



President commutes 20 death sentences in nine years
POLITY
President commutes 20 death sentences in nine years
The President commuted death sentences to life imprisonment in at least 20 cases over the past nine years, based on the recommendations received from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
These commutations were based on the clemency power of the President under Article 72 of the Constitution.
Article 72:
It says that the President shall have the power to grant pardons, reprieves, respites or remissions of punishment or to suspend, remit or commute the sentence of any person convicted of any offence.
Pardon –A pardon completely absolves the offender from all sentences and punishment and disqualifications and places him in the same position as if he had never committed the offence.
Commutation– Commutation means exchange of one thing for another. In simple words to replace the punishment with less severe punishment. For example for Rigorous imprisonment-simple imprisonment.
Reprieve– Reprieve means temporary suspension of death sentence. For example- pending a proceeding for pardon or commutation.
Respite – Respite means awarding a lesser punishment on some special grounds. For example- the Pregnancy of women offender.
Remissions– Remission means the reduction of the amount of sentence without changing its character, for example, a sentence of 1 year may be remitted to 6 months.
The President can exercise these powers:
- In all cases where the punishment or sentence is by a court martial.
- In all cases where the punishment or sentence is for an offence against any law relating to a matter to which the executive power of the Union extends.
- In all cases where the sentence is a sentence of death.
Supreme Court verdict on president clemency powers:
1. In Maru Ram case , the Court expressed a view in favour of laying down some guidelines for the purpose of exercising power under Art.72 in order to avoid any allegation of arbitrary exercise of power.
2.In Kuljeetsingh case , court observed following grounds for mercy :
1.Personality of the convict (such as age, sex, or mental deficiency) or circumstances of the case (such as provocation or similar justification). Thus, if the convict was very young, or a woman, or a mentally challenged person, or if the offence was committed under distress, these were considered as relevant factors for the grant of clemency.
2. Has the appellate court expressed doubt on the reliability of evidence but has nevertheless decided on conviction?
3. Is it alleged that fresh evidence is obtainable, mainly with a view to seeing whether a fresh inquiry is justified?
4. Has the High Court, on appeal, reversed an acquittal or has it, on appeal, enhanced the sentence?
5. Is there any difference of opinion in the Bench of High Court judges, necessitating reference to a third judge?
6. Was the evidence duly considered in fixing responsibility, if it was a gang murder case?
7. Were there long delays in the investigation and the trial? Or remit the sentence imposed on him”.
SOCIETY
Food safety agency FSSAI launches ‘Trans Fat Free’ logo
Union health minister Harsh Vardhan formally launched the “Trans Fat Free” logo during the 8th International Chefs Conference in the national Capital.
The use of the logo by restaurants and food manufacturers, however, is voluntary.
As part of the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)-led ‘Eat Right India’ movement, the target is to reduce the industrially produced trans fatty acids on food supply to less than 2% by 2022.
Trans Fats:
- Industrial trans fats are made by adding hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils to make them more solid, and to increase the shelf life of foods..
- Trans fat are largely present in partially hydrogenated vegetable fats/oils, vanaspati, margarine and bakery shortenings, and can be found in baked and fried foods.
- An estimated 5,40,000 people die each year globally of cardiovascular diseases, and consumption of food laced with industry trans fats is a contributing factor.

Eat Right Movement:
FSSAI :
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is an autonomous body established under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India.
- The FSSAI has been established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 which is a consolidating statute related to food safety and regulation in India.
- FSSAI is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the regulation and supervision of food safety.
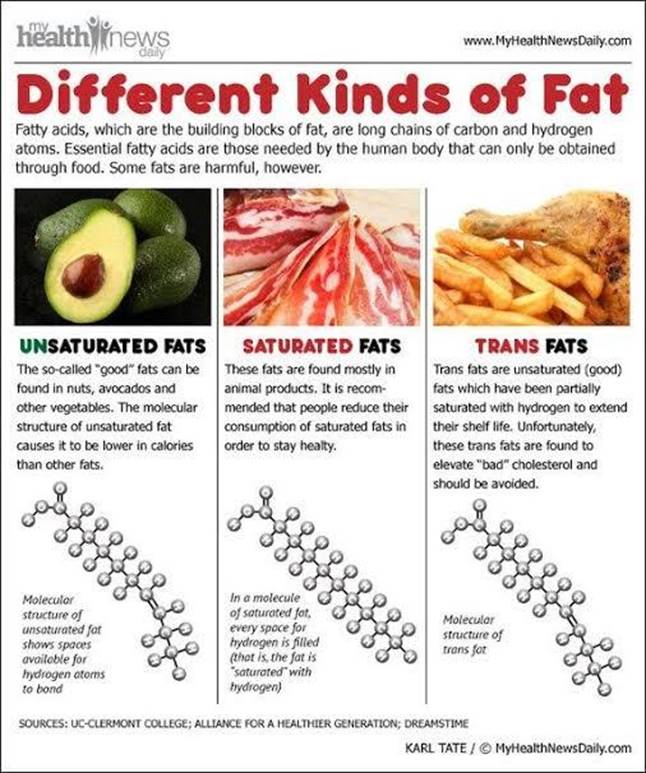
Different types of fats :
SECURITY
Explained: Telangana’s idea of supplying medicines to remote areas by drones
The Telangana government has adopted a framework to use drones for last-mile delivery of essential medical supplies such as blood and medical samples in an effort to increase the access to healthcare to communities across the state.
The framework has been co-designed by the World Economic Forum (WEF) and Apollo Hospitals Group Health net Global Limited.
Application of drones :
- Reduction of the time taken to transport material.
- Improvement of the supply chain efficiency.
- In Rwanda, where drone-related pilot projects have been implemented on a national scale to deliver medical supplies without delay and at scheduled intervals.
Regulations of drones:
- A drone is an aircraft that operates without a pilot on board and is referred to as an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV).
- It has three subsets: Remotely Piloted Aircraft (RPA), Autonomous Aircraft, and Model Aircraft.
- An RPA can be further classified into five types on the basis of weight: Nano, Micro, Small, Medium and Large.
- The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) under the Ministry of Civil Aviation acts as the regulatory body in the field of civil aviation, responsible for regulating air transport and ensuring compliance to civil aviation requirements, air safety, and airworthiness standards.
- The DGCA’s drone policy requires all owners of RPAs, except drones in the smallest ‘Nano’ category, to seek permission for flights, and comply with regulations including registration, and operating hours (only during the day) and areas (not above designated high security zones).
- The food delivery platform Zomato has tried out a drone to deliver a payload of up to 5 kg to a distance of 5 km, flying at a maximum speed of 80 km/h; however, regulations do not yet allow the delivery of food by drones.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved