



Defence Acquisition Council Chaired by Raksha Mantri gives a big impetus to indigenous industry
The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC), chaired by Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh, met today and accorded approval for Capital Procurement for the Defence forces amounting over Rs. 3300 crores of indigenously designed and developed equipment.
DAC accorded approval for three projects to be indigenously designed, developed and manufactured by the Indian industry.
- Third generation Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGM): It would provide ‘Fire and Forget’ and “Top Attack” capabilities to the troops in an armoured battle.
- Auxiliary Power Units (APUs) for the T-72 and T-90 Tanks: the APUs would enable incorporation of various upgrades to Fire Control System and Night Fighting capabilities of the Tanks. Both these projects will be progressed under the ‘Make-II’ Category and will provide a boost to indigenous research and development in the Private Sector.
- The third indigenous project pertains to discrete Electronic Warfare (EW) systems for the mountain and High Altitude terrain, which would be designed and developed by DRDO and manufactured by design cum production partner from the Indian industry.
Defense Minister inaugurated strategically important ‘Col Chewang Rinchen Setu’, a bridge built by Border Roads Organisation (BRO) over River Shyok, connecting Durbuk and Daulat Beg Oldie in Eastern Ladakh
- Sandwiched between strategic Karakoram and Chang Chenmo ranges, the ‘Col Chewang Rinchen Setu’ is a 430-metre bridge built at an altitude of about 15,000 feet using Micro Piling Technology.
- The construction has been completed in record time within 15 months.
- Countrywide coverage: The projects are being implemented in 111 districts of 17 states having the international borders with Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- The projects will focus on developmental needs of people living within 50 kms of the international border.
- Construction of roads, schools, primary health centres and helipads in remote and inaccessible hilly areas,
- Promotion of rural and border tourism,
- Promotion of sports activities,
- Protection of heritage sites, supply of drinking water etc.
- Skill development training to farmers for the use of modern and scientific technique in farming, organic farming
Source: PIB
Underlining that the “Internet has emerged as a potent tool to cause unimaginable disruption to the democratic polity”, the Centre informed the Supreme Court it will take another three more months to revise and notify “extant rules” for “effective regulation of intermediaries” such as social media platforms “keeping in view the ever growing threats to individual rights and nation’s integrity, sovereignty, and security”.
- Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp were providing voice and video calling over Internet services without holding telecom licences.
- Petitioners have been providing Internet service, including Internet telephone, under a license agreement with the government, but Face book Messenger and Whatsapp have been doing it illegally.
- Present licensing regime, Internet telephony is a purely licensed service, permitted only under the UAS/ISP or Unified License granted under Section 4 of the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885.
- Need to bring WhatsApp under the regulatory framework was now more essential given that WhatsApp provided end-to-end encryption. The same is a serious threat to national security
- With the widespread penetration of mobile phones in the country, it has become even more imperative to check the operation of Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp.
- Increased use of social media, and in particular Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp by various organisations which indulge in anti-national and terrorist activities”.
- Some of the examples of such unregulated activities leading to serious threats are the 26/11 Mumbai terrorist attacks and the Muzaffarnagar riots, Paris terrorist attacks of 13/14 November 2015 carried out by ISIS.
- Unregulated functioning of Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp is a threat to the national security.
- Court observed why social mediashould not be subjected to licence fees and security considerations like other ISPs.
- It asked for rules to ensure accountability of intermediaries like Facebook.
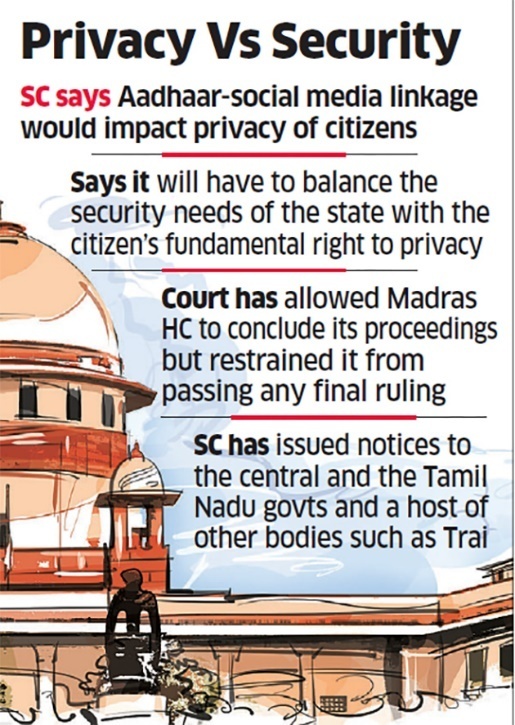
- There has been an enormous rise in the number of people using the Internet and social media and an “exponential rise in hate speech, fake news, public order, anti-national activities, defamatory postings, and other unlawful activities using Internet/social media platforms”.
- The Ministry had sought three more months to complete the entire process.
- The government pointed out that there was already a rule on intermediaries, The Information Technology (Intermediaries Guidelines) Rules, 2011, notified on April 13, 2011.
- As Internet has emerged as a potent tool to cause unimaginable disruption to the democratic polity, it was felt that the extant rules to be revised for effective regulation of intermediaries keeping in view the ever growing threats to individual rights and nation’s integrity, sovereignty, and security”.
The Data Security Council of India (DSCI), in partnership with the National Cyber Security Coordinator’s office, unveiled a platform that will enlist businesses and research entities working across 25 such areas.
- The platform, TechSagar, will provide actionable insights about capabilities of various companies and start-ups, academia and research.
- It will allow targeted search, granular navigation and drilldown methods using more than 3,000 niche capabilities.
- The repository currently features over 4,000 entities.
- TechSagarwill be frequently updated with new entities and information to maintain its relevancy and usefulness.
The steady decline in the proportion of young workers, those between 18 and 30, under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) has halted and has begun to rise in the wake of demonetisation and the rollout of GST.
- An analysis of age-wise data of persons employed in MGNREGA indicates that the share of workforce in the 18-30 age bracket began moving up after financial year 2017-18.
- The total number of young workers (18-30 years) employed under the job guarantee scheme was more than 1 crore in 2013-14 which came down to 58.69 lakh in 2017-18.
- In 2013-14, the ratio of young workers among total MGNREGA workers was 13.64 per cent, which came down to 7.73 percent in 2017-18 before rising to 9.1 percent in 2018-19, and 10.06 percent in 2019-20.
- It could be a reflection of rural distress and lack of employment opportunities.
- When they are unable to find job, they turn to MGNREGA. MGNREGA is stopgap arrangement for them.
The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) has the following objectives:
- Provide 100 days of guaranteed wage employment to rural unskilled labour
- Increase economic security
- Decrease migration of labour from rural to urban areas
- Grassroots-driven approach to employment generation.
- Programmes under the act are demand driven.
- The scheme is funded by the central government, which bears the full cost of unskilled labour and 75% of the cost of material for works undertaken under this law.
- The central and state governments audit the works undertaken under this act through annual reports prepared by CEGC (Central Employment Guarantee Council) and the SEGC (State Employment Guarantee Councils).
- Reduced the distress in agriculture & economy due low agricultural productivity & small land-holding size thus provided them better livelihood opportunities.
- Most of MGREGA work is directed towards building irrigation canals, tanks etc. thus provides resources base for further rural development.
- It has reduced rural distress & intensive urban migration.
- The provisions like work up to 5 km from home, equal wages promotes women empowerment, gender parity & directed towards backward section of society.
- The programme has generated over 1,980 crore person-days. In the short span of 10 years that the Act has been in existence, it has generated 19.86 billion person-days of employment benefitting 276 million workers, with more than half the jobs going to women workers and almost a 3rd to members of scheduled castes and scheduled tribes.
- It has resulted into social upliftment for all sections including SC/ST. The percentage of Scheduled Caste workers benefitted under the scheme has consistently been about 20% and of Scheduled Tribe workers has been about 17%.
- The legislation has reduced distress migration in traditionally migration-intensive areas.
- MGNREGA has played a much larger role in revitalizing the labour market in rural areas. Not only has it led to the creation of a class of workers who are using the MGNREGA as a safety net, but also these workers are also able to use it as a bargaining tool for extraction of higher wages.
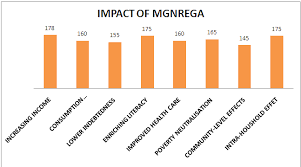
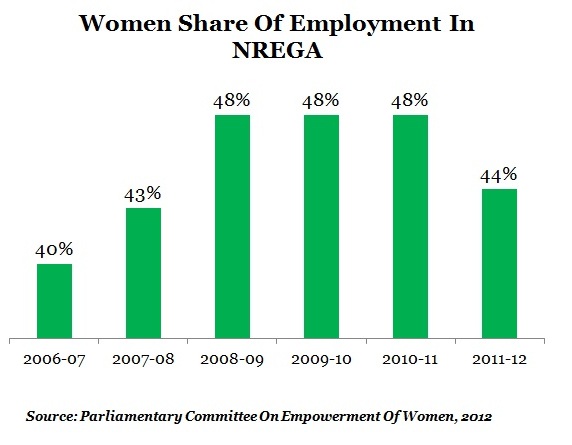
- Ridiculously low wage rate: Currently, MGNREGA wage rates of 17 states are less than the corresponding state minimum wages.
- Insufficient budget allocation: MGNREGA’s success at the ground level is subject to proper and uninterrupted fund flow to the states.
- Regular payment delays: The Union Ministry of Rural Development considers wages paid once the FTO (Fund Transfer Order) is signed by the second signatory. However, delays take place even in the processing of signed FTOs, for which the Management Information System (MIS) does not calculate compensation.
- Workers penalised for administrative lapses: The ministry withholds wage payments for workers of states that do not meet administrative requirements within the stipulated time period
- The banking puzzle: The rural banks are highly de-capacitated in terms of staff and infrastructure and thus always remain hugely crowded. The workers normally have to visit the banks more than once to withdraw their wages.
- Faulty MIS data: The increase in corruption and weakening accountability has roots in the excessive dependence of implementation of MGNREGA on technology (real-time MIS being one of them). There is a growing pile of evidence on how real-time MIS has made MGNREGA less transparent for workers, reduced accountability of frontline functionaries and aided in centralisation of the programme.
- Non-payment of unemployment allowance: There are a huge number of unemployment allowances being shown in the MIS currently.
- Genuine job cards being deleted to meet 100% DBT targets: Genuine job cards are being randomly deleted, as there is a huge administrative pressure to meet 100 per cent Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) implementation targets in MGNREGA.
- Too much centralisation weakening local governance: A real-time MIS-based implementation and a centralised payment system has further left the representatives of the Panchayats Raj Institutions with literally no role in implementation, monitoring and grievance redress of MGNREGA schemes.
- Administration not honouring local priorities: MGNREGA could be a tool to establish decentralised governance. However, with the administration almost dictating its implementation, it is literally a burden now for the people and especially for the local elected representatives.
- Geo MGNREGA is a path breaking initiative that uses space technology for geo-tagging all assets created under MGNREGA for improved planning, effective monitoring, enhanced visibility and greater transparency.
- Direct benefit transfer: To further streamline the fund flow mechanism and bring down delay in payment of wages, the Ministry of Rural Development has implemented National Electronic Fund Management System (NeFMS) in 21 States and 1 Union Territory.
- Initiative has been taken to simplify MGNREGA through issuance of Annual Master Circular (AMC) for FY 2016-17 by superseding 1039 circulars/advisories issued earlier.
- Reduction in number of Registers being maintained at Gram Panchayat level to seven simplified Registers from an average of 22 Registers has been implemented.
- The programme is progressing towards a more independent and empowered system of Social Audit and Internal Audit to ensure growth with accountability through a trained community cadre of social auditors drawn from women SHGs.
- The Ministry has taken up skill development of the MGNREGA workers through initiatives like Bare Foot Technicians and Project LIFE (Livelihood in Full Employment) in order to move them up the skilling ladder.
- The Ministry initiated Inter State Exchange Programmes, a process ensuring sharing of ideas and good practices.

There is no clarity on the types of firecrackers that individuals and family’s conscious of reducing their pollution footprint should buy.
- Supreme Court had ruled that only “green firecrackers” having low emission and permissible sound limits were to be sold and used.
- It had also fixed a timeslot for fireworks — between 8 pm and 10 pm on Diwali, and between 11.45 pm and 12.30 am on Christmas Eve and New Year.
- This decision followed a complete ban on the sale of firecrackers in Delhi by the Supreme Court in November 2016.
- The Union Ministry of Science and Technology launched environment-friendly firecrackers developed by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) laboratories.
- CSIR-NEERI (CSIR-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute) states that it has been working since January 2018 to develop new and improved formulations for reducing emissions from fireworks.
- CSIR-NEERI developed new formulations for reduced emission light and sound emitting crackers (SWAS, SAFAL, STAR) with 30% reduction in particulate matter using Potassium Nitrate (KNO3) as oxidant”.
- Firecrackers use a proprietary additive that acts as a dust suppressant.
- The usage of chemicals is less in green crackers.
- Some of the ‘green crackers’ have also replaced barium nitrate as an oxidiser for combustion.Barium nitrate hurts health when inhaled, causing irritation in the nose, throat and lungs. High exposure to barium nitrate can also cause nausea and irregular heartbeat.
- According to NEERI, these exploit the exothermic heat of materials such as zeolite, clay and silica gel for burning, and also match the performance of commercial firecrackers in terms of sound.
- Among the new firecrackers developed are environment-friendly versions of traditional anar, chakri, sparklers, and other light-sound emitting firecrackers.
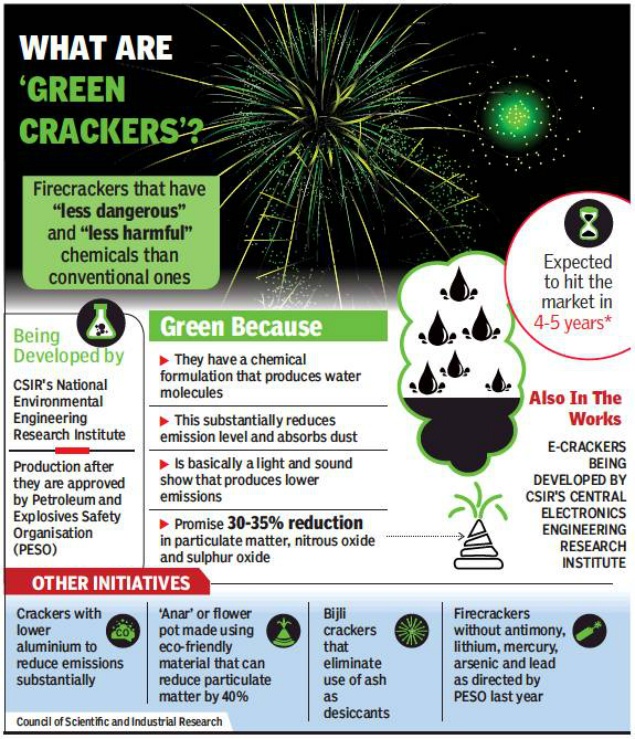
Identification of Green Crackers:
- Union Minister Dr Harsh Vardhan has said a Quick Response (QR) code will be put on the firecrackers to differentiate them from conventional ones.
- The cost of these firecrackers would be the same as conventional ones, and that they are already available in the market.
- The composition of firecrackers is disclosed to manufacturers after signing of a Memorandum of Understanding and a non-disclosure agreement.
- Following this, manufacturers have to apply to the Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organisation (PESO) for authorisation.
- The samples thus produced are submitted to CSIR for emission testing.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved