



A Constitution Bench led by Chief Justice of India Ranjan Gogoi will deliver its judgment in the cross-appeals filed by the Hindu and Muslim sides challenging the three-way partition of the disputed 2.77 acres of the Ram Janama bhoomi-Babri Masjid land among Ram Lalla, the Nirmohi Akhara and the Sunni Waqf Board in September 2010.
- It initiated after a mediation attempt across the religious divide “to heal hearts and minds” failed to deliver.
- It is second highest and longest case after the historic Keshavananda Bharti case.
- The testimonies in the appeals alone ran into 54 volumes, consisting of 13,426 pages. Which has been translated into English and filed by the Uttar Pradesh government
- The Allahabad High Court’s Justice S.U. Khan had described the disputed Ram janma bhoomi-Ayodhya property as a “small piece of land where angels fear to tread”.
- Presently, the Centre, under the Ayodhya Act of 1993, is holding the acquired land, which includes the disputed area, as a non-partisan, statutory receiver.
The Indian government has revoked author AatishTaseer’s Overseas Citizen of India card.
- His Father was a citizen of Pakistan and it makes him ineligible for OCI card.
- An Overseas Citizen of India, or OCI, is a category introduced by the government in 2005.
- Government of India merged OCI and PIO (Person of India Origin) in 2015.
- One has to be a citizen of India on or after January 26, 1950, or child or grandchild of such a person.
- According to Section 7A of the OCI card rules, an applicant is not eligible for the OCI card if he, his parents or grandparents have ever been a citizen of Pakistan or Bangladesh.
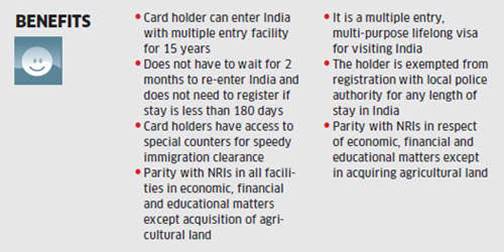
- They are exempt from registering with Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO) no matter how long their stay.
- After staying for a period of five years, he/she are eligible to apply for Indian citizenship.
- OCI cardholders are provided with special immigration counters.
- They can open special bank accounts in India.
- They can buy non-farm property and exercise ownership rights and can also apply for a driver’s license and PAN card.
- They do not get voting rights.
- They cannot hold a government job.
- They cannot purchase agricultural or farm land.
- They cannot run public office.
- They cannot travel to restricted areas without government permission.
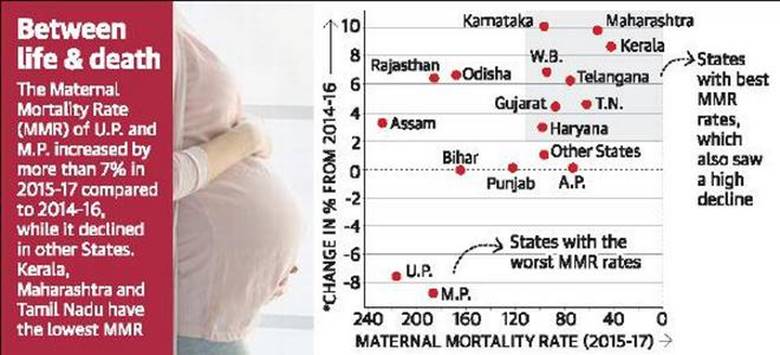
- India’s Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) has seen a decline from 130 per 1 lakh live births in 2014-2016 to 122 per 1 lakh live births in 2015-2017.
- A decline of 8 points (6.2%) was observed during this period.
- Figure has declined from 167 in 2011-2013 to 130 in 2014-2016 and to 122 in 2015-17.
- Government has categorized States into three groups: empowered action group (EAG), southern States and other States to understand maternal mortality rates better.
- The decline is important for India as 11 States have achieved the National Health Policy target of MMR 100 per lakh live births well ahead of 2020.
- Reasons behind it :
- Increase in institutional deliveries
- Focused approach towards aspirational districts
- Inter-sectoral action to reach the most marginalized and vulnerable mothers.
- Focus on quality and coverage of health services through public health initiatives under the National Health Mission such as LaQshya.
- Other schemes like Poshan Abhiyan, Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan, Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram, Janani Suraksha Yojana and Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana have contributed to this decline.
- Not a single mother or newborn dies due to a preventable disease.
- Move towards zero preventable maternal and newborn deaths through the recently launched Surakshit Matritva Aashwasan Initiative (SUMAN).
- WHO said that progress puts the country on track towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target of an MMR below 70 by 2030.
It is measured as the number of maternal deaths per lakh live births.
- The Sample Registration System (SRS) is a large-scale demographic survey for providing reliable annual estimates of Infant mortality rate, birth rate, death rate and other fertility & mortality indicators at the national and subnational levels.
- It comes under Registrar General of India.
The major causes of maternal deaths as per RGI-SRS (2001-03) are :
- Hemorrhage: 38% occur mainly because of post-partum Hemorrhage.
- Sepsis: 11%, because of any infection during pregnancy, labor and in post-partum period.
- Abortion: 8%, because of unsafe abortions.
- Hypertensive disorders: 5%, because of High Blood pressure during pregnancy.
- Obstructed labor: 5%
- Other causes: 34%- includes anaemia and various other causes
- Promotion of institutional deliveries through Janani SurakshaYojana (JSY).
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram (JSSK) entitles all pregnant women delivering in public health institutions to absolutely free and no expense delivery, including caesarean section.
- Maternal Death Review (MDR) is being implemented across the country both at facilities and in the community.
- Under National Iron Plus Initiative (NIPI), through life cycle approach, age and dose specific IFA supplementation programme is being implemented.
- Launch of India Newborn Action Plan (INAP) with an aim to reduce neonatal mortality and stillbirths to single digit by 2030.
- Universal Immunization Programme (UIP): Vaccination protects children against preventable diseases.
- Nutritional Rehabilitation Centres (NRCs) have been established for management of severe acute malnutrition in children.
Union government decided to import onion as its efforts to increase supply by banning exports and setting stock limits for retailers and traders also failed to tame prices.
- Public sector trading agency Metals and Minerals Trading Corporation of India (MMTC) has been requested to immediately import a substantial amount of onions from Dubai and other countries.
- A team of officials of MMTC, National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED), the Department of Agriculture and the Department of Consumer Affairs has been directed to visit Turkey and Egypt on an urgent basis to take stock of the supplies in these countries and facilitate imports.
- Until November 30, the phytosanitary and fumigation norms have also been liberalised.
- NAFED is taking steps to speed up its domestic procurement, especially from Alwar in Rajasthan.
- Earlier government had imposed stock limits on onion traders to facilitate release of stocks in the market and prevention of hoarding by traders.
- Government has asked the State Governments to enforce the stock limits strictly and carry out anti-hoarding operations against the unscrupulous traders by organising raids.
- Government has created buffer stocks and released it to maintain price.
- In the Union Budget 2018-19, a new Scheme “Operation Greens” was announced on the line of “Operation Flood”, with an outlay of Rs.500 crores to promote Farmer Producers Organizations (FPOs), agri-logistics, processing facilities and professional management. Accordingly, the Ministry has formulated a scheme for integrated development of Tomato, Onion and Potato (TOP) value chain.
- The scheme will have two-pronged strategy of Price stabilisation measures (for short term) and Integrated value chain development projects (for long term)
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-national/norms-eased-for-onion-imports/article29927807.ece
Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal has briefed the Union Council of Ministers on the country’s decision not to join the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
- The threat of circumvention of Rules of Origin due to tariff differentials.
- A long-standing request of India that the base rate of customs duty be changed from 2014 to 2019.
- A request was also made for tariff lines to be on an auto-trigger safeguard mechanism along with a review clause at a periodicity of three, as India’s experience with free trade agreements (FTAs) has been that it often leads to huge import surges.
- An exclusion of Most Favoured Nation (MFN) obligations was sought in the investment chapter. Having MFN for all RCEP members means that without adequate safeguards, the RCEP could end up being an FTA with China through the back door with a huge trade deficit on the Indian side.
Nearly half of the government-owned listed companies are yet to comply with the minimum public shareholding norms that at least 25% stake should be held by the public
- Government, in the Union Budget early this year, proposed increasing the minimum public holding in all listed entities to 35% from the current 25% limit.
- The capital markets regulator mandated the current 25% minimum public shareholding norm way back in 2010.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the Regulator for the Securities market in India owned by Government of India.
- This statutory body was established through the SEBI Act, 1992.
- SEBI has to be responsive to the needs of three groups, which constitute:
- Issuers of securities
- Investors
- Market intermediaries

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved