



Madhya Pradesh grapples with spiralling neonatal deaths
Recently when police slapped sedition charges on a school in Bidar, Karnataka, spotlight has been on reports that the police questioned the children.
- The Karnataka State Commission for Protection of Child Rights has pulled up the district police for violations, including repeated questioning of the children.
- A public interest petition has been filed in the Karnataka High Court seeking a departmental inquiry against the policemen who allegedly questioned the children.
- How do the law in India and resolutions of the UN address the issue of questioning children?
- What are the safeguards for children being made witnesses?
- Convention on the Rights of the Child since 1992: In all actions concerning children, whether undertaken by public or private social welfare institutions, courts of law, administrative authorities or legislative bodies, the best interests of the child shall be a primary consideration.
- United Nations: Justice in Matters involving Child Victims and Witnesses in Crime: Model Law provides that authorities treat children in a caring and sensitive manner, with interview techniques that “minimise distress or trauma to children”.
- The investigator shall avoid repetition of the interview during the justice process in order to prevent secondary victimisation of the child.
- Under Section 118 of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872, there is no minimum age for a witness.
- Children as young as three years old have deposed before trial courts in cases of sexual abuse.
- Trials involving children as witnesses have primarily been in cases of child sexual abuse.
Delhi High Court guidelines:
- A vulnerable witness is defined as anyone who has not completed 18 years of age.
- It underlines the importance of the criminal justice system needing to respond proactively, sensitively and in an age-appropriate manner when dealing with children.
Juvenile Justice Act:
- Police should not be in its uniform while interviewing a child.
- Interviews of children be done by specialised units of police who are trained to sensitively deal with them.
- A Special Juvenile Police Unit is to be constituted by the state government in each district and city, headed by a police officer not below the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police, and including two social workers, at least one of whom must be a woman, and both of whom should be experienced in the field of child welfare.
- The Act also provides for a Child Welfare Committee in every district to take cognisance of any violations by the authorities in their handling of children.
POSCO act:
- The Act states that interviews should be conducted in a safe, neutral, child-friendly environment, including allowing them to be conducted from homes.
- It says a child should not be made to recount the incident in question multiple times.
- The Act also allows for a support person, who could be trained in counselling, to be present with the child to reduce stress and trauma.
Reference: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-child-witness-bidar-sedition-case-6271393/
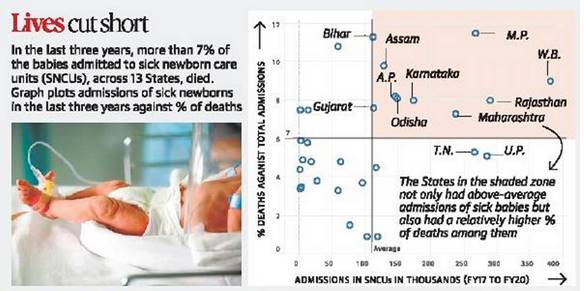
- Madhya Pradesh has recorded the highest percentage of newborn deaths of 11.5% against the total admissions to government-run sick newborn care units (SNCUs) in the past three years across the country.
- Staff crunch
- Low community referrals
- Absence of a special neonatal transport service to health centres
- The non-availability of enough units to cater to increasing institutional deliveries.
- There is a dedicated service to transport pregnant women to hospitals from remote areas, there is none for neonates, who are mostly dependent on the 108 ambulance service.
- Several districts had under-reported deaths as well.
- The National Health Mission (NHM) was launched by the government of India in 2013 subsuming the National Rural Health Mission and National Urban Health Mission.
- It was further extended in March 2018, to continue until March 2020.
- It is headed by Mission Director and monitored by National Level Monitors appointed by Government of India.
- Community Health volunteers called Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) have been engaged under the mission for establishing a link between the community and the health system.
- ASHA Programme is expanding across States and has particularly been successful in bringing people back to Public Health System and has increased the utilization of outpatient services, diagnostic facilities, institutional deliveries and inpatient care.
- The Rogi Kalyan Samiti (Patient Welfare Committee) / Hospital Management Society is a management structure that acts as a group of trustees for the hospitals to manage the affairs of the hospital.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women and to reduce neo-natal mortality and maternal mortality.
- It is operated under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare as part of the National Rural Health Mission.
- It provides cash benefit to eligible pregnant women if they choose to deliver in a health facility, irrespective of their age and the number of children they have.
- Free ambulance services are provided in every nook and corner of the country connected with a toll free number and reaches within 30 minutes of the call.
- It was introduced to provide free to and fro transport, free drugs, free diagnostic, free blood, and free diet to pregnant women who come for delivery in public health institutions and sick infants up to one year.
- The CMS is an environmental treaty of the UN (UNEP) that provides a global platform for the conservation and sustainable use of migratory animals and their habitats.
- It is the only global convention specialising in the conservation of migratory species, their habitats and migration routes.
- The pact was signed in 1979 in Germany and is known as the Bonn Convention.
- CMS brings together the States through which migratory animals pass, the Range States, and lays the legal foundation for internationally coordinated conservation measures throughout a migratory range.
- India is a temporary home to several migratory animals and birds.
- The important among these include Amur Falcons, Bar-headed Geese, Black-necked cranes, Marine turtles, Dugongs, Humpbacked Whales, etc.
- The Indian sub-continent is also part of the major bird flyway network, i.e., the Central Asian Flyway (CAF) that covers areas between the Arctic and Indian Oceans, and covers at least 279 populations of 182 migratory water-bird species, including 29 globally threatened species.
- India has also launched the National Action Plan for the conservation of migratory species under the Central Asian Flyway”.
Reference: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/convention-of-migratory-species-india-6271330/
The Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (WWS), though home to more than half the number of tigers present in Kerala, may not be notified as a tiger reserve as the proposal lacks public support.
- Would ensure financial aid from the Centre and the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA),
- Better conservation and management of the tiger population
- Help generate more employment opportunities failed to impress the state authorities.
- Lack of Public support
- Notification would bring in stringent restrictions on development activities in the district.

- Guwahati (Assam) has yielded a new species of lizard – the urban bent-toed gecko.
- It is markedly different in molecular structure, blotch and colour from the Cyrtodactylusguwahatiensis, or the Guwahati bent-toed gecko, that was discovered two years ago.
- Though the urban bent-toed gecko falls within the khasiensis group, it differs from other members of this group in mitochondrial sequence data as well as aspects of morphology such as the number and arrangement of certain pores in males, the number of mid-ventral scales and colour pattern.
- Mukurthi National Park (MNP) is a 78.46 km2 (30.3 sq mi) protected area located in the western corner of the Nilgiris Plateau west of Ootacamund hill station in the northwest corner of Tamil Nadu state in the Western Ghats mountain range of South India.
- The park was created to protect its keystone species, the Nilgiri tahr.
- The park is characterised by montane grasslands and shrub lands interspersed with sholas in a high altitude area of high rainfall.
- It is home to an array of endangered wildlife, including Royal Bengal tiger and Asian elephant, but its main mammal attraction is the Nilgiri tahr.
- The park is a part of Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, India's first International Biosphere Reserve.
- Construction of fire lines: Fire lines are described as an artificially formed break in foliage or forest cover to control the spread of wildfires by limiting the amount of combustible vegetation available.
- No cool burning: It is done in a controlled manner by artificially creating small, localised fires to limit the amount of vegetation available in any given area, meaning any fires that occur during the summer will not have any build-up of “vegetative fuel” to use to become a large, uncontrollable fire.
- The removal of invasive trees, such as wattle is also set to be stepped up in the national park.
- It is a Geo Imaging Satellite.
- It will be the first of two planned Indian Earth observatory (EO) spacecraft to be placed in a geostationary orbit of around 36,000 km.
- It will apparently be in a fixed spot looking over the Indian continent at all times.
- All Indian EOs have been placed so far in a 600-odd-km orbits and circle the earth pole to pole.
- With this satellite, which has high-resolution cameras, we can keep a constant watch on our borders, monitor any changes in the geographical condition of the country.
- Exploring the feasibility of a joint venture in India for the production of various sub systems of “air defence missile systems like Tunguska, Kavadrat, the OSA-AKA, Pechora air defence system as well as the Shilka self-propelled air defence gun system”.
- Agreements on emerging technologies — Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, block chain and robotics based on Russian technologies
- They come under the Intergovernmental Agreement (IGA) on joint manufacturing of spares in India signed last September for mutual cooperation in manufacturing of spares, components, aggregates and other material related to Russian or Soviet-origin arms and defence equipment.
- The issue of [Jammu and Kashmir] that needs to be addressed is that of vacation of the territories illegally and forcibly occupied by Pakistan.
- Further issues, if any, would be discussed bilaterally.
- There is no role or scope for third party mediation.
- He had offered his offices and was “ready to help if both countries agree for mediation.
- Guterres was “deeply concerned” about situation in Kashmir and called on India and Pakistan to “de-escalate, both militarily and verbally”.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved