Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT), the premier Telecom R&D Centre of the Department of Telecommunications, Ministry of Communications, organized a three-day National Workshop on Cryptology - NWC2022, in association with Cryptology Research Society of India (CRSI) and IEEE Communications Society.

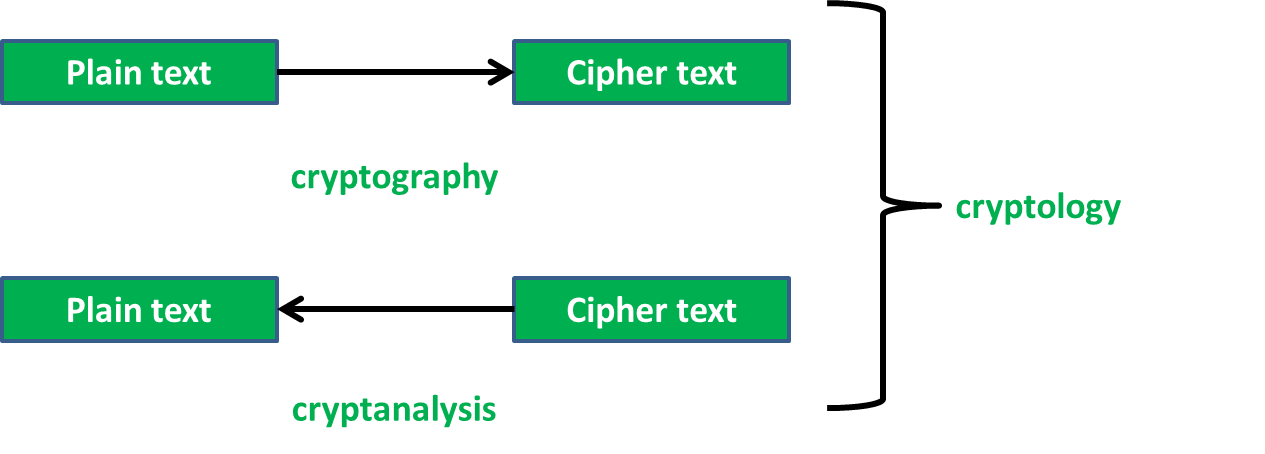
Cryptology
- The scientific research of cryptography and cryptanalysis is known as cryptology.
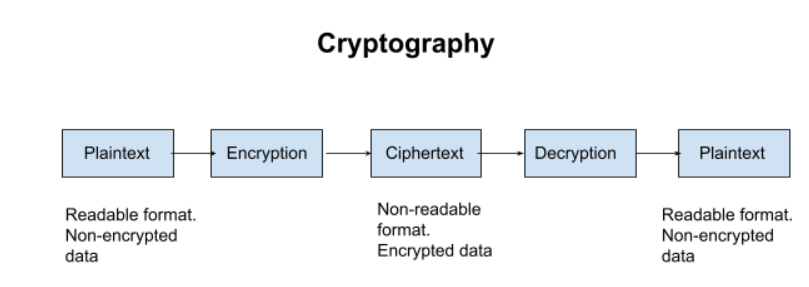
- Cryptography is associated with the process of converting ordinary plain text into unintelligible text and vice-versa. It is a method of storing and transmitting data in a particular form so that only those for whom it is intended can read and process it. Cryptography not only protects data from theft or alteration, but can also be used for user authentication.
Analysis
- Throughout history, world events have changed because of secret messages. Secrets that were kept and secrets that were not.
- In the world of diplomacy, knowing what your enemy is planning helps you to prepare, but it is also important that your enemies do not know what you have planned.
- Cryptology is the study of codes, both creating and solving them. Cryptography is the art of creating codes.
- The part of Cryptology that deals with studying secret messages and breaking the system is called Cryptanalysis. Information gathered from the foreign signals environment enables our Government to make important decisions.
- During the period of World War II, cryptography was utilized to ensure the confidentiality of written messages.
Description
- Earlier cryptography was effectively synonymous with encryption but nowadays cryptography is mainly based on mathematical theory and computer science practice.
Modern cryptography concerns with:
- Confidentiality - Information cannot be understood by anyone
- Integrity - Information cannot be altered.
- Non-repudiation - Sender cannot deny his/her intentions in the transmission of the information at a later stage
- Authentication - Sender and receiver can confirm each
Cryptography is used in many applications like banking transactions cards, computer passwords, and e- commerce transactions.
Three types of cryptographic techniques used in general.
- Symmetric-key cryptography
- Hash functions.
- Public-key cryptography
- Symmetric-key Cryptography: Both the sender and receiver share a single key. The sender uses this key to encrypt plaintext and send the cipher text to the receiver. On the other side the receiver applies the same key to decrypt the message and recover the plain text.
- Public-Key Cryptography: This is the most revolutionary concept in the last 300-400 years. In Public-Key Cryptography two related keys (public and private key) are used. Public key may be freely distributed, while its paired private key, remains a secret. The public key is used for encryption and for decryption private key is used.
- Hash Functions: No key is used in this algorithm. A fixed-length hash value is computed as per the plain text that makes it impossible for the contents of the plain text to be recovered. Hash functions are also used by many operating systems to encrypt passwords.

|
Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT)
The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) is an Indian Government owned telecommunications technology development centre. It was established in 1984 with initial mandate of designing and developing digital exchanges. C-DOT has expanded to develop intelligent computer software applications.
|
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1878669












