




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended
Context
About
|
Didymos is the twin-asteroid system Didymos is a binary near-Earth asteroid. |
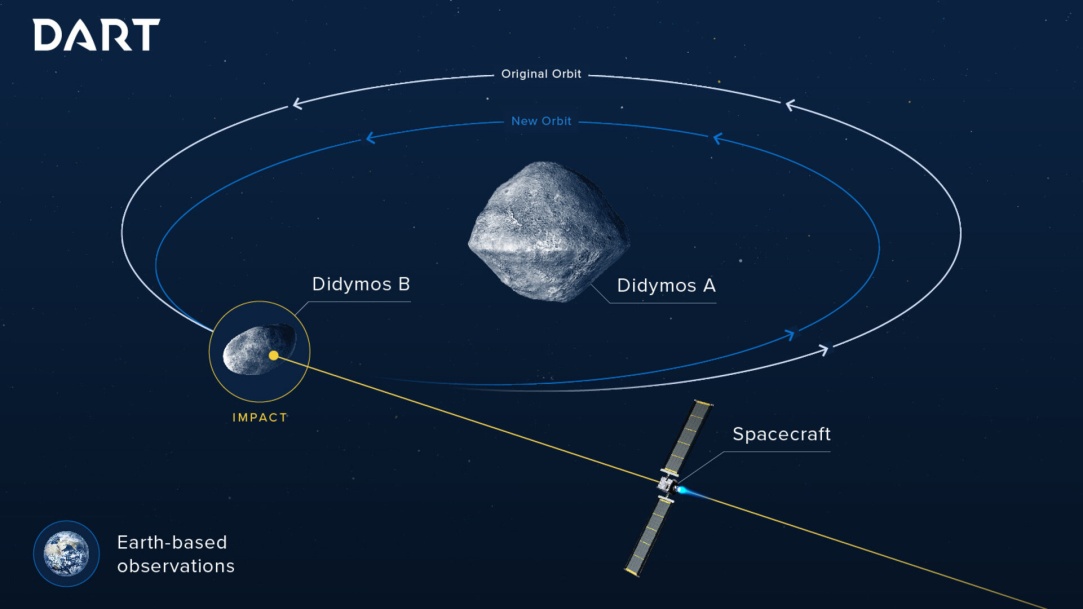
Hera
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/nasa-dart-mission-asteroid-explained-7617692/






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved