



Recent reports have shown that more than 10 women die every day due to unsafe abortions in India and backward abortion laws only contribute to women seeking illegal and unsafe options.
Recently cabinet approved amendment in the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971 (MTP Act).
- It divides the whole pregnancy period into three phases.
- Phase 1 is up to 12 weeks where abortion can be sought with the advice of a single medical practitioner. The reason of abortions lies to threat to life for mother as well for child.
- Phase 2 is from 12 to 20 week where abortion can be sought with the advice of two medical practitioners. The reason of abortions lies to threat to life for mother as well for child.
- Beyond 20 weeks, termination may be carried out where it is necessary to save the life of the pregnant woman.
- This act also includes grave incidences like pregnancy arising out of rape or pregnancy arising out of the failure of contraceptives
- The act is bias against unmarried women as it allows only married women to abort in case of failure of contraceptives.
- It doesn’t give decision making powers related to abortion to women. It restricts autonomy of women.
- Abortion beyond 20 weeks are not allowed even in case of detection of foetal abnormalities. It puts additional burden on women.
- The Supreme Court has recognised women’s right to make reproductive choices and their decision to abort as a dimension of their personal liberty (in Mrs. X v. Union of India, 2017)
- It has recognized right of women for undertaking reproductive choices falling within the realm of the fundamental right to privacy (in K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India, 2017).
- It does not allow abortion on request.
- Extension of time period for abortion from 20 week to 24 week only in case of grave injuries like rape survivor or victim of incest.
- It doesn’t address biasness against unmarried women.
However, The MTP amendment bill provide a critical juncture where a foetus with abnormalities can be aborted based on recommendation of a medical board.
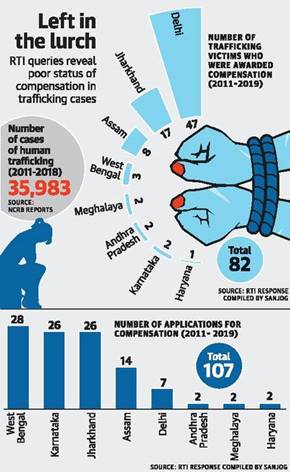
- Between March 2011 and April 2019 only 82 human trafficked victims were awarded compensation.
- However, between 2011 and 2018, the total number of cases of human trafficking recorded in the country, according to NCRB reports, was 35,983.
- Among the 82 survivors who were awarded compensation, only 77 received the relief amount.
- The study also suggests grave inconsistencies on the part of legal services authorities, which have provided the data. Delhi records show more survivors receiving compensation than those awarded compensation.
- There remains a lack of information provided to survivors on victim compensation
- Lack of initiative on the part of legal services authority
- Low investment on part of legal aid that results in very few survivors having access to compensation.
- From their rescue till rehabilitation, the survivors are in touch with multiple agencies but none of them take any steps to help them get compensation.
- The Section 357-A of Code of Criminal Procedure has provisions to compensate victims who suffered because of a crime.
- In 2012, following the national outrage over the Nirbhaya gang-rape and murder case, the government announced ₹1,000 crore fund to be used to combat sexual violence against persons – children or adults.
- Part of the Nirbhaya fund is being used in the Victim Compensation Scheme – a national scheme to compensate survivors of rape, acid burns and trafficking among other forms of violence — for the last few years.
- The amount of compensation to victims of trafficking varies from State to State.
- In 2018, the Supreme Court directed NALSA (National Legal Services Authority) to frame a standardised victim compensation scheme.
- The government has introduced a Central Victim Compensation Fund (CVCF) scheme, with an initial corpus of Rs 200 crores, to enable support to victims of rape, acid attacks, human trafficking and women killed or injured in the cross border firing.
- To support and supplement the existing Victim Compensation Schemes notified by States/UT Administrations.
- To reduce disparity in quantum of compensation amount notified by different States/ UTs for victims of similar crimes.
- To encourage States/UTs to effectively implement the Victim Compensation Schemes (VCS) notified by them under the provisions of section 357A of Cr.P.C.
- The government wants to increase indigenous production in the Defence sector up to 70% and reduce imports.
- They are looking for innovations in defence technology and are ready to support them.
- In 2020-2021, five to six two GWh battery-manufacturing plants would come up and NITI Aayog was ready encourage those who come up with proposals.
- India is also considering getting lease of lithium mines abroad so that manufacturing cells will be easy, which costs 40% of the battery.
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is an agency of the Government of India, charged with the military's research and development, headquartered in New Delhi, India.
- It was formed in 1958 by the merger of the Technical Development Establishment and the Directorate of Technical Development and Production of the Indian Ordnance Factories with the Defence Science Organisation.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- DRDO's pursuit of self-reliance and successful indigenous development and production of strategic systems and platforms such as Agni and Prithvi series of missiles; light combat aircraft, Tejas; multi-barrel rocket launcher, Pinaka; air defence system, Akash; a wide range of radars and electronic warfare system.
- India has quadrupled its imports of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries.
- More than tripled its import bill on the product.
- 175 million such batteries were imported in 2016, 313 million in 2017, 712 million in 2018 and 450 million from January 1, 2019, till November 30.
- The cost of these imports rose from $383 million (₹2,600 crores approx) in 2016 to $727.24 million (₹5,000 crore approx.) in 2017, $1254.94 million (₹8,700 crore) in 2018 and $929 million (₹6,500 crore) in 2019.
- Indian manufacturers source Li-ion batteries from China, Japan and South Korea.
Roadmaps:
- A phased roadmap to implement battery manufacturing at Giga-scale will be considered with initial focus on large-scale module and pack assembly plants by 2019-20, followed by integrated cell manufacturing by 2021-22.
- Details of the PMP for Batteries shall be formulated by the Mission. The Mission will ensure holistic and comprehensive growth of the battery manufacturing industry in India.
- The Mission will prepare the necessary roadmap that will enable India to leverage upon its size and scale to produce innovative, competitive multi-modal mobility solutions that can be deployed globally in diverse contexts.
- The Mission will define the roadmap for transformative mobility in “New India” by introducing a sustainable mobility ecosystem and fostering Make-in-India to boost domestic manufacturing and employment generation in the country.
Impact:
- The Mission will drive mobility solutions that will bring in significant benefits to the industry, economy and country.
- These solutions will help improve air quality in cities along with reducing India’s oil import dependence and enhance the uptake of renewable energy and storage solutions.
- The Mission will lay down the strategy and roadmap which will enable India to leverage upon its size and scale to develop a competitive domestic manufacturing ecosystem for electric mobility.
- The actions in this regard will benefit all citizens as the aim is to promote ‘Ease of Living’ and enhance the quality of life of our citizens and also provide employment opportunities through ‘Make-in-India’ across a range of skillsets.
- A lithium-ion battery or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery.
- Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used for portable electronics and electric vehicles and are growing in popularity for military and aerospace applications.
- Li-ion batteries use an intercalated lithium compound as the material at the positive electrode and typically graphite at the negative electrode.
- The batteries have a high energy density, no memory effect and low self-discharge.
- Decided to promote turmeric cultivation by replacing prohibited cannabis cultivation while all nine gram panchayats will be covered under integrated farming.
- Government will follow bottom up approach of development to enhance participation in the schemes.
- Implementation of the Forest Rights Act (FRA) will be given priority before embarking on path of development.
- Approval and sanction of community forest rights (CFR) and individual forest rights (IFR) under the FRA will be taken up in the mission mode.
- The government will emulate model of Maharashtra where CFR has been granted in expeditious manner for making tribal is partners in development.
- A plan has been mooted to install lift irrigation points to make irrigation facilities available round the year.
- Odisha government constructed a bridge to end the remoteness of the region.
- Security forces provide protection to lay roads in the region.
To combat the LWE menace in a holistic manner, Government of India formulated a National Policy and Action Plan in January 2015, which envisages a multi pronged approach comprising security measures, development measures, ensuring Rights and Entitlements of local communities etc.
- Deployment of CAPF Battalions,
- Provision of helicopter and UAVS
- Sanction of India Reserve Bns (IRBS)/Special India Reserve Bns (SIRBS)
- Funds are provided under Modernisation of Police Force (MPF), Security Related Expenditure (SRE) Scheme and Special Infrastructure Scheme (SIS) for capacity building of State Police, intelligence agencies and Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFS).
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) to be reviewed to ensure effective choking of fund flow to LWE groups.
- Fast tracking building infrastructure, with a focus on solar lights, mobile towers with 3G connectivity, and road-rail connectivity.
- Indian Army or specialized forces - such as Greyhounds - to train forces to take on Naxals.
- Two Skill Development related Schemes, namely, ‘ROSHNI’ and ‘Skill Development in 34 Districts affected by Left Wing Extremism’ are being implemented by the Ministry of Rural Development and Ministry of Labour and Employment respectively.
- Under Integrated action plan government is creating public infrastructure and services.
- Targeted implementation of forest rights act have brought trust among the local population.
- MGNREGA have been useful in enhancing the income opportunities for local population thus effectively negating Naxalites propaganda.
- Government sustained focus by creating health and education opportunities for poor tribals have been successful in bringing them back to normal course.
- Incidents of violence have seen a 20% decline with a 34% reduction in related deaths in 2017 as compared to 2013.
- The geographical spread of LWE violence also shrunk from 76 districts in 2013 to just 58 districts in 2017.
- Besides, just 30 of these districts account for 90% of the LWE violence in the country.
India’s first ‘darknet’ narcotics operative held by the central anti-narcotics agency under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act.
- Darknet refers to the deep hidden internet platform that is used for narcotics sale, exchange of pornographic content and other illegal activities by using the secret alleys of the onion router (ToR) to stay away from the surveillance of law enforcement agencies.
- Owing to its end-to-end encryption, darknet is considered very tough to crack when it comes to investigating criminal activities being rendered over it.
- The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) is the nodal drug law enforcement and intelligence agency of India responsible for fighting drug trafficking and the abuse of illegal substances.
- It was created for the full implementation of The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 and fight its violation through the Prevention of Illicit Trafficking in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1988.
- Drugs follow disposable income. People started taking cocaine to reduce workload stress and anxiety.
- Poor people engage in low cost tobacco consumption leading to spread of cancer, posh people engage in Opium, Heroin and LSD.
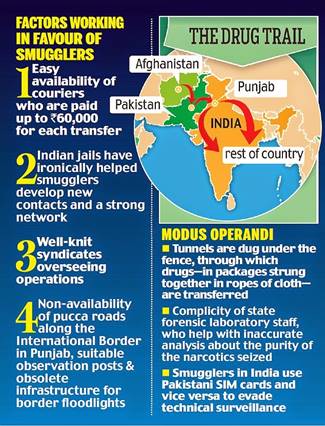
- India is in the middle of two major illicit opium production region in the world the Golden Crescent (Iran-Afghanistan-Pakistan) in the west and the Golden Triangle (South-East Asia) in the east.
- Deep web platforms allowing usage of crypto-currencies have deepened the drug network.
- Latin American cartels are also increasing their presence in South Asia to benefit from increased drug trade.
- Money from drugs are used in financing terrorism like Taliban, terrorism in Kashmir.
- Porous border, corruption in police services, human trafficking further provide impetus to drug trafficking.
- Many illegal pharma companies also engage in production of illicit drugs.
- Increases terrorism, human trafficking.
- Affects peace and stability of the country.
- Places a heavy burden on public Health system.
- Reduces potential and spirt of the youth.
- It diverts precious economic resources, weakens the family structure and weaken the demographic dividend.
- Enacted legislation such as the Narcotics Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS)
- Focus on physical security of the borders and coasts by strengthening patrolling and surveillance
- Seizing of the drugs by law enforcement agencies.
- Arrest of foreign nationals in drug related cases.
- Revived the scheme of “Financial Assistance to States for Narcotics Control”.
- Constituted Narco-Coordination Centre (NCORD).
- Signed Bilateral Agreements/Memoranda of Understanding with neighbouring countries to deal with drug menace.
- Government has scheduled 07 new substances into the list of Narcotic drugs in the year 2017 so that action can be taken against trafficking in these substances.
- Proper Financial investigation in each narcotic case to stop the inflow of money into economic system.
- Co-operating with voluntary organizations in the endeavour to prevent abuse of narcotics and synthetic drugs.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved