Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context: The World Health Organization (WHO) said that it is monitoring a new variant of the novel coronavirus, BA.2.86, also known as BA.X.
About BA.2.86
- 2.86 is also known as BA.X.
- It has so far been detected in the US, Denmark and Israel.
- The WHO has classified BA.2.86 as a VUM.
- A very limited amount of information is available right now on BA.2.86 but a large number of mutations are occurring.

WHO monitors the different COVID variants under three categories —
- A variant under monitoring (VUM), meaning the global health agency is tracking the variant closely and
- A variant of interest (VOI) or a variant of concern (VOC) if there is evidence that it is more transmissible, more likely to cause severe disease or evades immunity.
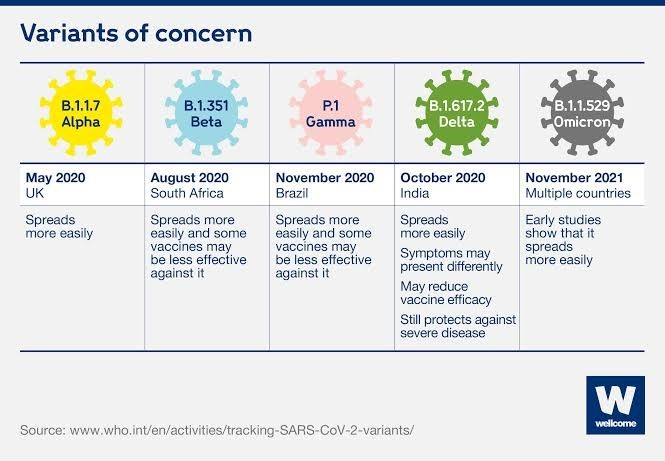
SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions
- Viruses like SARS-CoV-2 continuously evolve as changes in the genetic code (caused by genetic mutations or viral recombination) occur during the replication of the genome.
- SARS-CoV-2 has consistently mutated throughout the pandemic, resulting in variants that are different from the original SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Rising cases and declining deaths
- In the last 28-day period (July 17 to August 13, 2023), over 4 million new COVID-19 cases and over 2,300 deaths were reported from WHO’s six regions.
- This was an increase of 63 per cent and a decrease of 56 per cent, respectively, compared to the previous 28 days.
- However, four WHO regions have reported decreases in the number of both cases and deaths of which the Western Pacific Region has reported an increase in cases and a decrease in deaths.
- As of August 13, 2023, over 769 million confirmed cases and over 6.9 million deaths have been reported globally.
Issues of reporting and testing
- The reported cases do not accurately represent infection rates due to the reduction in testing and reporting globally.
- During the 28-day period, less than half or 44 per cent (104 of 234) of countries reported at least one case to WHO.
- The statistic does not reflect the actual number of countries where cases exist.
EG.5 variant
- Cases of the subvariant of COVID-19 called EG.5, are increasing in Europe.
- 5 is a sublineage of the Omicron variant and was designated a VOI earlier this month.
- Globally, EG.5 (dubbed Eris) and XBB.1.16 (Arcturus) are the most prevalent VOIs reported since their emergence from 101 and 50 countries, respectively, according to the WHO.

Way ahead
- There is a need for closer monitoring.
- Surveillance, sequencing and COVID-19 reporting are critical to track down and detect new variants.
- There is a need for global cooperation in monitoring and reporting framework.
- Countries must continue to build healthcare infrastructure to safeguard from future pandemics.
- Countries must share data of any new strain or mutations in a time bound manner as any delay in action could prove to be fatal like Covid-19.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Emerging new variants of Coronavirus strains calls for strengthening monitoring, surveillance and reporting mechanisms along with preparing for future epidemics. Critically evaluate.( 250 words)
|
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/health/who-us-cdc-are-now-tracking-new-covid-variant-ba-2-86-91247












