



GST Council may reduce tax on Electric vehicles
GST Council may reduce tax on Electric vehicles
News Important For: GS Paper – 3 I Technology, Environmental regulation -
Context
The GST Council to decide on lowering tax rates for electric vehicles.

About
â— The 36th meeting of the Council is also likely to decide the valuation of goods and services in solar power generating systems and wind turbine projects for the purposes of levying GST.
â— Reduction in the tax rate on electric vehicles, easing tax issues for the solar sector and deliberation on the tax rate on lotteries is expected as per the government’s vision of popularising electric vehicles.
â— In the Budget also government had announced additional income tax deduction of up to 1.5 lakh Rs on the interest paid on loans taken to purchase electric vehicles.
â— In the previous meeting the Council asked the Fitment Committee to review the matter of reducing the GST rate on electric vehicles from 12% to 5%.
Electric Vehicle Ecosystem
â— Functioning of EVs require charging stations and availability of electricity. Reduction of GST on batteries could be expected.
â— Owners of EV have the advantage of much lower running costs.
â— Reduced harmful exhaust emissions is good for health as well as environment

Solar Sector
â— GST Council is expected to discuss the tax incidence for solar sector.’
â— Presently, 70% of the cost of a solar plant is considered as goods and is taxed at 5%.
â— Rest 30% is considered as services and is taxed at 5%.
â— Solar manufacturers approached the Council saying that the break up of goods and services is more along the lines of a 90-10 split rather than 70-30. So they requested the council to incorporate the same.
â— Appropriation of the right proportion of goods and services to solar projects is needed as the present allocation makes such projects incur more tax costs, which cannot be passed on as input tax credits.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/gst-council-may-reduce-tax-on evs/article28701830.ece
India’s shifting strategic concerns
News Important For: GS Paper – 2 I International Relations
Context
The Structural trends in South Asia and the US President’s recent claim that India sought US mediation in Kashmir
Analysis
â— Structural trends in South Asia have been changing over the past several years.
â— Evaluating the India-Pakistan equation over the past five years, it seems that both sides have a perception that each holds advantageous position.
â— Pakistan’s ties with the U.S. and China renewed, while China reassured Pakistan with strategic commitments and bilateral partnerships.
â— Pakistan Army perceives itself in a position of strength where Washington, Beijing, and even Moscow has recognized Pakistan’s role in a future settlement on the conflict in Afghanistan.
â— Both India and Pakistan perceive themselves to be in a comfortable strategic position.
Pakistan’s Benefactors
â— Both U.S. and China have overlapping interests in regional stability and avoidance of major sub continental conflict.
â— India seeks a structural transformation in Pakistan’s domestic policies and external behaviour.
â— Both U.S. and China prefer competent civilian governance structures in Pakistan.
â— Washington considers the Pakistan’s Army as an insurance card for persisting security challenges such as regime survival for U.S. client states in West Asia as well as for the containment of Iran.
â— For China, a stable Pakistan can be a partner in the Belt and Road initiative and future continental industrial and energy corridors.
â— Both the U.S. and China seek a strong, stable and secure Pakistan that controls its destabilizing behaviour because it undermines their wider regional interests.
The way forward
â— It is true that both the U.S. and China benefit from a more normalized Pakistan, but India’s policymakers should remain clear-eyed that neither country would be willing to expend much strategic capital in an ambitious policy to reorder the domestic scene or civil-military relations in Pakistan.
â— In both the cases, Indian statecraft is essential to reorient perceptions of the great powers.
â— India has the right and capacity to adopt an active defence posture which would play an important role in shaping how third parties view Indian interests and thereby assume constructive roles in managing Pakistani behaviour.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/shifting-strategic-concerns/article28701738.ece
Bill to ban unregulated deposit schemes passed
News Important For: GS Paper – 2 I Government policies and interventions aimed at development
Context
Lok Sabha passed the Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Bill, 2019 by voice vote.

Key features of Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Bill, 2019
â— Substantive banning clause which bans Deposit Takers from promoting, operating, issuing advertisements or accepting deposits in any Unregulated Deposit Scheme. The Bill bans unregulated deposit taking activities altogether, by making them an offence ex-ante rather than the existing legislative-cum-regulatory framework which only comes into effect ex-post with considerable time lags.
â— Creation of three different types of offences, namely, running of Unregulated Deposit Schemes, fraudulent default in Regulated Deposit Schemes, and wrongful inducement in relation to Unregulated Deposit Schemes.
â— Severe punishment and heavy pecuniary fines to act as a deterrent.
â— Provisions for disgorgement or repayment of deposits in cases where such schemes nonetheless manage to raise deposits illegally.
â— Attachment of properties / assets by the Competent Authority, and subsequent realization of assets for repayment to depositors.
â— Clear-cut timelines have been provided for attachment of property and restitution to depositors.
â— Creation of an online central database, for collection and sharing of information on deposit-taking activities in the country.
Source link:
Draft New Education Policy offers Contentious remedies for a structural malady in Medical studies
News Important For: GS Paper – 3 I Education, Health sector
Context
The Draft National Education Policy’s provisions for Medical Education.
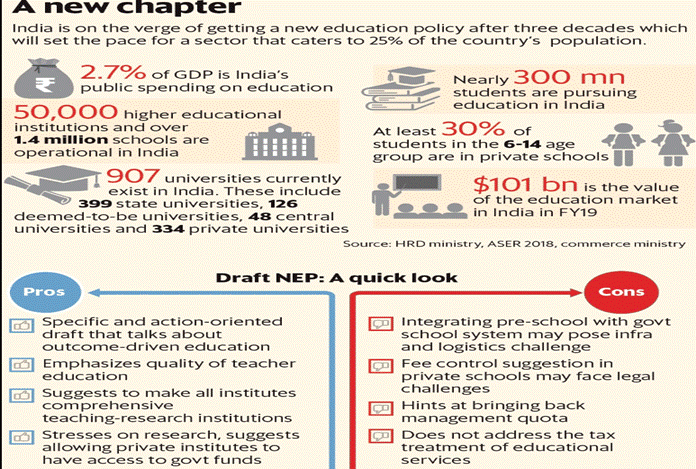
Analysis
â— Medical education should provide a cadre of personnel to take care of the health needs of the country, therefore education policy in the modern world has to take into consideration social objectives.
â— The draft New Education Policy (NEP) talks about equity, inclusiveness and sustainable development, but the recommendations to fulfil these objectives are unclear.
â— The policy document stresses the need for a flexible education system.
Medical Education Provisions
â— Fees in medical colleges, both public and private will be left to be decided by the institutions themselves, but at the same time the policy asserts that the cost of education should be lowered.
â— The policy states that all private institutions should be not-for-profit but there are no clear recommendations for the same.
â— It also states that no student should be deprived of an education due to lack of finances but the solution suggested is scholarships only.
â— National Medical Commission Bill has a provision of regulating fees only for 50% of seats in medical colleges
â— National Exit Examination for MBBS as the mode of entry to postgraduate courses.
Centralization in Medical Education
â— High level of centralization in medical education by the National Medical Commission contradicts the objectives of autonomy and adaptation to local needs.
â— The policy document also considers the separation of the functions of regulation, funding, accreditation and standard setting as necessary.
â— Lack of adequate respectable employment opportunities for MBBS graduates is the main driver of the thirst for a postgraduate degree and has debased the MBBS degree.
â— Privatisation of healthcare delivery in India led to the concentration of personnel in those parts where the public has the capacity to pay.
â— The policy document does not recognize that inequity in health care is caused by the poorly regulated for-profit sector.
Source link:
India’s first dragon blood-oozing tree
News Important For: GS Paper – 3 I Environment Conservation and biodiversity.
Context
Researchers for the first time have discovered dragon blood tree in India.

About
â— The tree has been discovered in Assam.
â— The dragon’s blood is a bright red resin used since ancient times as medicine, body oil, varnish, incense and dye. Its sap turns bright red after coming in contact with air.
â— Researchers discovered Dracaena cambodiana, a dragon tree species in the Dongka Sarpo area of West Karbi Anglong.
â— In India, the Dracaena genus belonging to the family Asparagaceae is represented by nine species and two varieties in the Himalayan region, the northeast and Andaman and Nicobar Islands but Dracaena cambodiana is the only true dragon tree species.
â— Dracaena cambodiana is an important medicinal plant as well as an ornamental tree.
â— It is a major source of dragon’s blood, a precious traditional medicine in China. Several antifungal and antibacterial compounds, antioxidants, flavonoids, etc.have been extracted from various parts of the plant.
â— Recent overexploitation to meet the increasing demand for dragon’s blood has resulted in rapid depletion of the plant.
â— For this reason, the species is already listed in the inventory of Rare and Endangered Plants of China.
â— The population size of the dragon tree species in Assam was estimated to be fewer than 50 mature individuals.
â— The habitat of the plant is severely fragmented due to open excavation of a stone quarry and there is continuing decrease in its area of occupancy and number of mature individuals.
â— The study advocates conservation programme for Dracaena cambodiana in view of its medicinal, ornamental and ecological values.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/indias-first-dragon-blood-oozing-tree/article28701517.ece
Milky Way’s violent birth decoded
News Important For: GS Paper – 3 I Science and Technology, Recent developments and their applications.
Context
Scientists recently discovered the origin of the Milky Way.
Analysis
â— The Milky Way merged with another smaller galaxy in a colossal cosmic collision roughly 10 billion years ago.
â— The union of the Milky Way and the so called dwarf galaxy Gaia Enceladus increased our galaxy’s mass by about a quarter and triggered a period of accelerated star formation lasting about 2to 4 billion years.

â— Galaxies of all types, including the Milky Way, began to form relatively soon after the Big Bang explosion that marked the beginning of the universe some 13.8 billion years ago, but were generally smaller than those seen today and were forming stars at a rapid rate.
â— High Precision measurements of the position, brightness and distance of around a million stars within 6,500 light years of the sun, obtained by the Gaia space telescope, helped pinpoint stars present before the merger and those that formed afterward.
â— Certain stars with higher content of elements other than hydrogen or helium arose in the Milky Way and others with lower such content originated in Gaia Enceladus, owing to its smaller mass.
â— It was not a star destroying calamity.
â— The distances between stars in a galaxy are very huge.
â— A galaxy is basically empty space and two galaxies intermix, change their global shape and star formation takes place and the smaller one stops forming stars.
Source link:
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/indias-first-dragon-blood-oozing-tree/article28701517.ece

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved