



Operation ‘Clean Art’ to crack down on illegal trade in mongoose hair

- Operation Clean Art was the first pan India operation to crack down on the smuggling of mongoose hair in the country.
- Operation Clean Art was conceived by WCCB with the singular aim of ensuring that the mongoose hair brush trade is closed down across the country.
- The mongoose is listed in Schedule II Part 2 of the Wildlife Protection Act.
- Any smuggling or possession of its body part is a non-bailable offence.
- Signed first maritime cooperation agreement.
- Cooperation in Polar Science
- Agreement with Sweden is scientific in nature.
- Defense is one critical area of cooperation between two countries, where Swedish company Saab is applying for tender of 114 jets by Indian air force.
Paris, London, and Berlin on Saturday welcomed six new European countries to the INSTEX barter mechanism. governments of Belgium, Denmark, Finland, the Netherlands, Norway, and Sweden have joined INSTEX as shareholders.
- Circumvent U.S. sanctions against trade with Iran by avoiding the use of the dollar.
- INSTEX functions as a clearing house allowing Iran to continue to sell oil and import other products or services in exchange.
- It is supposed to be a financial channel and a special mechanism for transferring money in spite of U.S. sanctions on Iran.
Who is a farmer? What is the government’s definition of a farmer, and how many farmers are there in India by that definition?
Government failed to answer these questions in RajyaSabha.
FARMER’ will refer to a person actively engaged in the economic and/or livelihood activity of growing crops and producing other primary agricultural commodities and will include all agricultural operational holders, cultivators, agricultural labourers, sharecroppers, tenants, poultry and livestock rearers, fishers, beekeepers, gardeners, pastoralists, non-corporate planters and planting labourers, as well as persons engaged in various farming related occupations such as sericulture, vermiculture and agro-forestry.
- Most schemes meant for farmers’ welfare, including the procurement of wheat and paddy at minimum support prices, are effectively available only for land owners.
- Women farmers are not recognized as they lack land ownerships.
- The government’s ambiguity has serious implications for the design and beneficiaries of the schemes meant to help them, including its flagship PM-KISAN (Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi).
- Uniform representation for all States for reflecting true federalism.
- Each member is given a minimum of five minutes to convey views meaningfully.
- Currently, members are given time according to the strength of their party in the House.
- Independent or nominated members get less time like MPs from smaller parties.
- Smaller States should have six members at the very least.
- Fixing a minimum time limit for each members is doable.
- For equal representation of states, legal opinion has to be undertaken and will require constitutional amendment.
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-national/elders-seek-more-time-to-speak/article30133640.ece
The Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI) put on hold amendments to six important rules of its new constitution that were approved by the Supreme Court.
- Powers of its office-bearers and the apex council.
- The president and secretary’s tenure/period in office.
- Relaxation in the age cap of 70 for its representative to the ICC.
- Relief from the obligation to approach the Supreme Court to obtain its approval for every amendment.

The era of low tariffs for Indian consumers seems to have ended as major telcos — Vodafone Idea Limited (VIL), Bharti Airtel Limited and Reliance Jio — have hiked tariff by up to 40% for prepaid customers.
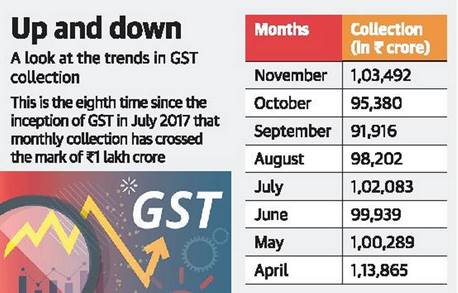
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) revenue in November came in at Rs. 1,03,492 crore, crossing the Rs. 1 lakh crore mark once again.
- Average collections in the financial year 2019-20 so far stand at Rs. 1,00,646 crore.
- The GST from domestic transactions saw a growth of 12%, the highest during the year.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax (or consumption tax) imposed in India on the supply of goods and services. It is a comprehensive multistage, destination based tax: comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all the indirect taxes. Goods and services are divided into five different tax slabs for collection of tax - 0%, 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%.
- central excise duty
- services tax
- additional customs duty
- surcharges
- state-level value added tax
- Octroi
Petroleum products, alcoholic drinks, and electricity are not taxed under GST and instead are taxed separately by the individual state governments.
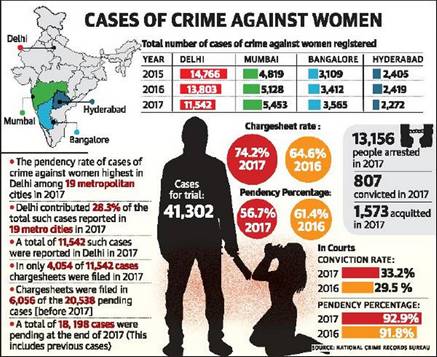
- With a conviction rate of just 33.2%, the Capital recorded 92.9% cases of crime against women pending in various district courts.
- Majority of cases under crime against women (CAW) was registered under “Cruelty by Husband or his Relatives” (27.9%), followed by “Assault on Women with Intent to Outrage her Modesty” (21.7%), “Kidnapping and Abduction of Women” (20.5%) and “Rape” (7.0%).
- Witnesses turn hostile.
- lack of statement from eyewitness which delays the process.
- Separate teams for investigation and law and order in all police stations.
- Cases of molestation, rape and other heinous crimes against women are treated on priority basis.
- Dynamic identification of crime-prone areas.
- Deployment of police resources.
- Dedicated women helpline no. 1091.
- Exclusive women help desk at police stations.
- Anti-stalking services for women.
- Stationing all-woman PCR vans in vulnerable areas.
- Informing civic agencies regarding dark patches for rectification.
- Self-defence training for women/girls.
- Special drives against tinted glasses in public transport vehicles.
About NCRB:
- The National Crime Records Bureau, abbreviated to NCRB, is an Indian government agency responsible for collecting and analysing crime data as defined by the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and Special and Local Laws (SLL)
- NCRB is headquartered in New Delhi and is part of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Government of India.
- NCRB was set-up in 1986 to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
Objectives of NCRB:
- Create and maintain secure sharable National Databases on crimes and criminals for law enforcement agencies and promote their use for public service delivery.
- Collect and process crime statistics at the national level and clearing house of information on crime and criminals both at National and International levels.
- Lead and coordinate the development of IT applications and create an enabling IT environment for Police organizations.
- National repository of fingerprints of all criminals.
- To evaluate, modernize and promote automation in State Crime Records Bureaux and State Finger Print Bureaux.
- Training and capacity building in Police Forces in Information Technology and Finger Print Science.
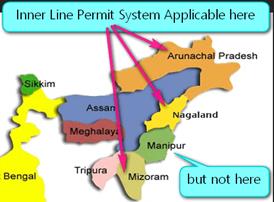
In the run-up to the likely introduction of the Citizenship Amendment Bill during the current session of Parliament, the concept of Inner Line Permit has been part of the conversation.
- The Bill would protect such regions and states where the Inner Line Permit (ILP) is applicable and autonomous administration.
- The ILP is based on the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation Act (BEFR), 1873.
- A special permit is required by "outsiders" from other regions of India to enter the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, and Mizoram.
- This ILP provision was made to give special protection to the indigenous people.
- ILP certificate can be used only for travel and not for permanent residency in the area.
- Outsiders cannot buy property in the state.
- An ILP is issued by the state government concerned.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved