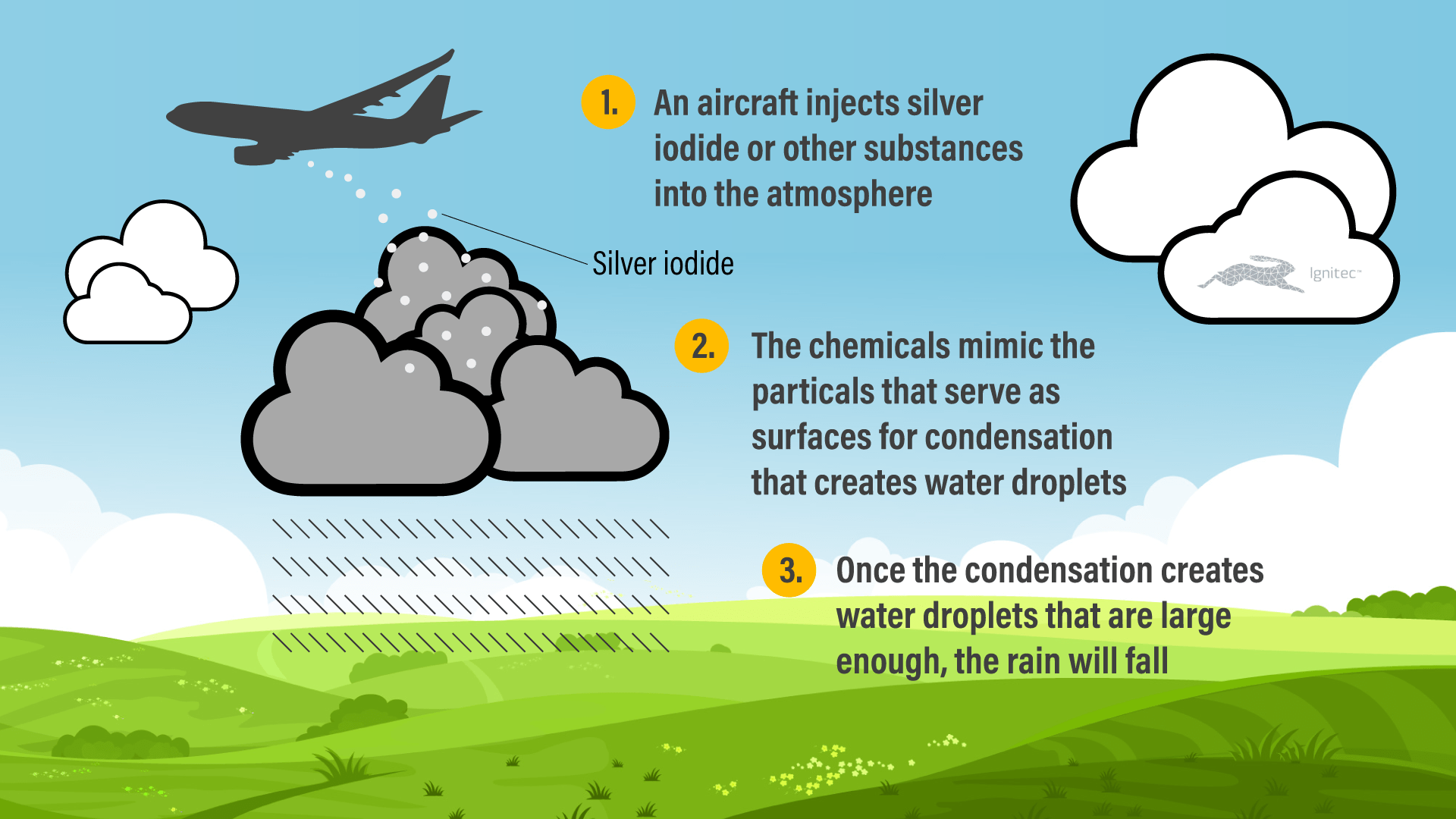
Process of Cloud Seeding
- Identifying Suitable Clouds: Cloud seeding operations target clouds that have the potential to produce precipitation but may require enhancement.
- Deploying Seeding Agents: Seeding agents are introduced into the target clouds using aircraft, ground-based generators, or other delivery methods.
- Nucleation and Growth: The seeding agents act as nuclei around which water vapour condenses or freezes, leading to the formation of larger ice crystals or water droplets.
- Precipitation Formation: As the seeded particles grow in size, they eventually become heavy enough to fall as raindrops or snowflakes, resulting in increased precipitation at the ground level.
Effectiveness and Challenges
The effectiveness of cloud seeding can vary based on several factors, including cloud type, atmospheric conditions, and the choice of seeding agents. Some key considerations and challenges include:
- Variable Results: Cloud seeding outcomes can be unpredictable and depend on local meteorological conditions, making it challenging to guarantee specific precipitation increases.
- Environmental Concerns: There are ongoing debates regarding the environmental impacts of cloud seeding, including potential alterations to natural precipitation patterns and ecological consequences.
- Scientific Research: Continued research and evaluation are essential to assess the efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and potential risks associated with cloud seeding operations.
Conclusion
- Cloud seeding is a complex weather modification technique used to influence cloud properties and enhance precipitation through the introduction of seeding agents. While cloud seeding offers potential benefits for water resource management and weather hazard mitigation, its application requires careful consideration of scientific, environmental, and ethical factors. Ongoing scientific advancements and monitoring efforts are essential to better understand and optimize cloud seeding practices.
Must Read Articles:
CLOUD SEEDING
Source:
The Hindu
Britannica
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Cloud seeding aims to increase precipitation by introducing:
1. Hygroscopic materials that attract water vapour.
2. Ice nuclei that trigger ice crystal formation in supercooled clouds.
3. Coagulants that merge small water droplets into larger ones.
4. Heat sources that increase convection and cloud development.
How many of the above statements are correct?
A) Only one
B) Only two
C) Only three
D) All four
Answer: C
|


















