Description
 Copyright infringement not intended
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.nytimes.com/2024/05/09/world/asia/cook-islands-seabed-mining.html
Context: The Cook Islands' proposal to conduct seabed mining to extract minerals for electric car batteries has sparked debate between supporters who emphasise economic benefits and lower dependence on fossil fuels and opponents who are concerned about potential environmental damage.
Details
- The Cook Islands has been exploring the feasibility of ocean floor mining. Research vessels discovered vast mineral deposits, particularly cobalt and manganese-rich nodules, on the seabed. These minerals are crucial for electric vehicle batteries, contributing to the global transition away from fossil fuels.
- Seabed mining could significantly boost the nation's economy, potentially generating tens of billions of dollars.
Environmental Concerns
- Environmentalists and scientists have raised alarms about the potential ecological damage from seabed mining. More than 800 scientists and countries like France and Britain advocate for a moratorium on seabed mining due to its unknown long-term impacts. Critics fear that seabed mining could disrupt deep-sea ecosystems, harming marine life and habitats irreversibly.
- The Cook Islands government is exploring seabed mining as part of its pursuit of economic independence. However, critics accuse the government of aggressively promoting mining without considering potential adverse effects. Concerns have been raised about potential conflicts of interest, with accusations of close ties between government officials and mining companies.
.jpg)
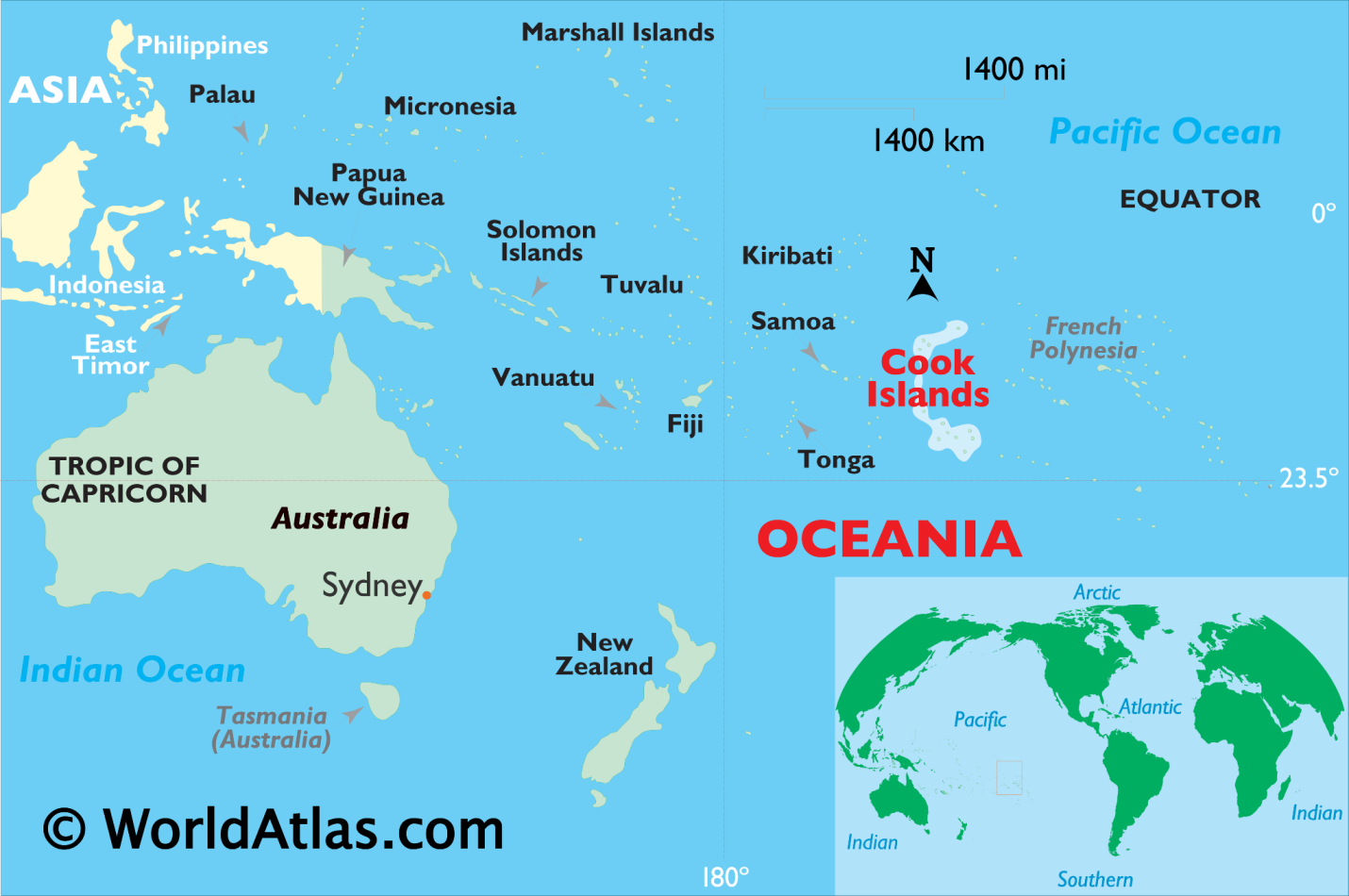
About Cook Island
- The Cook Islands consist of 15 islands scattered across the South Pacific Ocean, covering a total land area of approximately 236.7 square kilometres.
- The Islands are the result of volcanic activity. The islands are divided into two main groups: the Southern Cook Islands, which include the main island of Rarotonga, and the Northern Cook Islands.
- The islands experience distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season typically occurs from November to April, bringing higher rainfall and occasional tropical cyclones. The dry season, from May to October, is characterised by cooler temperatures and less precipitation.
- Tourism is the primary industry in the Cook Islands. Other significant sectors include offshore banking, pearl farming, and marine and fruit exports.
- Woodcarving, weaving, and tivaevae (patchwork quilts) are integral to the Cook Islands' culture. Each island has its unique artistic traditions, with techniques passed down through generations.
- The surrounding waters of the Cook Islands host unique marine species, including the rare Peppermint angelfish. Conservation initiatives focus on preserving marine ecosystems and reducing threats to biodiversity.
|
The Cook Islands operates under self-governance but is in free association with New Zealand. Since the beginning of the 21st century, the Cook Islands have managed its own independent foreign and defence policies, although it relies on New Zealand for external defence.
|
Source:
The Hindu
Wikipedia
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Some experts argue that seabed mining could be a more sustainable alternative to terrestrial mining, as it avoids land degradation and displacement of communities. Evaluate the validity of this argument, considering factors such as energy consumption, carbon footprint, and potential for habitat restoration in both scenarios.
|
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9





 Copyright infringement not intended
Copyright infringement not intended










