



3 years on, a mere 30% of Poshan Abhiyaan funds used
SOCIETY
3 years on, a mere 30% of Poshan Abhiyaan funds used
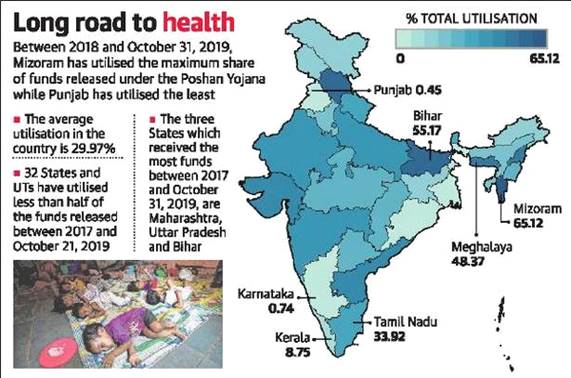
The State governments and the Union Territories utilized a mere 30% of the funds released under the Poshan Abhiyaan, or the National Nutrition Mission, since it was launched in 2017.
Reasons behind non usage:
- The POSHAN Abhiyaan programme has been conceptualized to be implemented in phases. The fund utilization is generally slow in the initial phase of such incremental schemes.
- A number of activities, which have been planned under the scheme like the Integrated Child Development Services-Common Application Software meant to monitor anganwadis have had a slow start.
- Lack of political will and action to tackle the issue of malnutrition is the major reason why the governments have failed to utilize the available funds under the scheme.
About the Poshan Abhiyan:
- The Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nutrition or POSHAN Abhiyaan (National Nutrition Mission), is the Government of India’s flagship programme, which is aimed at improving nutritional outcomes among pregnant women, lactating mothers and children.
- It aims at reducing the level of stunting, underweight, anaemia and low birth weight by 2022.
- POSHAN Abhiyaan is a multi-ministerial convergence mission with the vision to ensure the attainment of malnutrition-free India by 2022.
- It will create synergy, ensure better monitoring, issue alerts for timely action and encourage States/UTs to perform, guide and supervise the line Ministries and States/UTs to achieve the targeted goals.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) is implementing POSHAN Abhiyaan.
- For the implementation of POSHAN Abhiyaan, the four-point strategy/pillars of the mission are:
- Inter-sectoral convergence for better service delivery
- Use of technology (ICT) for real-time growth monitoring and tracking of women and children
- Intensified health and nutrition services for the first 1000 days
- Jan Andolan
Funding Pattern:
- 50% of the sanctioned amount would be through budgetary support of the governments. The remaining 50% is from the World Bank or other multilateral development banks.
- The budgetary support amount is further divided into 60:40 between the Centre and the States, 90:10 for the north-eastern region and the Himalayan States and 100% for the Union Territories without legislature.
POLITY
CAA is perfectly legal and Constitutional, says Law Minister Ravi Shankar Prasad
Union Law Minister Ravi Shankar Prasad has clarified that while there was a “possibility” that the National Register for Citizens (NRC) “may take place”, it would only be through a due legal process, with rules for it being defined “through adequate consultation”.
Constitutional provisions for CAA:
Article 246:
- Under Article 246 of the Constitution, Parliament has got the exclusive power to make laws with respect to the matters listed in the Union List of the Seventh Schedule.
- Item 17 in the Union List deals with citizenship and naturalization of aliens. Therefore, only Parliament has got sovereign powers to legislate on citizenship.
Violation of article 14:
- The main arguments against the CAA have been that it goes against Article 14 of the Constitution, which guarantees equality before the law and equal protection before the law.
- Supreme Court has stated that if there is a reasonable classification of groups who form a class by themselves, then that legislation will be valid.
- A persecuted, victimized group based on the faith of six communities from the three countries Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh, which are declared Islamic countries, form that reasonable classification.
Concern of it being religion specific law:
- The Law Minister defending the CAA states that historically-persecuted minorities should be given priority in granting citizenship.
- The whole group of minorities mentioned in the CAA provisions have been persecuted only because of faith.
- The dwindling numbers in the three countries mentioned in the provisions of the CAA clearly point to the level of religious persecution against the minorities.
Palpable fear among the minorities that the CAA along with a possible NRC could only disadvantage muslims:
- CAA does not relate to any Indian. The CAA involves granting citizenship to people and is not about taking away anyone’s citizenship.
- The Census Act mandates that the statistics of individuals and households cannot be disclosed. The NPR, which is a register of usual residents and not citizens, can help release data, which can be used by both the centre and the states for better targeting of welfare schemes.
- NPR has legal backing. Rule 3, sub-clause 4 of the citizenship rules 2013, states that the Central Government may decide the date by which a population register might be prepared.
- NRIC would be implemented only through a due legal process ensuring that it would not lead to harassment of genuine citizens.
Need for the amendment:
- The CAA only intends to hasten the process of citizenship through naturalization for the group of communities mentioned in the CAA provisions.
- Individual asylum, protection for people of all religions and from all countries will continue to exist.
SECURITY
Chief of Defence Staff can serve till 65, says government
Changes:
- The government has issued a gazette modifying the Service Rules of the Army, Navy and Air Force to enable the appointment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and fixing the upper age limit at 65.
- The service regulations have been amended and not the Acts. The Centre amended the Army Rules 1954, Naval (Discipline and Miscellaneous Provisions) Regulations, 1965, Naval Ceremonial, Conditions of Service and Miscellaneous Regulations, 1963 and Air Force Regulations, 1964.
- The service chiefs have a tenure of three years or 62 years of age, whichever is earlier, and it remains unchanged. Notably, however, the tenure of the CDS has not been fixed.
Navy plans 24 submarines to strengthen fleet
To strengthen its underwater fleet, the Navy plans to build 24 submarines, including six nuclear attack submarines, a parliamentary panel was told.
Parliamentary Panel’s report:
- The Navy has stated that there are presently 15 conventional submarines and two nuclear submarines in its fleet.
- The Navy has two nuclear submarines INS Arihant and INS Chakra, with the latter being leased from Russia.
- Along with the Arihant Class SSBNs, which are nuclear-powered submarines equipped with nuclear missiles, the Indian Navy has plans to build six nuclear attack submarines.
- The Ship, Submersible, Ballistic, Nuclear (SSBN) is a nuclear powered ballistic missile submarine.
Concerns of Navy:
- The Indian Ocean Region, the area of operations of the Navy, has witnessed rising activities of the Chinese Navy.
- A majority of the conventional submarines in the Indian Navy are over 25 years old. Thirteen submarines are between 17 and 32 years, impairing the capability of the Indian submarines.
- Due to the delay in the new submarine construction projects like the six submarines under Project 75 being carried out at Mazagaon Docks, Mumbai, the Defence Ministry has approved Medium Refit cum Life Certification or MRLC of six older submarines.
- The MRLC of submarine Sindhuraj was held up due to sanctions imposed by the U.S. on Russia.
- The sanctions imposed on Russia by the U.S. under its Countering America’s Adversaries through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) have severely impaired the capabilities of Russia to service the submarines it has leased out to India.
ENVIRONMENT
Madhya Pradesh gets its first elephant colony
Details:
- Elephants are generally migratory in nature and often travel hundreds of miles to look for newer habitats with enough food and water.
- The ‘Tiger State’ of Madhya Pradesh, which in the 2019 census recorded the most number of estimated tigers at 526, thus securing the title, presently has no know-how on dealing with elephants.
- The increased presence of elephants might lead to increased instances of man-animal conflicts.
- The local forest staff will need to be imparted training on the techniques to avert man-animal conflicts.
- Given their dietary differences there is no competition between the two species. The presence of elephants will not alter the movement of tigers in the area.
Red sand boa rescued in M.P., five nabbed
- A red sand boa snake, worth around Rs.1.25 crore, was rescued from five persons, who were trying to sell it.
- The rare non-poisonous snakes are used for making certain medicines, cosmetics and in black magic, and are in huge demand in the international market.
- The accused have been charged under the Wildlife (Protection) Act.
About Wildlife Protection Act:
This Act provides for the protection of the country’s wild animals, birds and plant species, in order to ensure environmental and ecological security.
Features of the act:
- The Act provides for the formation of wildlife advisory boards, wildlife wardens, specifies their powers and duties, etc.
- It helped India become a party to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). CITES is a multilateral treaty with the objective of protecting endangered animals and plants.
- For the first time, a comprehensive list of the endangered wildlife of the country was prepared.
- The Act prohibited the hunting of endangered species.
- Scheduled animals are prohibited from being traded as per the Act’s provisions.
- The Act provides for licenses for the sale, transfer and possession of some wildlife species.
- It provides for the establishment of wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, etc.
- Its provisions paved the way for the formation of the Central Zoo Authority. This is the central body responsible for the oversight of zoos in India. It was established in 1992.
- The Act created six schedules, which gave varying degrees of protection to classes of flora and fauna.
- Schedule I and Schedule II (Part II) get absolute protection and offences under these schedules attract the maximum penalties.
- The schedules also include species which may be hunted.
- The National Board for Wildlife was constituted as a statutory organization under the provisions of this Act.
- This is an advisory board that offers advice to the central government on issues of wildlife conservation in India.
- It is also the apex body to review and approve all matters related to wildlife, projects of national parks, sanctuaries, etc.
- The chief function of the Board is to promote the conservation and development of wildlife and forests.
- It is chaired by the Prime Minister.
- The Act also provided for the establishment of the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- It is a statutory body of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change with an overall supervisory and coordination part, performing capacities as given in the Act.
- Its mandate is to strengthen tiger conservation in India.
- It gives statutory authority to Project Tiger which was launched in 1973 and has put the endangered tiger on a guaranteed path of revival by protecting it from extinction.

© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved