



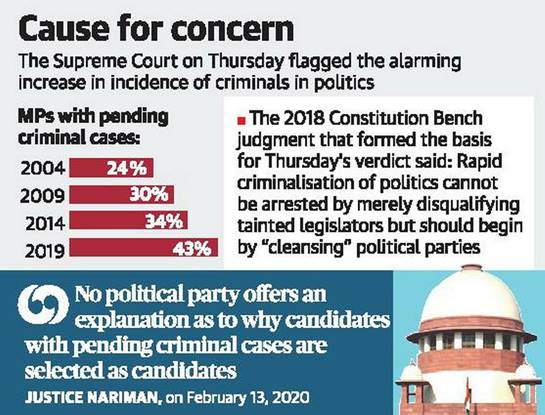
Publish criminal history of candidates, SC orders parties
The Court also issued the following directions in exercise of our constitutional powers under Articles 129 and 142 of the Constitution of India
- It shall be mandatory for political parties [at the Central and State election level] to upload on their website detailed information regarding individuals with pending criminal cases (including the nature of the offences, and relevant particulars such as whether charges have been framed, the concerned Court, the case number etc.) who have been selected as candidates, along with the reasons for such selection, as also as to why other individuals without criminal antecedents could not be selected as candidates.
- The reasons as to selection shall be with reference to the qualifications, achievements and merit of the candidate concerned, and not mere "winnability" at the polls.
- This information shall also be published in:
(a)One local vernacular newspaper and one national newspaper;
(b)On the official social media platforms of the political party, including Face book& Twitter.
- These details shall be published within 48 hours of the selection of the candidate or not less than two weeks before the first date for filing of nominations, whichever is earlier.
- The political party concerned shall then submit a report of compliance with these directions with the Election Commission within 72 hours of the selection of the said candidate.
- If a political party fails to submit such compliance report with the Election Commission, the Election Commission shall bring such non-compliance by the political party concerned to the notice of the Supreme Court as being in contempt of this Court's orders/directions.
Court observed that In 2004, 24% of the Members of Parliament had criminal cases pending against them; in 2009, that went up to 30%; in 2014 to 34%; and in 2019 as many as 43% of MPs had criminal cases pending against them.
- No law should provide protective shield to the corrupt public official and court is taking proactive steps to mitigate the abuse of law by criminals to enter the electoral system.
- Free, fair and transparent representation is key for success of democracy and Supreme Court is custodian to protect the constitution.
- With government reluctancy in framing a law to bar the criminals entry in the democracy, it is court where the people can find the last resort.
- Supreme Court interventions cannot be held as biased in nature as a political party intervention can be.
- Supreme Court follows the rationality in framing its guidelines. Its approach has been of reforming political parties along with information available with the voters.
- The Supreme Court judgment of May 2, 2002 mandated that candidates disclose their criminal antecedents, if any, as also their financial and educational background.
- In Ramesh Dalal vs. Union of India 2005, the Supreme Court held that a sitting Member of Parliament (MP) or Member of State Legislature (MLA) should also be subject to disqualification from contesting elections if he is convicted and sentenced to not less than 2 years of imprisonment by a court of law.
- The Supreme Court in Lily Thomas vs. Union of India 2013 held Section 8(4) as unconstitutional and void. Hence, now if a sitting member of Parliament or state legislature is convicted and sentenced to not less than 2 years of imprisonment, he will get immediately disqualified from being member of house.
- Supreme Court held that a voter could exercise the option of negative voting and reject all candidates as unworthy of being elected. The voter could press the ‘None of the Above’ (NOTA) button in the electronic voting machine (EVM).
- The order did not stand judicial scrutiny in terms of the parameters laid down by the Supreme Court.
- City Police Commissioner, discharging his duty as the District Magistrate (DM) had failed to give “reasons” for invoking section 144 against CAA.
- The order should not be construed to mean that the State is helpless to invoke the prohibitory order if the situation so warrants.
- The orders of restriction issued under Section 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (Cr.PC) could not be used as a tool to suppress legitimate expressions, opinions and grievances in a democracy.
- Orders issued under Section 144 should explain restrictions imposed in anticipation of a threat to law and order or to prevent loss of life and property.
- Divergent views and disapproval of government action could not lead to imposition of Section 144.
- The power was meant to be used only in case of public emergency or in the interest of public safety.
- Magistrates could not apply a strait-jacket formula without assessing the objective and material facts.
A plan to restore and preserve the nearly 800-year-old Konark Sun temple in Odisha would be drawn up soon.
- It is a world heritage site declared under UNESCO.
- The temple at Konark is a monumental representation of the sun god Surya's chariot.
- Built in the 13th century, it is one of India's most famous Brahman sanctuaries.
- Its 24 wheels are decorated with symbolic designs and it is led by a team of six horses.
- The Sun Temple is the culmination of Kalingan temple architecture, with all its defining elements in complete and perfect form.
- The temple represents a chariot of the Sun God, with twelve pairs of wheels drawn by seven horses evoking its movement across the heavens.

‘Future of Earth, 2020’ report:
- It is released by ISRO.
- It enlists five global risks:
- Climate change mitigation and adaptation;
- Extreme weather events;
- Major biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse;
- Food crises;
- Water crises
- The report was prepared with an aim of reducing carbon footprint and halting global warming below 2 degree Celsius by 2050.
- Humans have now “significantly altered” 75% of our planet’s land area;
- About a quarter of species in assessed plant and animal groups are threatened.
- Right-wing populism, a breed of politics that exploits people’s fears during times of economic decline and growing inequality, and that focuses on nationalist tendencies to clamp down on borders and reject immigrants. It represents denial of climate change.
- Extreme heat waves can accelerate global warming by releasing large amounts of stored carbon from affected ecosystems.
- The loss of biodiversity also weakens the capacity of natural and agricultural systems to cope with climate extremes, increasing our vulnerability to food crises.

The Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) has published a notice, amending lists of developing and least-developed countries that are eligible for preferential treatment with respect to CVD investigations.
- Countries not given special consideration have lower levels of protection against a CVD investigation.
- A CVD investigation must be terminated if the offending subsidy is de minimis (too small to warrant concern) or if import volumes are negligible.
- The de minimis thresholds and import volume allowance are more relaxed for developing and least-developed countries.
- India, along with Brazil, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam were taken off the list since they have at least a 0.5% share of the global trade, despite having less than $12, 375 GNI (the World Bank threshold separating high income countries from others).
- India was taken off the list also because — like Argentina, Brazil, Indonesia and South Africa — it is part of the G20.
- Per capita Gross National Income or GNI
- Share of world trade
- Other factors such as organisation for economic co-operation and development (OECD) membership or application for membership, EU membership, and group of Twenty (G20) membership.
The Fifteenth Finance Commission will soon set up a panel to address issues related to fiscal policy for both the Centre and the States and present a road map for the same.
- Constituted a group on defence and internal security which has mandates:
- Fiscal panel will address the issue related to the debt and the deficit of the States as well as the Central government.
- It will have a fiscal road map that covers the Centre and the State government.
- The panel will be headed by Mr. Singh and have representation from the Comptroller and Auditor General of India, the Reserve Bank of India, the Ministry of Finance, the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) panel and some of the States.
- There was not a need for a new legal framework as the FRBM already gives a robust legal framework.
The first high-speed patrol boat being built for Vietnam under the $100-million Line of Credit (LoC) will be delivered by September.
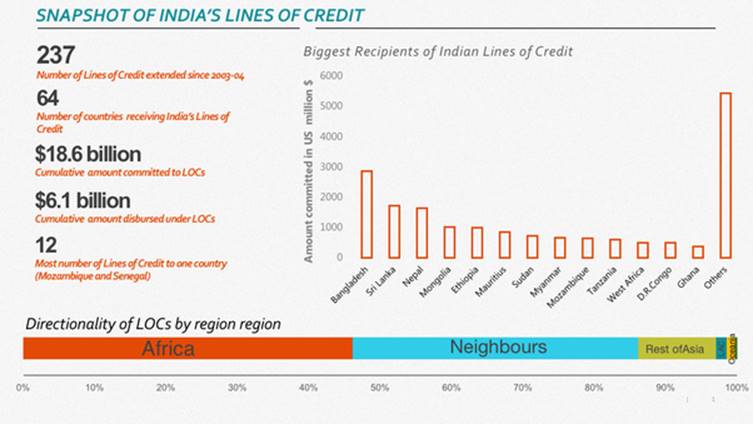
- A LOC is a ‘soft loan’ (not a grant) provided at concessional interest rates to developing countries.
- It has to be repaid by the borrowing government.
- It serves the foreign policy aim by increasing Indian presence in other geographies.
- It has a contract where 75% of the goods need to be purchased from India leading to enhancement of Make in India.
The Union Health Ministry has notified medical equipment used on humans as drugs under Section 3 of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act with effect from April 1, 2020.
- It requires online registration of these devices from the Central Licensing Authority, through an identified online portal established by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation for this purpose.
- A large number of commonly used items including hypodermic syringes and needles, cardiac stents, perfusion sets, catheters, orthopaedic implants, bone cements, lenses, sutures, internal prosthetic replacements etc are covered under the new rules.
- Faulty hip implantation by Johnson & Johnson had made government to take strict actions against faulty equipments. It required regulation of medical devices.
- Ensure that all medical devices meet certain standards of quality and efficacy.
- The notification will also make medical device companies accountable for quality and safety of their products.
- Manufacture or sale of substandard items is punishable with imprisonment of at least 10 years, which may extend to imprisonment for life.
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 is an act of the Parliament of India, which regulates the import, manufacture and distribution of drugs in India.
- The primary objective of the act is to ensure that the drugs and cosmetics sold in India are safe, effective and conform to state quality standards.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved