



An Expert Explains: How India is building up defence during lockdown
They are trying to find solutions that can broadly be put in three categories
- Science:
- Development of cheaper test kits
- Efforts towards vaccine development and repurposing of drugs.
- Technology :
- Products that are needed by the patients or healthcare professionals.
- Information technology:
- Effective information-based products on this disease.
- Develop information dashboards for Indian context, by, integrating data about where the concentration of infected people are.
- Ventilators
- Blood Oxygen Monitors
- Technology Development Board recently made a call for proposals from SMEs (small and medium enterprises) and start-ups for products that will be useful in the current situation.
- Government have already found close to 60 start-ups that have useful products in advanced stages of development.
- A call has been made through the Science and Engineering Research Board, asking for research proposals on COVID-19.
- Development of inexpensive test kits: test kits that are priced below Rs 500.
- All efforts that will contribute towards vaccine development would be supported and put on the fast track.
- Limited clinical trials on drugs that are approved elsewhere will be funded and fast-tracked.
Farmers are currently about to harvest —wheat, mustard, chana (chickpea), matar (field pea), potato, onion, garlic, zeera (cumin seed), coriander, fennel, red chilli, grapes, mango, summer tomato and other seasonal fruits and vegetables.
- Transportation: Will farmers, laborers and machines (combines, threshers and tractor trolleys) be able to move freely to harvest the produce and take it to the mandis?
- Availability of workers: There is a possibility of shortage of labour (the people who do unloading, cleaning, bagging and reloading of the grain that is auctioned or sold) and even gunny bags.
- Accessibility to market: The grocers in remote location at the greatest risk of running out of stocks if the lockdown continues without inter-state movement restrictions in agricultural commodities being removed.
- There is restrictions on truck to engage in long overhauls leading to issues of supply chain.
- The Uttar Pradesh government issued a direction to all district administrations and law-enforcement authorities to exempt all services, including labour, that are involved in agricultural production, processing and marketing from the current lockdown provisions.
- Government should give a clear-cut assurance that it will continue buying until the last grain is offered.
- The marketing of produce needn’t be limited to the APMC (agricultural produce market committee) mandi yard. Any flour or daal mill and even primary school premises can be designated as an APMC marketing area.
- Right time to dismantle all inter-state and intra-state movement restrictions in farm produce.
- Goods trains can be sent faster now to reach remote areas, so that the wholesale traders there can seamlessly supply to local grocers.
- Reduced the key interest rate sharply by 75 bps
- Allowed banks to defer payment of EMIs on home, car, personal loans as well as credit card dues for three months till May 31.
- The reverse repo rate was cut by 90 bps point to 4%.
- Reduced the cash reserve ratio of banks which released Rs. 1.37 lakh crores liquidity.
- Will increase the liquidity for banks.
- Aimed at prompting banks to lend more rather than keeping their excess liquidity with the RBI.
- It will see an infusion of Rs. 3.74 lakh crores into the banking system.
- It is the rate at which the central bank of a country (Reserve Bank of India in case of India) lends money to commercial banks in the event of any shortfall of funds. Repo rate is used by monetary authorities to control inflation.
- Repo Rate is set by the RBI for lending short-term money to banks.
- Reverse Repo Rate is actually the opposite of Repo Rate. The RBI borrows money at this rate from the banks for the short term. In other words, the banks park their excess funds with the central bank at this rate, often, for one day. The banks earn an interest rate on government securities purchased from the RBI for the given period. The Repo Rate always stands higher than the Reverse Repo Rate.
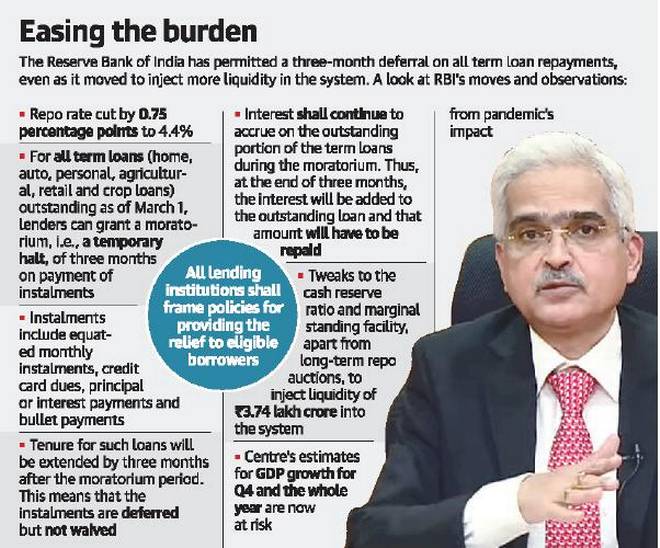
Reference: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/rbi-cuts-rates-allows-loan-moratorium/article31188500.ece
India is all set to join World Health Organization (WHO)’s “Solidarity Trial” aimed at rapid global search for drugs to treat COVID-19 infection.
About Solidarity trials
- India had so far stayed away from the multi-country trial, due to its small sample size. But with increasing number of cases India has decided to join this WHO endeavour.
- The Solidarity Trial will test four different drugs or combinations and compare their effectiveness in treating COVID-19 patients.
- Based on the study it could recommend the standard of care for hospital treatment of COVID-19 patients.
- The Solidarity Trial will test:
- Remdesivir (a combination of two drugs, lopinavir and ritonavir)
- Interferon beta
- Chloroquine
About WHO:
- Primary role is to direct and coordinate international health within the United Nations system.
- Main areas of work are health systems; health through the life-course; non-communicable and communicable diseases; preparedness, surveillance and response; and corporate services.
- The World Health Assembly is attended by delegations from all Member States, and determines the policies of the Organization.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that is concerned with world public health.
- The WHO is a member of the United Nations Development Group.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved