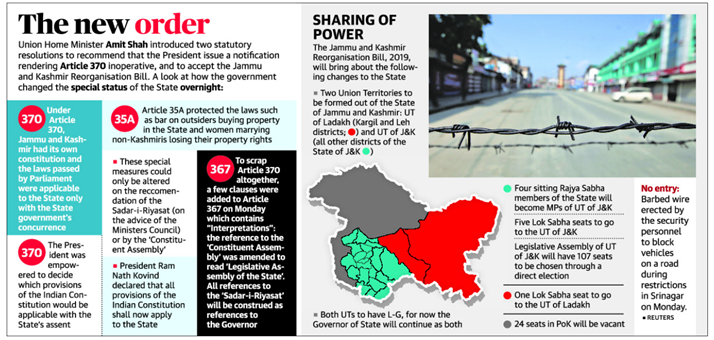
J&K loses its special status, divided into two UTs
News Important for: GS Paper – 2 I structure, Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure.
Context
The central government has abolished the special status of Jammu and Kashmir through a presidential order.
New Order:
- The central government has issued a notification - The Constitution (Application To Jammu And Kashmir) Order, 2019.
- This will override the Order of 1954 and in effect scrapping Article 370 of the Constitution.
- The government has revoked the ‘special status’ granted to the State under Article 370.
- The decision calls for reorganizing the State into two Union Territories — Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Only Jammu and Kashmir will have legislative Assembly and Ladakh will not have one.
Article 370:
- Article 370 of the Indian Constitution deals with the special status given to the state of Jammu & Kashmir.
- It was proposed that “Kashmir state” would have special powers to be excluded from the purview of the laws that the Parliament of India would make.
- Article 370 of the Indian Constitution provided that only Articles 1 and 370 itself would apply to J&K.
- The application of other Articles was to be determined by the President in consultation with the government of the state. Jammu and Kashmir to have the power to make its own laws.
- It was a 'temporary provision' that serves the purpose of granting special autonomous status to Jammu and Kashmir.
|
Article 35A
- In order to further strengthen Article 370 came another provision, Article 35A.
- Article 35A was added to the Indian Constitution by a Presidential order in 1954.
- This provision allows the President to make certain “exceptions and modifications” to the Constitution for the benefit of ‘State subjects’ of J&K.
- The Fundamental Right to Property is still guaranteed in the state. Also, certain special rights are granted to the permanent residents of the state with regard to public employment, acquisition of immovable property, settlement and government scholarships.
- It disallows people from outside the state from buying or owning immovable property or settle permanently, or avail themselves of state-sponsored scholarship schemes.
- Only the Jammu-Kashmir assembly can change the definition of Permanent Residents through a law ratified by a two-thirds majority.
|
Concerns:
- The manner in which the exercise is being carried out.
- The views of the people of Jammu and Kashmir were ignored.
- The Government must develop an external strategy that will facilitate a final settlement of the Kashmir question.
- The bill was passed without consulting Kashmir’s state legislature.
- Article 3 of the Constitution says that before parliament can consider a Bill that diminishes the area of a state or changes its name, the Bill must be “referred by the President to the Legislature of that State for expressing its views thereon”. The representation of people by a representative authority.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/jk-loses-its-special-status-divided-into-two-uts/article28829005.ece
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Surrogacy regulation Bill passed in Lok Sabha
News Important for: GS Paper – 3 I Regulation, Women empowerment
Context
Lok Sabha passed The Surrogacy (Regulation) Bill, 2019 which aim to ban commercial surrogacy to protect women from exploitation.
Provisions of the bill:
- The Bill will ensure to protect couples against exploitation.
- The bill provides for constituting a National Surrogacy Board, State Surrogacy Boards, and the Appointment of appropriate authorities for the regulation of the practice and process of surrogacy.
- It defines surrogacy as a practice where a woman gives birth to a child for an eligible couple and agrees to hand over the child to them after the birth.
- The Surrogacy (Regulation) Bill regulates altruistic surrogacy and prohibits commercial surrogacy.
- Altruistic surrogacy involves no monetary compensation to the surrogate mother other than the medical expenses and insurance coverage during the pregnancy.
- Commercial surrogacy includes surrogacy or its related procedures undertaken for a monetary benefit or reward (in cash or kind) exceeding the basic medical expenses and insurance coverage.
- Surrogacy is permitted only if, the intending couples who suffer from proven infertility condition or disease specified through regulations and for altruistic purpose only.
- It is not allowed for commercial purposes or producing children for sale, prostitution or other forms of exploitation.
- The intending couple should have a ‘certificate of essentiality’ and the surrogate mother should have a ‘certificate of eligibility’ issued by the appropriate authority.
- Certificate of essentiality certifies proven infertility of one or both members of the intending couple from a District Medical Board.
- Surrogacy clinics cannot undertake surrogacy related procedures unless they are registered by the appropriate authority.
- Offences and penalties for violating the provisions includes imprisonment up to 10 years and a fine up to 10 lakh rupees.
Objectives behind the Regulations:
- The Bill is aimed at ending the exploitation of women who are lending their womb for surrogacy.
- It aims to protect the rights of children born through surrogacy.
- It will also look after the interests of the couple that opt for surrogacy, ensuring that there are laws protecting them against exploitation by clinics
- The intending couple should have a ‘certificate of essentiality’ and the surrogate mother should have a ‘certificate of eligibility’ issued by the appropriate authority.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/lok-sabha-passes-surrogacy-bill/article28824277.ece
http://www.prsindia.org/billtrack/surrogacy-regulation-bill-2019
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Govt. unveils draft e-com norms
News Important for: GS Paper – 3 I Economic policy
Context
The central government has released draft guidelines on e-commerce that will regulate e-commerce in India.
e-commerce guidelines for consumer protection 2019:
The draft guidelines on e-commerce aims to protect the interest of online shoppers and consumers.
- It forbid influencing price of goods and services.
- The e-commerce entity needs to publish the name and contact details of the grievance officer on their website along with the mechanism by which users can lodge their complaints.
- The e-commerce firms need to ensure that personally identifiable information of customers is protected.
- These guidelines apply to business-to-consumer e-commerce, including goods and services.
- As per the draft, an e-commerce firm cannot falsely represent themselves as consumers or post reviews about goods and services in their name.
What is the advantages of the bill?
- The bill will act the guiding principles for e-commerce business
- It will prevent fraud, unfair trade practices.
- Protect the legitimate rights and interests of consumers.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-business/govt-unveils-draft-e-com-norms/article28828871.ece
************************************************************************