



Guaranteeing healthcare, the Brazilian way
As Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro visits New Delhi this Republic Day, one interesting field of cooperation to explore in the strategic partnership is healthcare.
- The Brazilian society achieved universal coverage by establishing a government-funded system.
- More than 100 million inhabitants have a universal health system.
- The Family Health Programme (Programa Saúde da Família), which relies on a community-based healthcare network, is the backbone of the rapid expansion of coverage in Brazil.
- The Unified Health System (SUS), which guaranteed free health coverage that included pharmaceutical services, has been written into the new Constitution in 1988.
- Life expectancy has increased from 64 years to almost 76 years, while Infant Mortality Rate has declined from 53 to 14 per 1,000 live births.
- Polio vaccination has reached 98% of the population.
- 95% of those that seek care in the SUS are able to receive treatment.
- Every year, the SUS covers more than two million births, 10 million hospital admissions and nearly one billion ambulatory procedures.
- Brazil spends only 3.8% of its GDP on the SUS, serving a population three times larger than that of the U.K, while UK spends 8% of its GDP on NHS.
- Health promotion and prevention activities
- Oversee whether family members are complying with any treatment they might be receiving
- Effectively manage the relationship between citizens and the healthcare system.
- Help to drastically reduced IMR and increases adult labour supply.
- Accessibility of services to the rural areas and poorest states of the country.
- Public health expenditure is still very low in India, at around 1.3% of GDP in the 2017-2018 fiscal years. It needs to be enhanced.
- One-size-fits-all approach for such heterogeneous regional realities is inconceivable; hence, region specific approach needs to be imagined.
- Regional disparities in terms of resources and institutional capabilities must be addressed.
Court convicted Thakur of aggravated sexual assault under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, gang rape, rape and other related offences under the Indian Penal Code and the Juvenile Justice Act.
Objective:
- Effectively address the heinous crimes of sexual abuse and sexual exploitation of children through less ambiguous and more stringent legal provisions.
- It defines a child as any person below eighteen years of age.
- It regards the best interests and well-being of the child as being of paramount importance at every stage, to ensure the healthy physical, emotional, intellectual and social development of the child.
- The offence is considered graver if it is committed by a police officer, public servant, any member of the staff at a remand home, protection or observation home, jail, hospital or educational institution, or by a member of the armed or security forces.
- The Act incorporates child friendly procedures for reporting, recording, investigation and trial offences.
- The Act provides for stringent punishments, which have been graded as per the gravity of offence.
- It defines different forms of sexual abuse, including penetrative and non-penetrative assault, as well as sexual harassment and pornography.
- It empowers the NCPCR and State Commission for Protection of Child Rights for monitoring the implementation of the provisions of this Act in such manner as may be prescribed.
Recently, government has brought amendments to make punishment more stringent for committing sexual crimes against children including death penalty. The amendments also provide for levy of fines and imprisonment to curb child pornography.
- The amendment is expected to discourage the trend of child sexual abuse by acting as a deterrent due to strong penal provisions incorporated in the Act.
- It intends to protect the interest of vulnerable children in times of distress and ensures their safety and dignity.
- The amendment is aimed to establish clarity regarding the aspects of child abuse and punishment thereof.
The Hindu Group is STEP, an online certification course, has been selected by the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) and All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) to be a part of the government’s National Educational Alliance for Technology (NEAT) programme.
- It is a certification course initiated by The Hindu.
- It is recognised for its use of Artificial Intelligence in improving language-learning outcomes for students.
- It aims for using technology for better learning outcomes in Higher Education.
- The objective is to use Artificial Intelligence to make learning more personalised and customised as per the requirements of the learner.
- There are a number of start-up companies developing this and MHRD would like to recognise such efforts and bring them under a common platform so that learners can access it easily.
- MHRD would act as a facilitator to ensure that the solutions are freely available to a large number of economically backward students.
- EdTech companies would be responsible for developing solutions and manage registration of learners through the NEAT portal.
- They would be free to charge fees as per their policy.
- As their contribution towards the National cause, they would have to offer free coupons to the extent of 25% of the total registrations for their solution through NEAT portal.
- MHRD would distribute the free coupons for learning to the most socially/economically backward students.
- AICTE would be the implementing agency for NEAT programme.
- Independent Expert Committees would be constituted for evaluating and selecting the EdTech solutions.
There is a recent controversy concerning the Kerala government’s move to challenge the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019. Kerala Governor Arif Khan has sought a report from the State government on why it chose to sue the Centre in the Supreme Court under Article 131 without first informing him.
- Governor is a formal head. The real executive powers are vested in the Council of Ministers, who is collectively responsible to the legislature.
- Even Article 167, under which information is sought by the Governor [from the Chief Minister], does not have dictatorial overtones as the Sarkaria Commission on Centre-State relations has held.
- Kerala’s suit will stand or fall on its own merits and not because of want of sanction from the Governor.
- There is no such constitutional convention.
- The State has filed this suit against the Centre. The Governor is the representative of the Union. Why should he be consulted beforehand?
- In case of an important legislation, normally the State government may apprise the Governor as a form of courtesy.
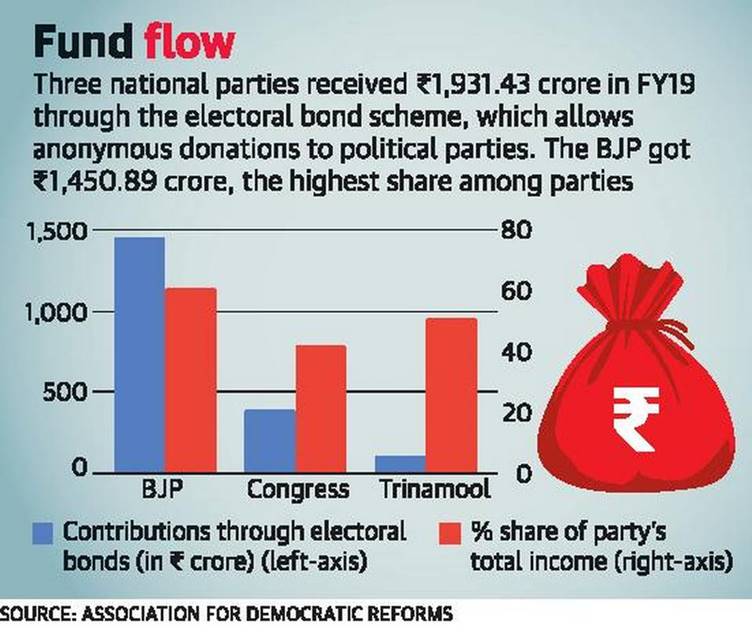
- Earlier, court passed an interim order directing political parties to provide complete information to the ECI in sealed covers on every single donor and contribution received by them until date through electoral bonds.
- However, it did not stay the operation of the scheme.
- If the matter has been argued for stay and it was not granted, we will also not grant it.
- The problem with these instruments is that, while the information of the person who is buying bond is known (to the bank); the donors’ identity is not known.
- A person, who buys the bond, can give it to another person who actually donates it to a political party and there is no record of the person who takes it from the person who buys it.
- Therefore, any person who wants to hide his identity can make some other person buy it and give it to him.
- It has almost become like the currency.
- There are possibilities of making electoral bonds a convenient channel for black money. The following provisions are controversial in that sense:
- Doing away with the 7.5% cap for corporate donations.
- No need for companies to reveal their political contributions in their profit and loss statements.
- Other Political Parties were not consulted.
- Individual candidates and new political parties would not be able to receive donations under the scheme, as there is a requirement of 1% vote share.
- The Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) also objected to the vote share requirement as discriminatory.
- Law Ministry recommended an amendment to a 6% vote share requirement, saying that the scheme should be aligned with the RPI Act.
- Only the government, through ministries, has access to information related to electoral bonds.

- Only those parties, which have 1% of all voters polled in the last Lok Sabha or state assembly polls, are eligible for funding through these bonds.
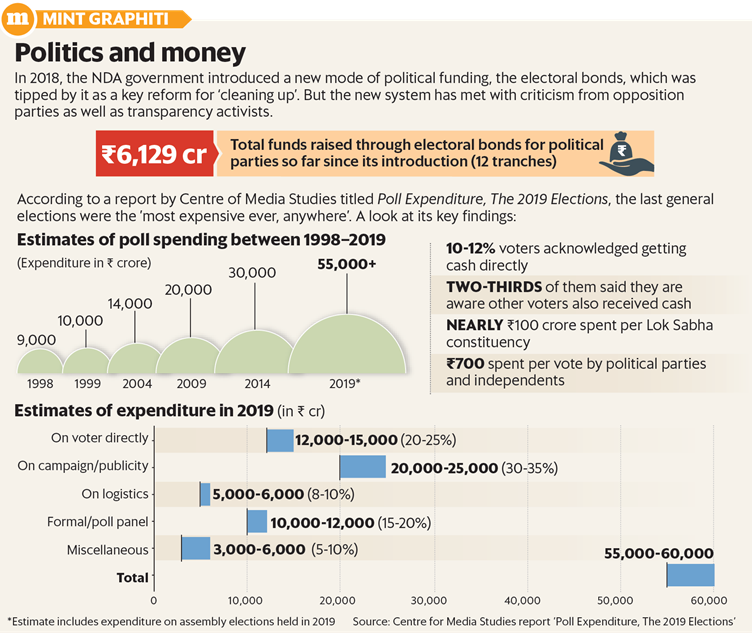
- The solution to this is setting up a national election fund where corporate houses and individual donors can contribute with 100% tax-free fund.
- The EC could be given the task of overseeing it.
- The money can then be divided among political parties mostly in kind and a part in cash.
- Communication restrictions, including the Internet ban, were “temporary”.
- We grab the headlines for militancy and terrorism. These are not the headlines conducive to investment.
- Abolition of Article 370 has ended system of the duality in Jammu & Kashmir.
- There are a few isolated incidents, which are so rare that they can be classified as crime.
- Only 10% of the area is affected by militancy and law and order incidents.
- Government is tackling these pockets and will ensure safety and security in a systematic manner.
- Jammu and Kashmir had a huge mining reserve and it was one area that could be exploited for production.
- J&K has reserves of limestone and gypsum that we can exploit for production. Government is revamping the land allocation policy.
The Indian Air Force inducted a squadron of Sukhoi-30 MKI fighter planes, with the capability to carry BrahMos missiles, at its Thanjavur airbase.
- The Indian Air Force would get more air power to strike from long standoff ranges on any target at sea or on land with accuracy by day or night and in all weather conditions.
- It is a twin jet multirole air superiority fighter developed by Russia's Sukhoi and built under licence by India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- The first Russian-made Su-30MKI variant was accepted into the Indian Air Force in 2002.
- The first indigenously assembled Su-30MKI entered service with the IAF in 2004.
- The Sukhoi Su-30MKI has a top speed of Mach 2 (2120 kmph) and has a maximum takeoff weight of 38,800 kg.
- The jet can carry a wide range of equipment from radars to missiles, bombs and event rockets.

A year after 10 water aerodromes were awarded to airlines for seaplane operations, the government is yet to seek environmental clearance for them.
- The process of seeking environmental clearance requires a lot of data such as bathymetric test.
- It will have to provide information about:
- Toilet waste from flights
- Disposal of trash collected during flights
- Waste from eateries and shops at the aerodromes.
- Impact of noise on the sensitive environment and presence of corals.
- Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) is a formal process used to predict the environmental consequences of any development project.
- Environment Impact Assessment in India is statutory backed by the Environment Protection Act in 1986, which contains various provisions on EIA methodology and process.
- EIA looks into various problems, conflicts and natural resource constraints that may not only affect the viability of a project but also predict if a project might harm to the people, their land, livelihoods and environment.
- Employees who draw wages or salaries directly or indirectly from a company are entitled to provident fund benefits under the Employees Provident Fund (EPF) Act.
- The term “employee” had been defined to include “any person” employed “directly or indirectly” under the PF Trust Regulations.
- Members of the union, and all other similarly situated contractual employees, are entitled to the benefit of provident fund under the PF Trust Regulations or the EPF Act.
- The Employees' Provident Fund Organisation (abbreviated to EPFO), a statutory body formed by the Employees' Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Labour and Employment, Government of India.
- EPFO assists the Central Board in administering a compulsory contributory Provident Fund Scheme, a Pension Scheme and an Insurance Scheme for the workforce engaged in the organized sector in India.
- It is also the nodal agency for implementing Bilateral Social Security Agreements with other countries on a reciprocal basis.
- It is the largest social security organisations in World in terms of the number of covered beneficiaries and largest in India interms of the volume of financial transactions undertaken.
- The ministry would explain several economic terms through interesting animated videos to help common person and students understand budget exercise in a simple way.
- The ministry also undertook this exercise before the Budget last year as well
- The ministry has also launched another campaign on Budget promises and delivery with tag '#HamaraBharosa'.
- This campaign focuses on promises and delivery.
- It has also been launched in 12 major regional languages
- It started with the health sector, unmanned level crossing and Housing for All.
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) lowered India’s economic growth estimate for the current fiscal to 4.8%.
- It listed the country’s much lower-than-expected GDP numbers as the single biggest drag on its global growth forecast for two years.
- Growth momentum should improve next year due to factors like the positive impact of corporate tax rate reduction.
- Global growth, estimated at 2.9% in 2019, is projected to increase to 3.3% in 2020 and inch up further to 3.4% in 2021.
- Indian growth rate is projected to improve to 5.8% in 2020 and 6.5% in 2021.
- Decline in rural demand growth
- An overall credit sluggishness for the lowering of India forecasts
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an organization of 189 countries.
- It is working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world.
- The IMF's primary purpose is to ensure the stability of the international monetary system—the system of exchange rates and international payments that enables countries (and their citizens) to transact with each other.
- The IMF provides loans to member countries experiencing actual or potential balance of payments problems to help them rebuild their international reserves, stabilize their currencies.
- The IMF’s employees come from all over the world; they are responsible to the IMF and not to the authorities of the countries of which they are citizens.
- Each member country of the IMF is assigned a quota, based broadly on its relative position in the world economy.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved