Govt. bats for sharing biological research data
News important for: GS paper 3 I Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects
Context
The government of India has released the draft document, called the Biological Data Storage, Access and Sharing Policy.
Analysis
- The draft note released on use and sharing of biological data asks researchers who collect such data with the use of public funds, to make the data public within two years.
- It highlights that several scientists who use government funds to conduct research and collect biological specimens and data such as DNA samples, cell and tissue samples often store them for long, and bar access to other researchers and scientists who may be interested.
- This leads to duplication of data collection exercises, lost opportunities to access data collected over the years and wastage of public money.
- The draft mentions that Raw (Level-1) data must be shared on a database identified and approved by the funding agency of the Government of India, within one year of generation of the data.
- If no such database is identified by the agency, then raw data can be made available to anyone working in any Indian institution, public or private, requesting for these data.
- Data generated from public funds to be open to private companies as well.
- The data has to be excised of all features that would identify individuals.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/government-bats-for-sharing-biological-research-data/article28264736.ece
Lok Sabha clears fresh Medical Council Bill
News important for: GS paper 2 I important aspects of governance, Health sector regulations.
Context
Indian Medical Council (Amendment) Bill, 2019 was passed by Lok Sabha.

About
· The bill provides for supersession of Medical Council of India for a period of two years.
· The new National Medical Commission (NMC) Bill will soon be introduced to replace Indian Medical Council.
· The bill has granted accreditation to a greater number of medical colleges, increased number of seats and reduced procedural hurdles.
· The Bill will also allow for the increase in the number of members in the Board of Governors to 12 from the existing seven.
Amendments approved in the National Medical Council bill from Indian Medical council:
- The final MBBS examination will be held as a common exam throughout country. It will serve as an exit test to be called as National Exit Test (NEXT).
- It removes provision dealing with a bridge course for AYUSH practitioners to practice modern medicine to a limited extent.
- Now state governments have been empowered to take necessary measures for addressing and promoting primary health care in rural areas.
- The maximum limit of 40% seats for which fee will be regulated in private medical institutions and deemed universities has been increased to 50% seat.
- The nominees of States and UTs in National Medical Commission (NMC) have been increased from 3 to 6. TNMC will comprise of 25 members of which at least 21 will be doctors.
- It provides severe punishment for any unauthorized practice of medicine or by quacks with imprisonment of up to 1 year along with the fine extending up to 1 lakh.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/lok-sabha-clears-medical-council-amendment-bill/article28264428.ece
Bengal introduces a 10% quota in jobs, education
News important for: GS paper 2 I functions and responsibilities of union and state, issues and challenges pertaining to federal structure.
About
- The west Bengal government decided a 10% reservation in government jobs and educational institutions to people belonging to the economically weaker sections (EWS).
- People covered under the SC, ST and OBC category are not eligible.
- The decision comes six months after the cabinet government approved a 10% quota in jobs and educational institutions for economically weaker sections (EWS) among general category.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/bengal-introduces-10-quota-in-jobs-education/article28264556.ece
Bangladesh seeks to synergise ties with India
News important for: GS paper 2 I India and its neighbourhood relations.
Context:
Bangladesh urged for the dignified return of the Rohingya refugees from camps in Chittagong to Myanmar.

Analysis
- The move comes after elections in India.
- The step of Bangladesh reflects the desire of greater association with India.
- The step also reflects Bangladesh diplomacy to be at par with India and China as it starts an energy deal with China connected to BRI.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/bangladesh-seeks-to-synergise-ties-with-india/article28264235.ece
High trading costs impact liquidity of the Indian equities: study
News important for: GS paper 3 I Indian economy and issues related to planning.
Context:
The recent study has shown that the turnover ratio of the Indian stock market has fallen significantly in the last 10 years.
Analysis
- The fall of Indian Stock Market has been higher compared with other leading markets of the world.
- As per the World Bank, the turnover ratio of the Indian stock market had fallen from 143 in 2008 to 58 in 2018.
- The fall in the stock market has been nearly 60% between 2008 and 2018, as per the World Bank report,
- The fall had been the highest among most leading markets of the world, barring the U.S. and the European Union.
- Market participants have been struggling hard with the government to bring down the overall cost of trading in equities in India.
- It is adversely affecting investors’ interest in the stock market.
- As part of their pre-budget recommendations of market to the government, capital market participants had sought rationalisation of the securities transaction tax (STT) apart from bringing back certain exemption benefits that were available earlier.
- Government stopped treating STT as tax paid and treated it as an expense that led to double taxation for the gains assessed under business income.
- Long-term capital gains (LTCG) tax was made nil while introducing STT in 2004, the transaction tax was not done away with when LTCG was reintroduced in 2018.
- The World Bank study is similar to a recent analysis by the Association of National Exchanges Members of India (ANMI).
- ANMI highlighted the fact that that India had very high trading costs due to huge margin requirements, especially in the derivatives segment.
Turnover Ratio:
- The turnover ratio is a universally accepted parameter to gauge trading volumes.
- It is the total value of the shares traded in a specific period divided by the average market capitalisation of that period.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/business/high-trading-costs-impact-liquidity-of-indian-equities-study/article28264706.ece
Need for intervention in primary healthcare
News important for: GS paper 2 I healthcare and health related issues.
Context
There is a need of primary healthcare in the country to boost the healthcare mechanism.
Analysis:
- The recent AES outbreaks highlight the vague primary health care system in the states and their poor capacity to handle outbreaks.
- To deal with AES outbreaks,
- apart from a robust health education drive and
- replenishing primary health centres (PHCs) with essential supplies,
- extensive deployment of peripheral health workers (ASHA workers) and
- Ambulance services to facilitate rapid identiï¬cation and management of suspected cases.
- Vacant doctor positions in PHCs must be urgently ï¬lled through deputation.
- Short term scaling up of the Poshan Abhiyaan and the supplementary nutrition programme — which makes available hot, cooked meals for preschool children at Anganwadis along with take home ration for mothers and distribution of glucose/ORS packets in risk households.
- In Bihar, one PHC caters to about 1 lakh people rather than the norm of 1 PHC per 30,000 people.
- Bihar, one of the most populous States, had a doctor population ratio of 1:17,685 in 2018, 60% higher than the national average, and with only 2% of the total MBBS seats in the country.
- There is also a one ï¬fth shortage of ASHA personnel, and nearly one third of the subhealth centres have no health workers at all.
- A study found that around 71% and 38% of funds meant for hot, cooked meals and take-home ration, respectively, under the supplementary nutrition programme, were not met.
- PHCs are inept as centres of general healthcare.
- This leads patients either directly to apex government hospitals situated far away or to unqualiï¬ed private providers.
- This results in a patient losing precious time in transit and landing up in a hospital in a critical and often irreversible stage of illness.
- Merely strengthening the tertiary care sector will be inefficient and ineffective.
About Acute Encephalitis Syndrome:
AES is largely preventable both before and just after the onset of the disease, and treatable with high chances of success on availability of medical intervention within 24 hours of symptoms.
- AES has been linked to two factors:
- litchi consumption by starving children
- And a long ongoing heat wave.
Conclusion:
- The solution of the problem is:
- in building more functional PHCs and subhealth centres
- Scaling up the cadres of ASHA workers
- strict monitoring of nutrition programmes
- Addressing the mal-distribution of doctors and medical colleges.
- The resultant robust primary care system can then be geared towards being more responsive to future outbreaks.
- bolster our technical capacity to better investigate the causes of such outbreaks and operationalise a concrete long-term strategy.
- There is a need to restore faith in community healthcare in the country.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-opinion/healthcares-primary-problem/article28267313.ece
How global warming could impact jobs in India
News important for: GS paper3 I Environment and ecology.
Context:
International Labour Organisation has released a report titled ‘Working on a warmer planet: The impact of heat stress on labour productivity and decent work’.
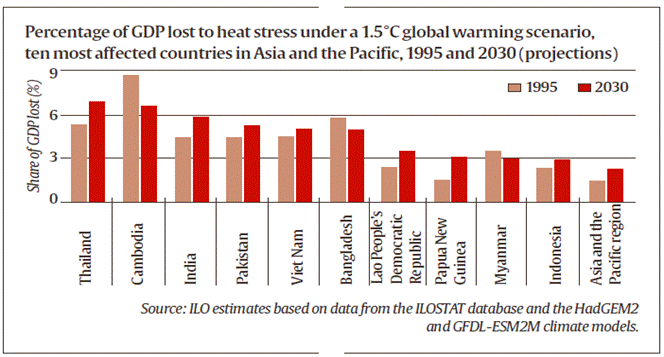
Analysis
- According to the study, by 2030, heat stress will cause a loss of 5.8% of working hours in India which is equivalent to 34 million jobs.
- India will be the worst affected country among all.
- The report makes its projections based on a global temperature rise of 1.5°C by the end of the century, and also on labour force trends.
- These projections suggest that in 2030, 2.2 per cent of total working hours worldwide will be lost because of higher temperatures.
- The loss will be equivalent to 80 million full-time jobs.
- This is equivalent to global economic losses of US$2,400 billion.
- The report projects losses in working hours as 9.04% in agriculture (in shade), 5.29% in manufacturing, 9.04% in construction, and 1.48% in services.
- The ILO says 940 million people around the world work in the agricultural sector, which is projected to account for 60% of working hours lost due to heat stress by 2030.
- In construction, an estimated 19% of global working hours is likely to be lost.
- Most of the impact in India will be felt in the agricultural sector, more and more working hours are expected to be lost in the construction sector.
- Heat stress affects both male and female workers.
- More inequality between low- and high-income countries and worsening working conditions for the most vulnerable, as well as displacement of people will be observed.
Heat waves:
- The report defines heat stress as heat in excess of what the body can tolerate without suffering physiological impairment.
- It generally occurs at temperatures above 35°C, in high humidity.
- Excess heat during work is an occupational health risk and restricts workers’ physical functions and capabilities, work capacity and thus, productivity.
Source link:
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/global-warming-climate-jobs-india-temperature-humidity-5811761/







